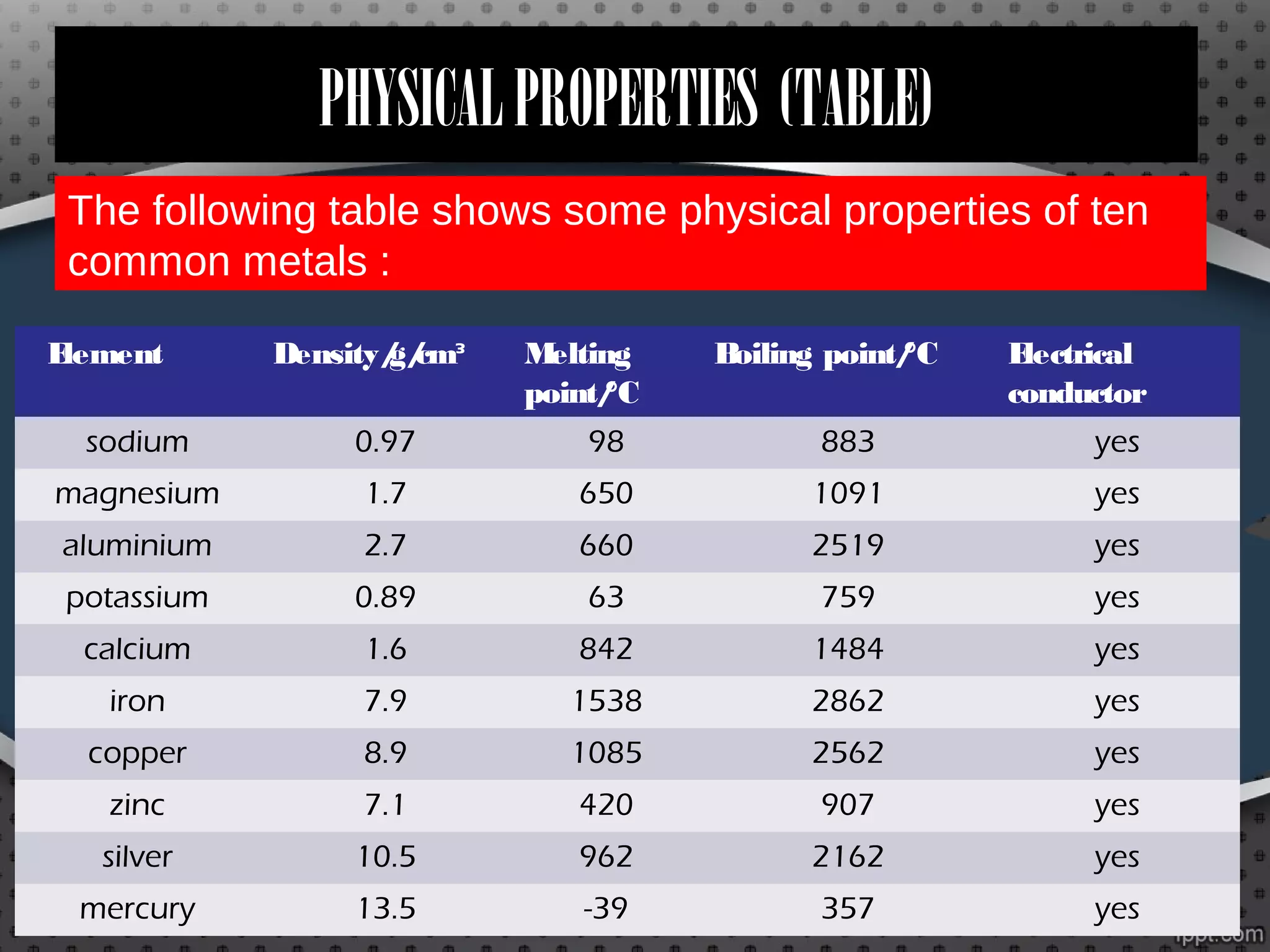
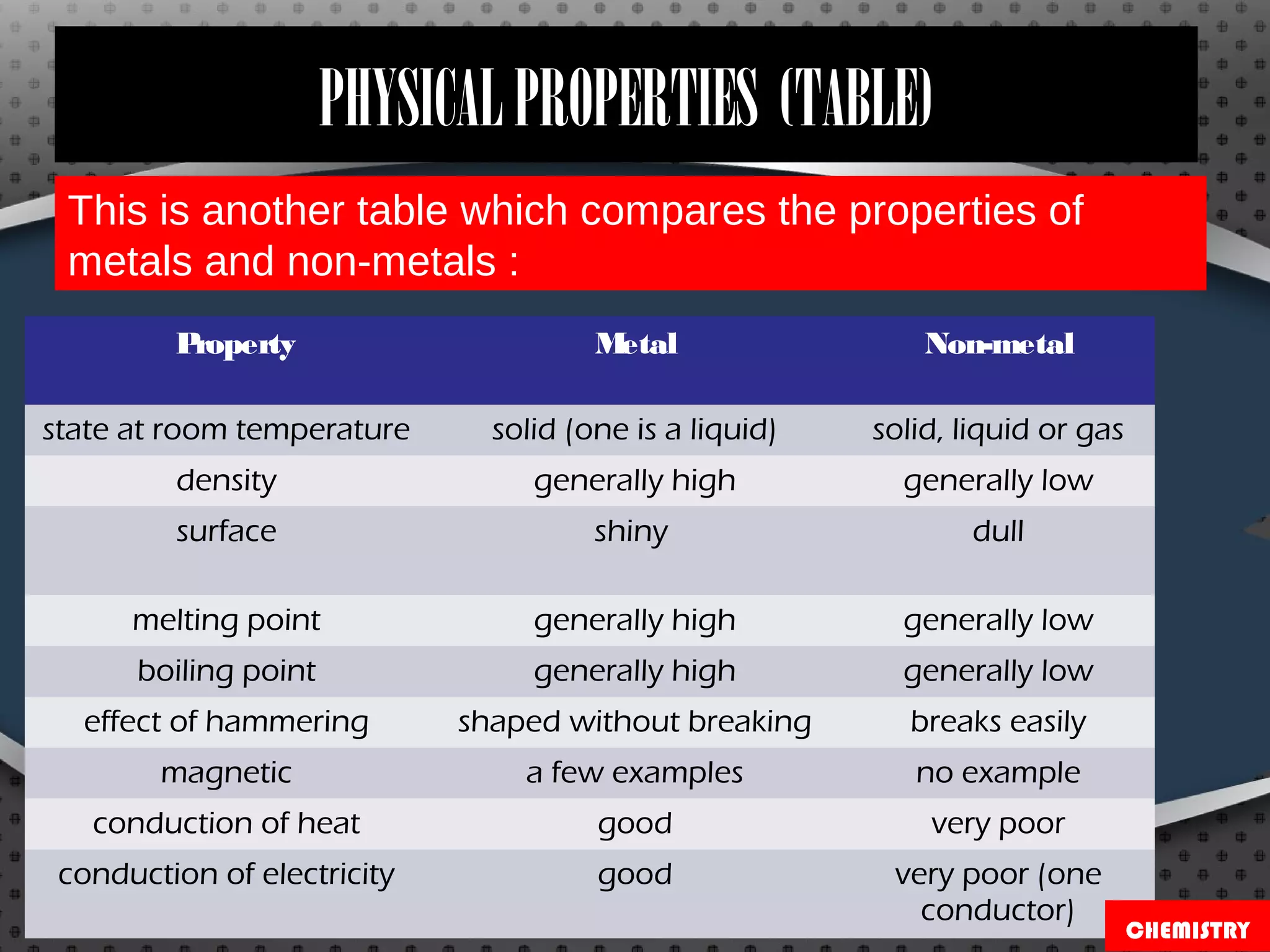
Metals and non-metals have distinct physical and chemical properties. Physically, metals tend to be solid, shiny, malleable, and good conductors of heat and electricity, while non-metals are usually brittle solids, liquids, or gases that are poor conductors. Chemically, metals react with non-metals like sulfur to form compounds called metal sulfides, and they react with oxygen to form metal oxides, which may dissolve in water to form bases. Non-metals also react with oxygen to form oxides, which dissolve in water to form acids like sulfurous acid. Common metals and non-metals have a variety of industrial and domestic uses based on their properties.