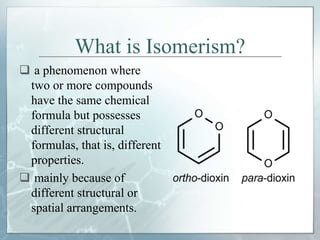
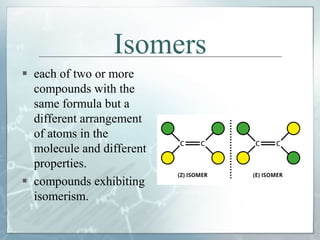
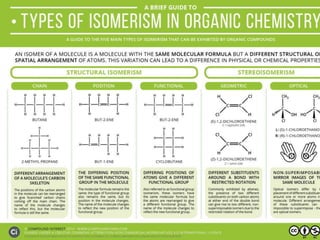
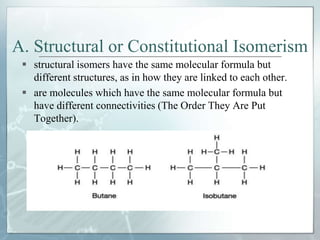
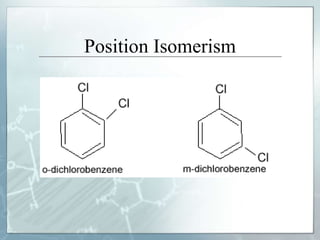
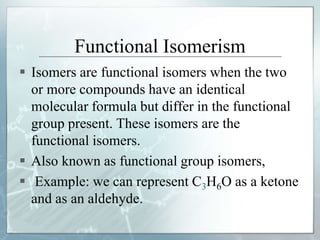
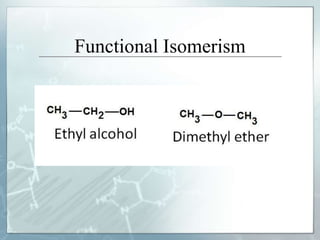
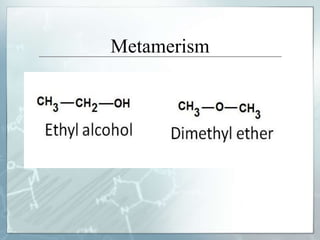
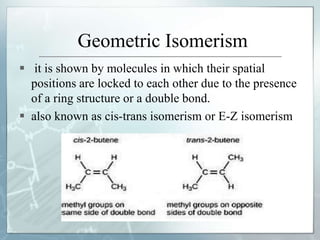
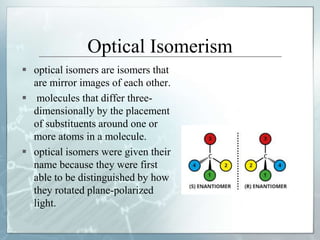
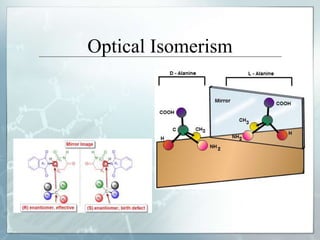
The document discusses isomerism, a phenomenon where compounds share the same chemical formula but differ in structures and properties due to varied arrangements of atoms. It outlines types of isomerism, including structural isomerism (with subtypes like chain, position, functional, and metamerism) and stereoisomerism (which includes geometric and optical isomerism). Various examples illustrate the concepts of isomerism and its implications in organic chemistry.