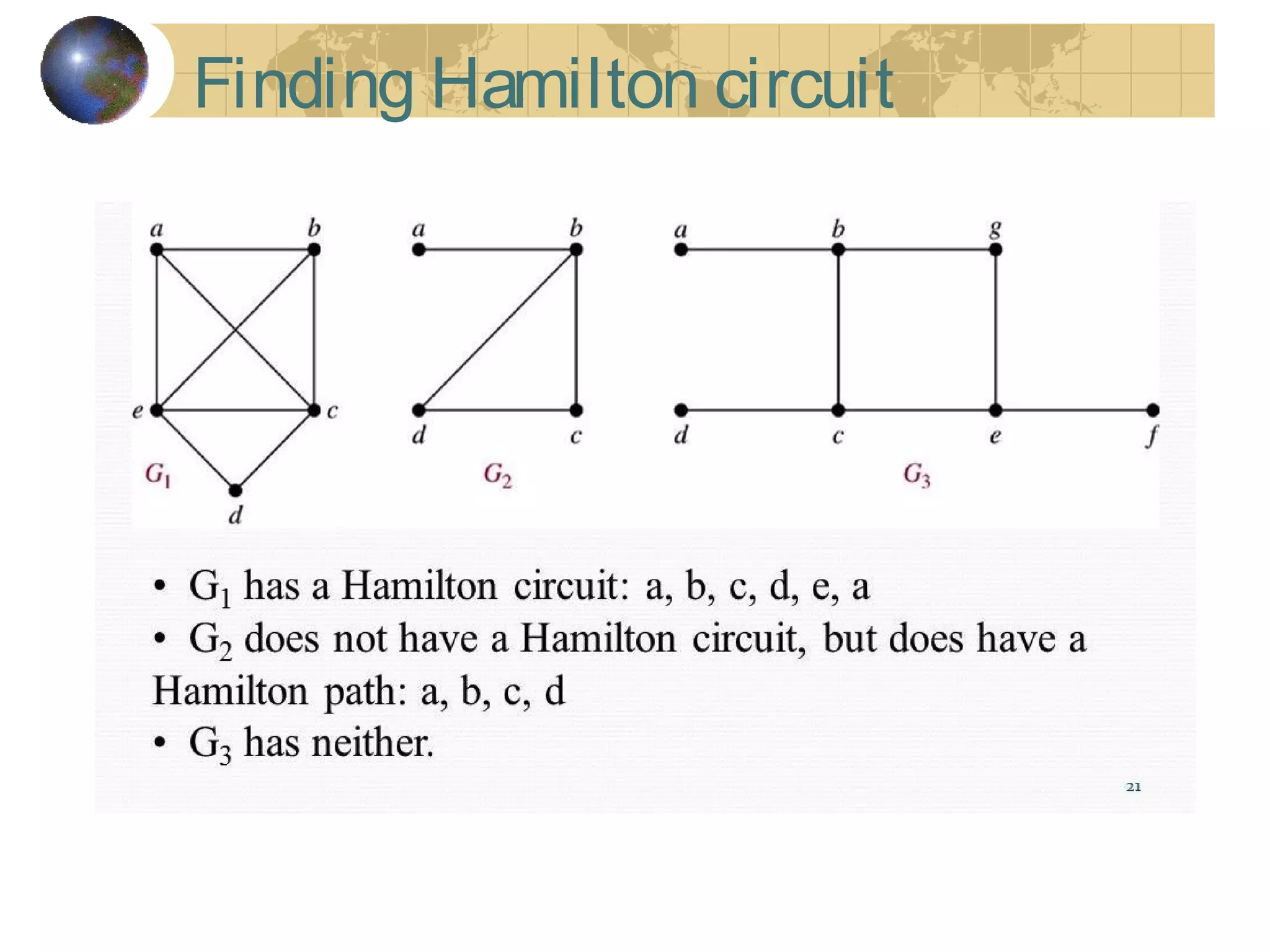
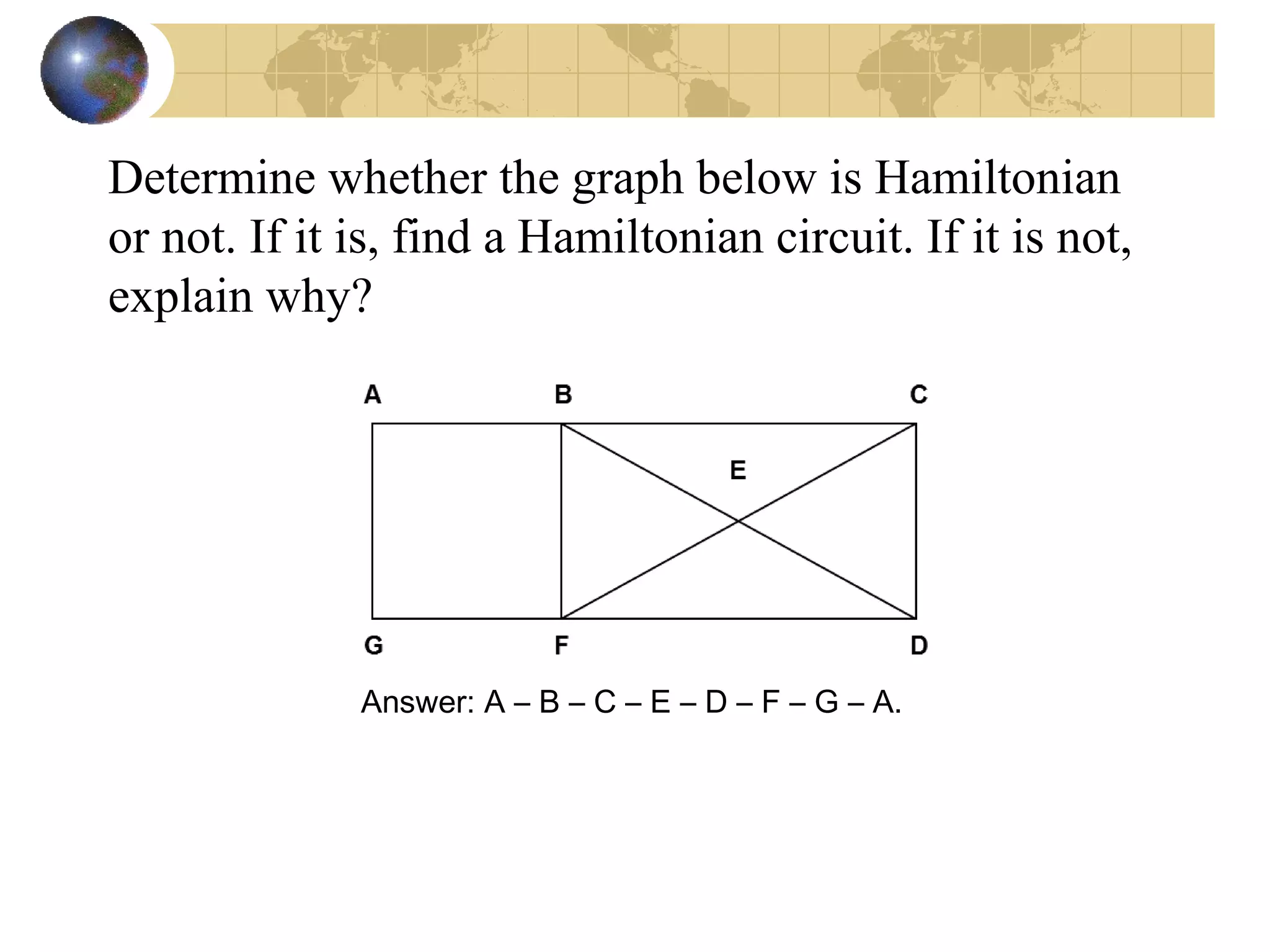
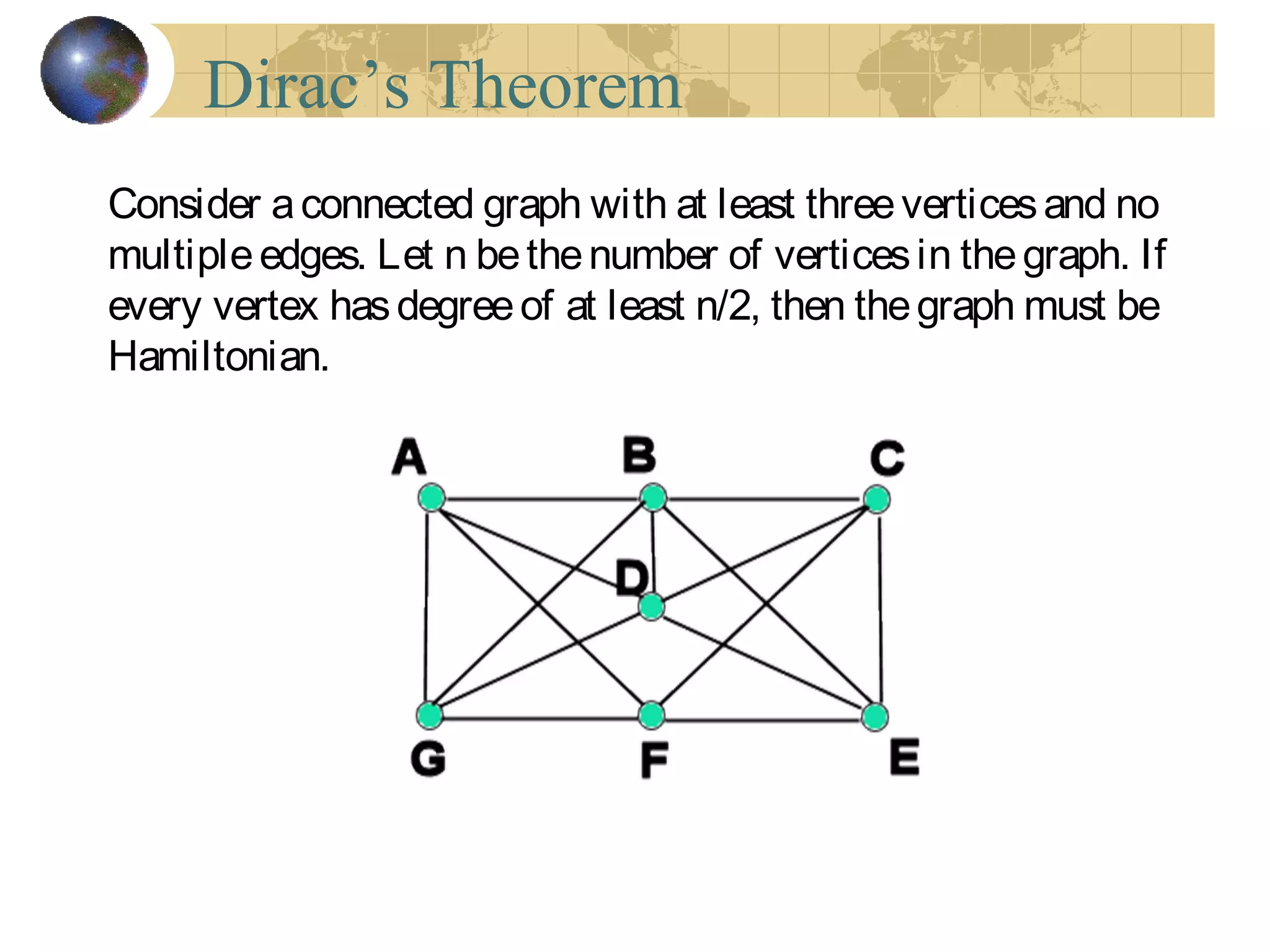
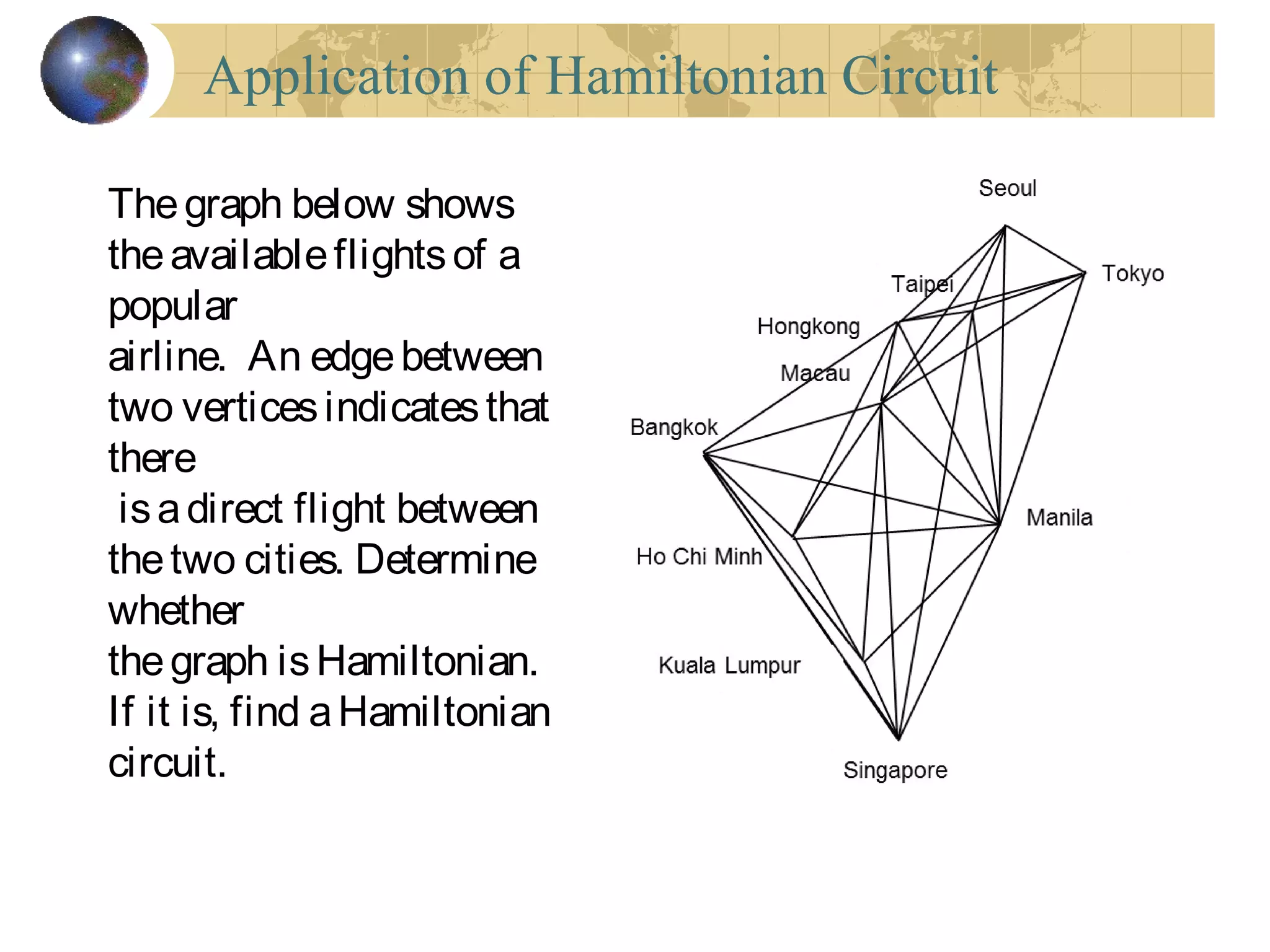
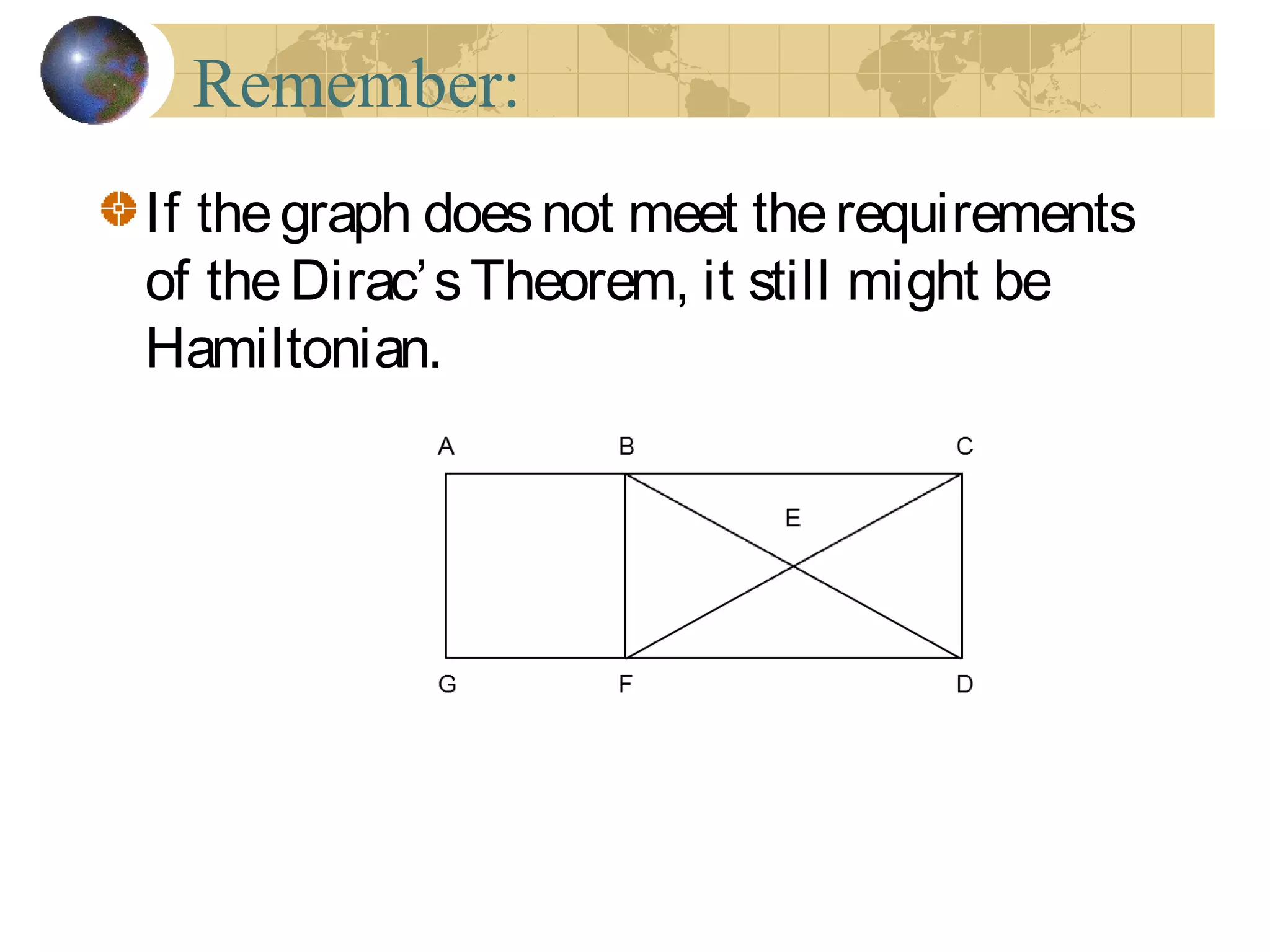
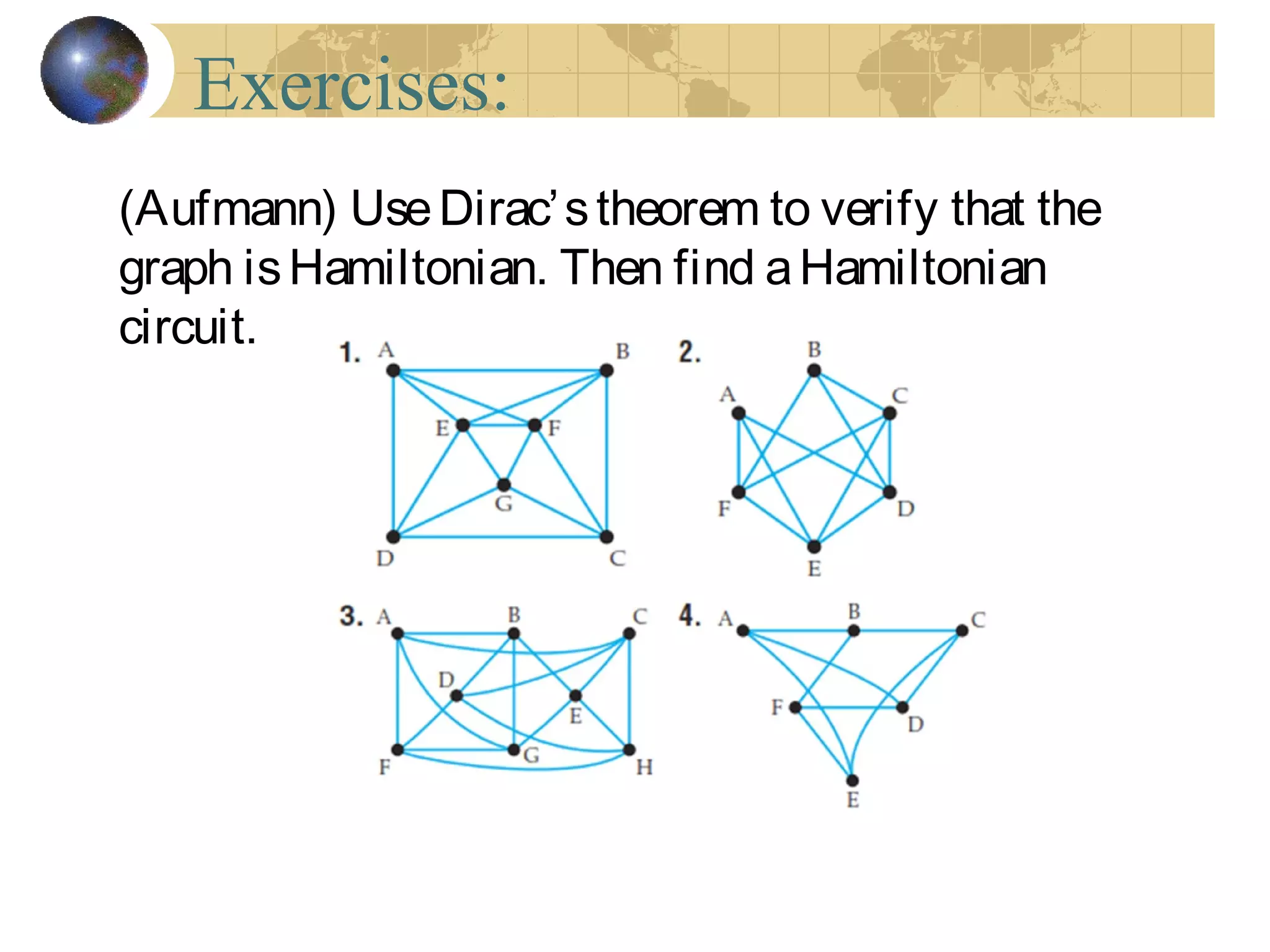
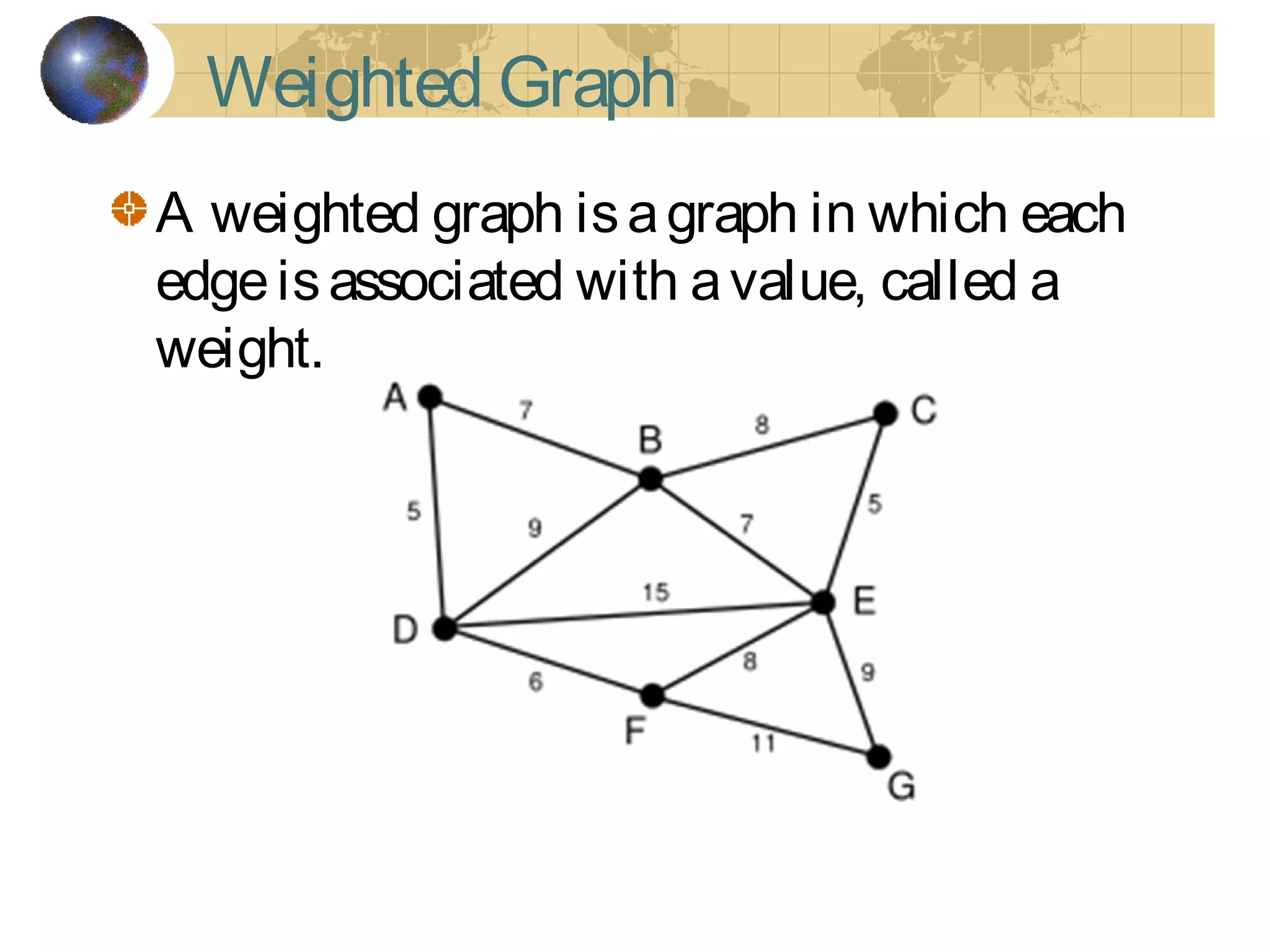
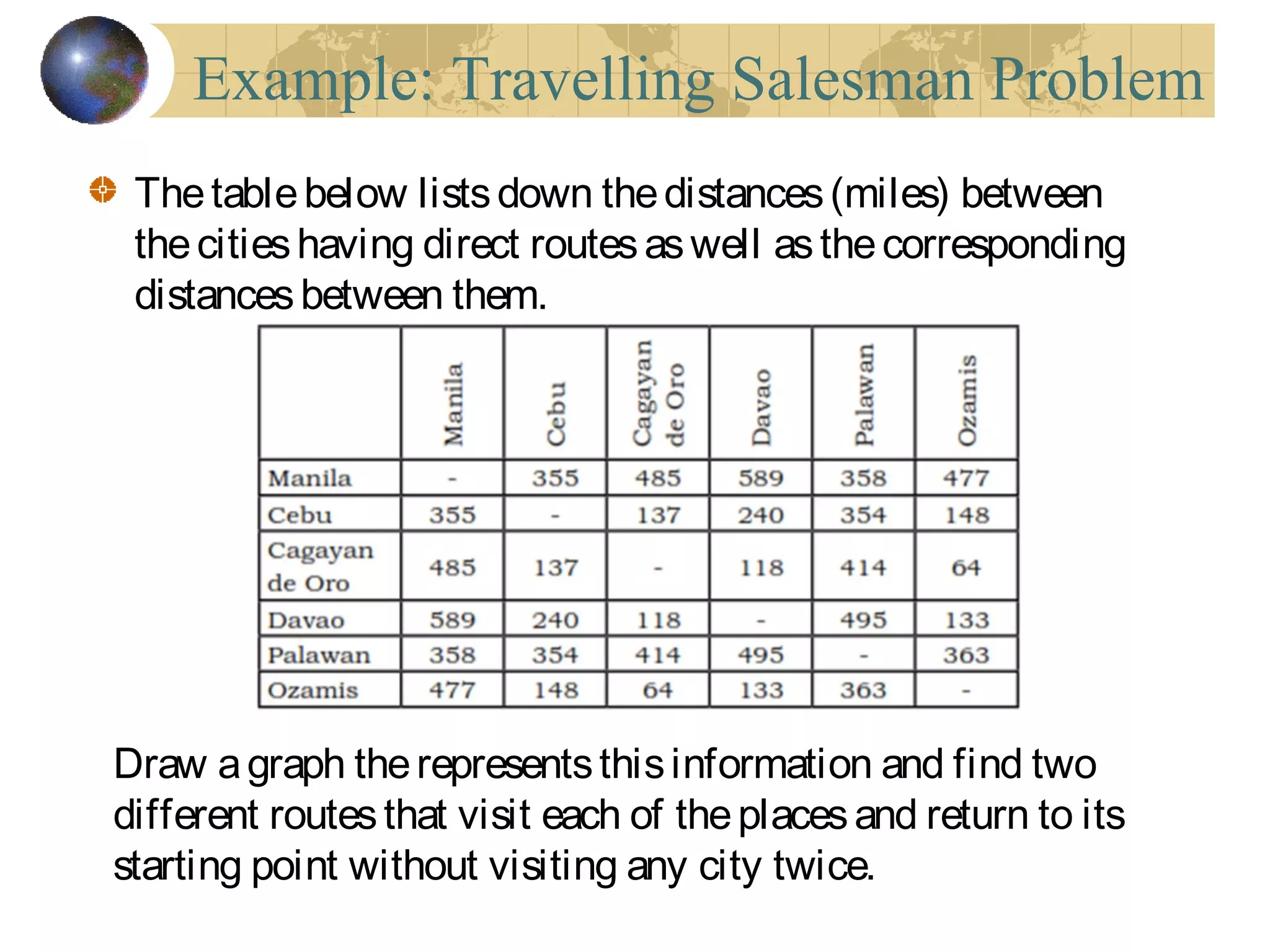
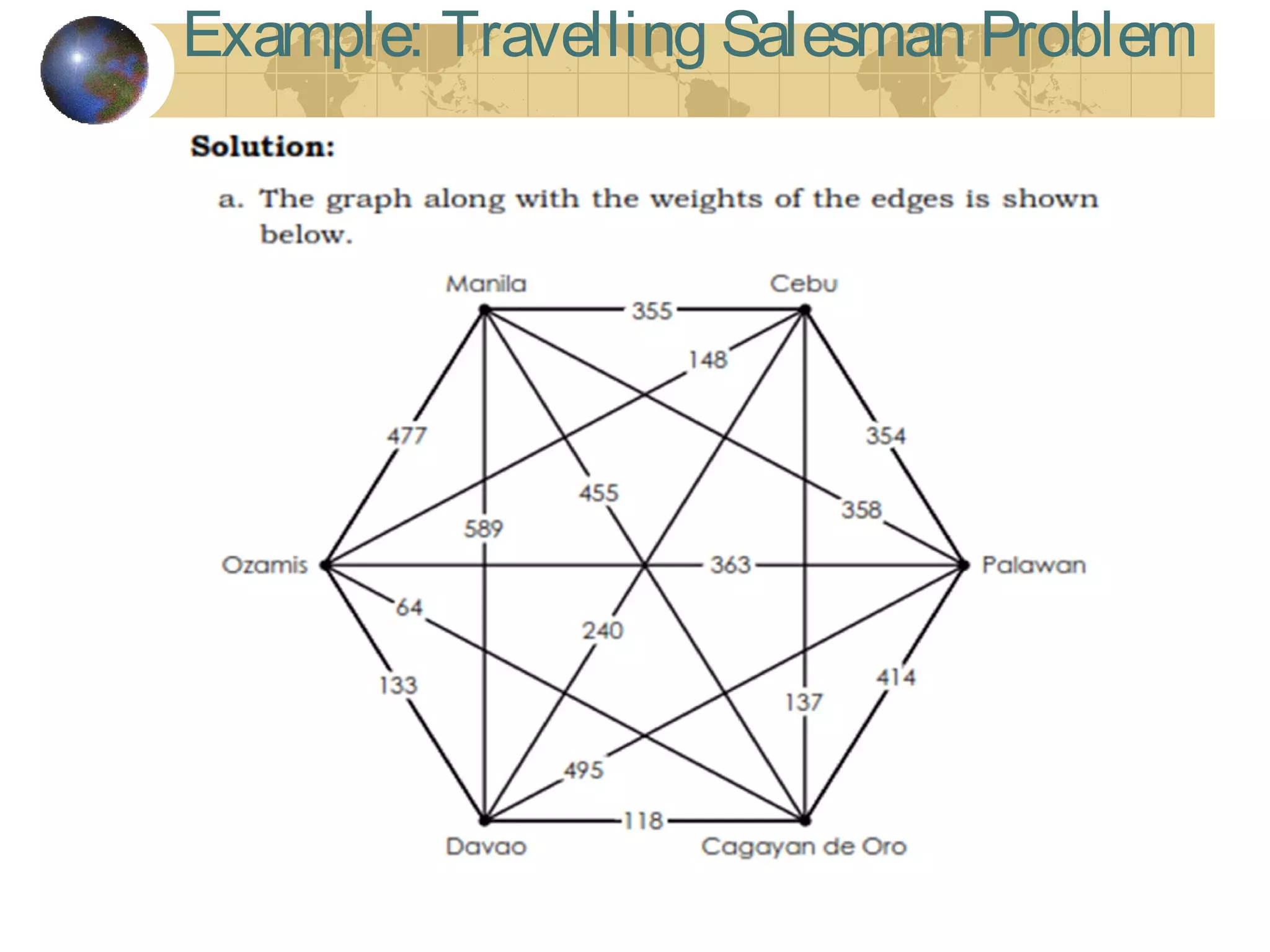
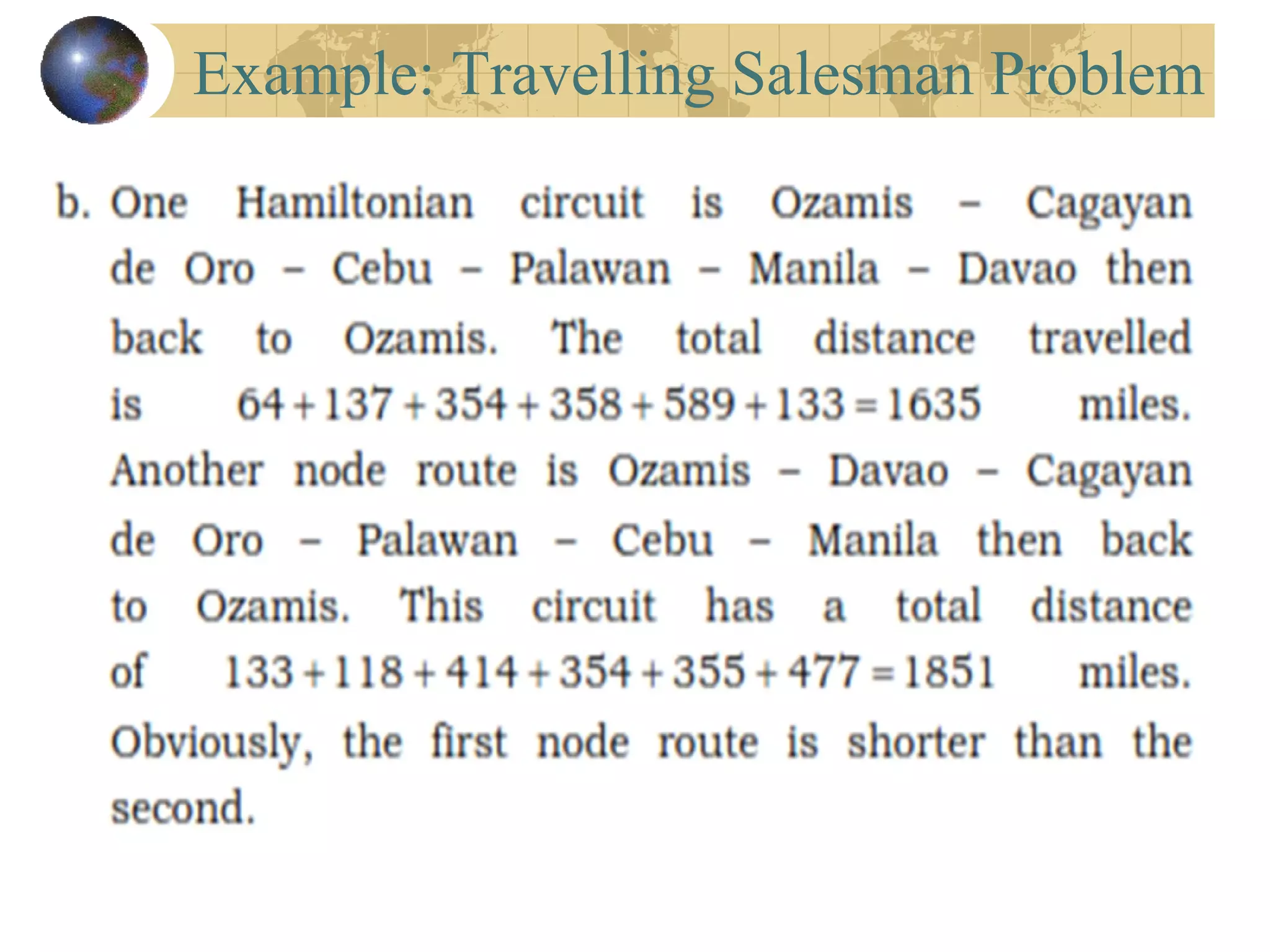
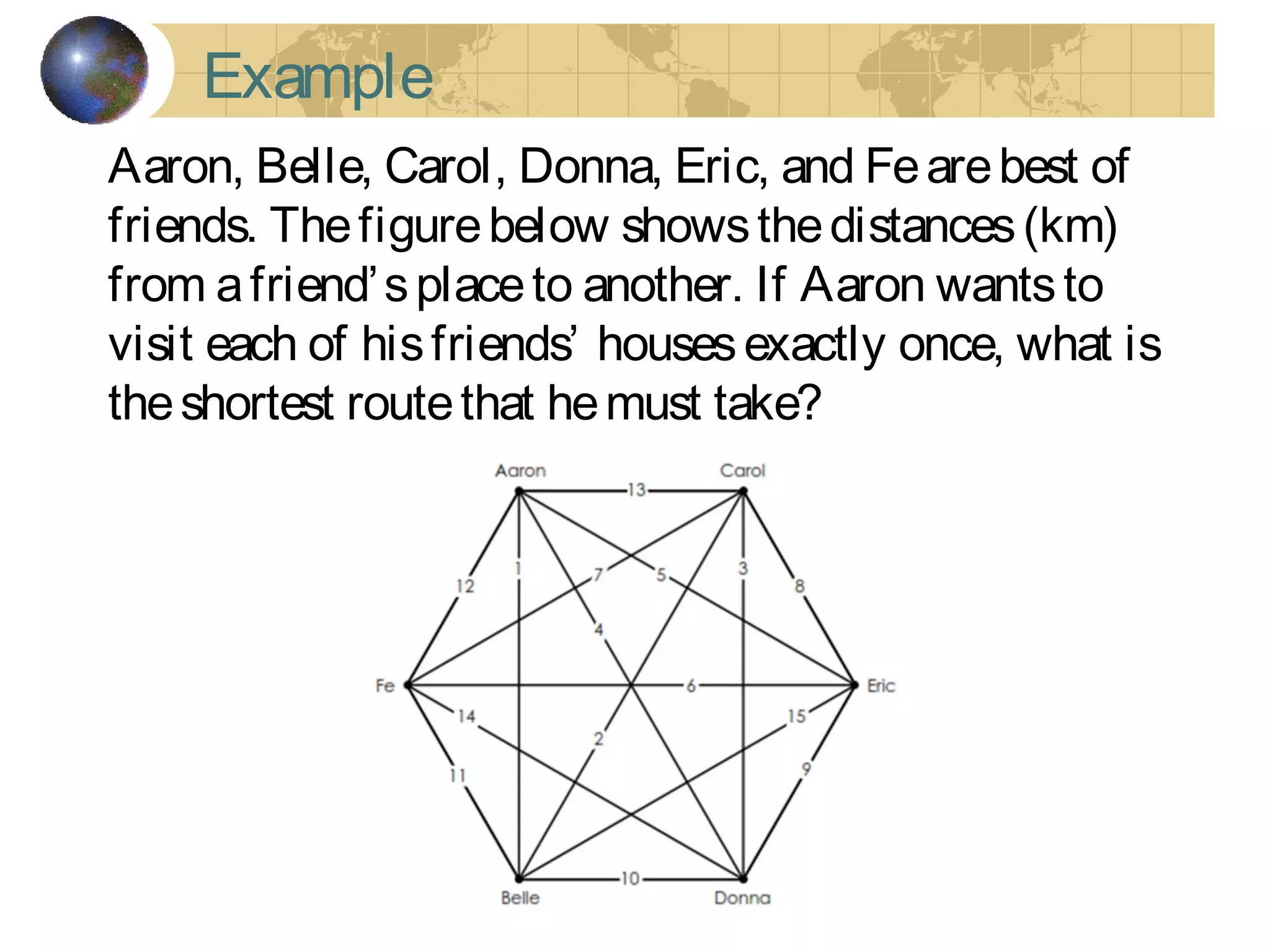
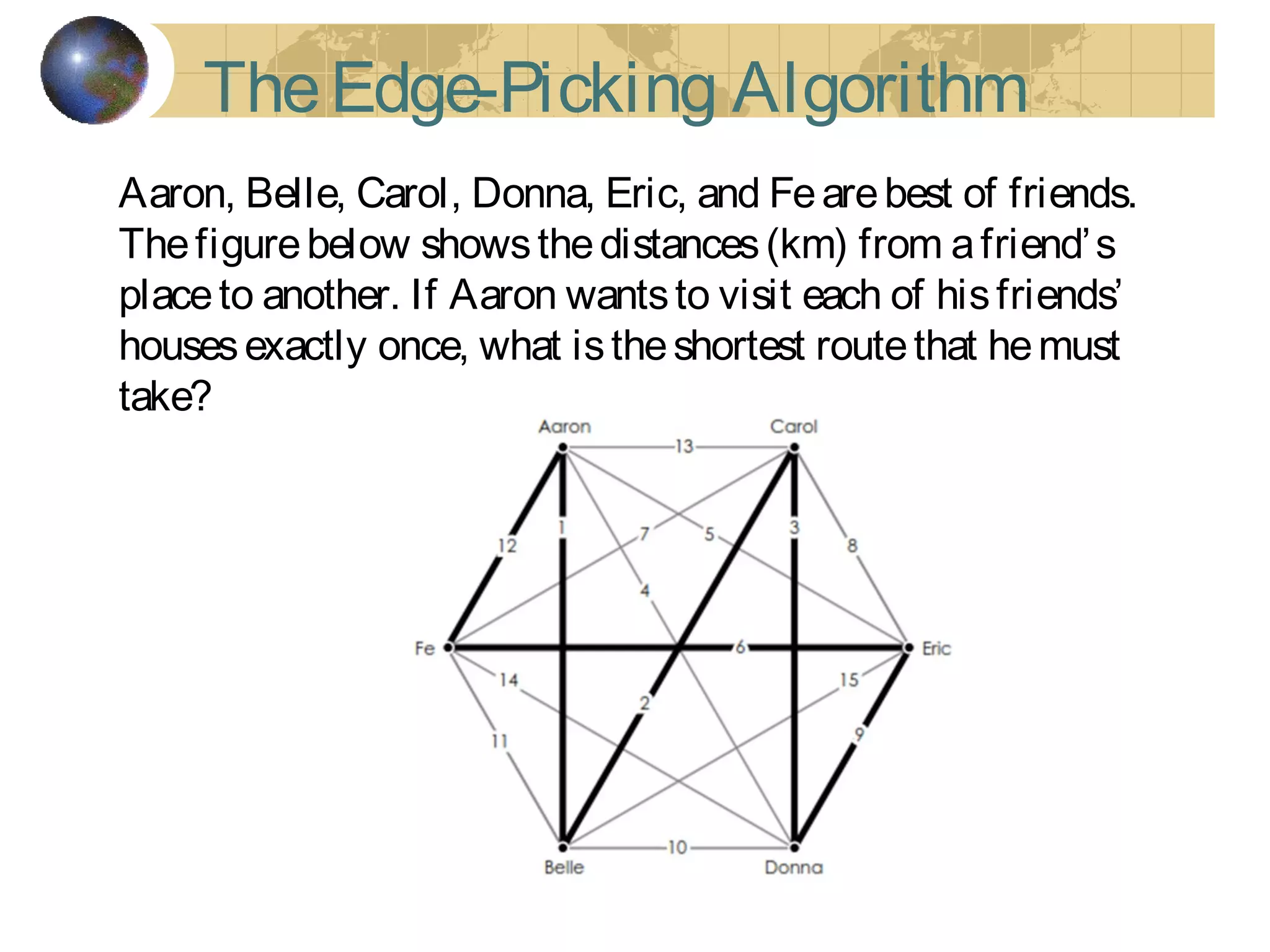
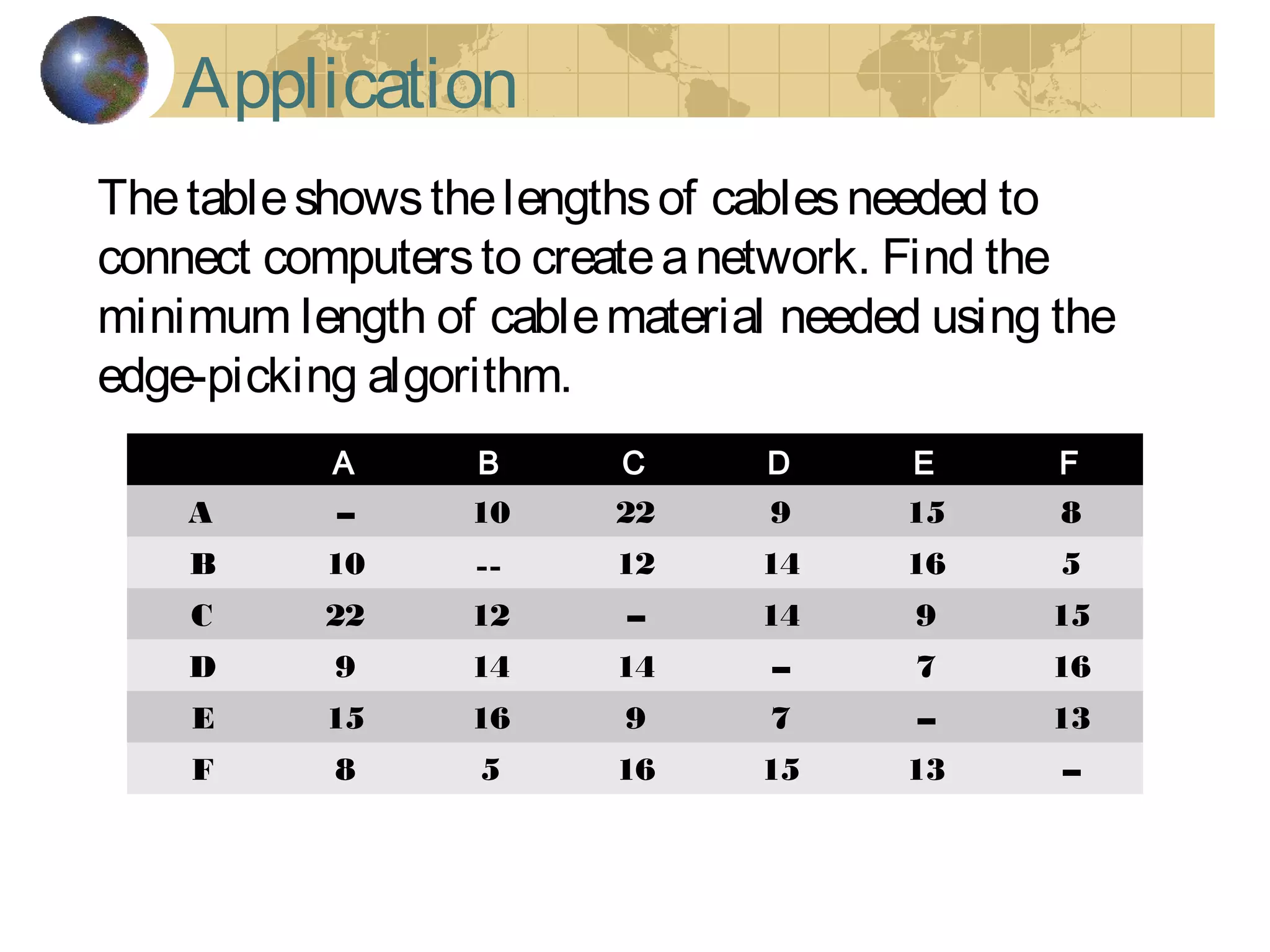
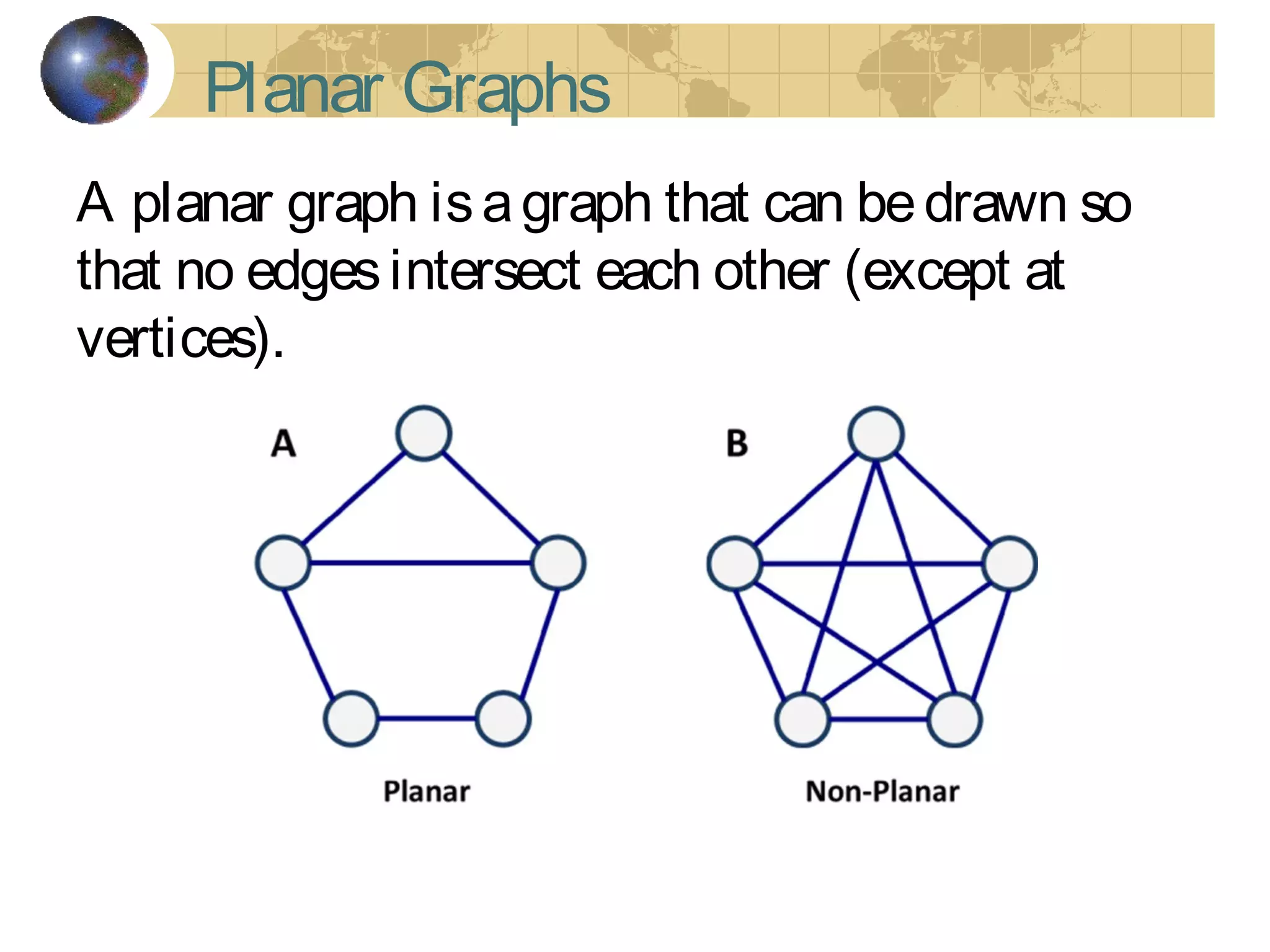
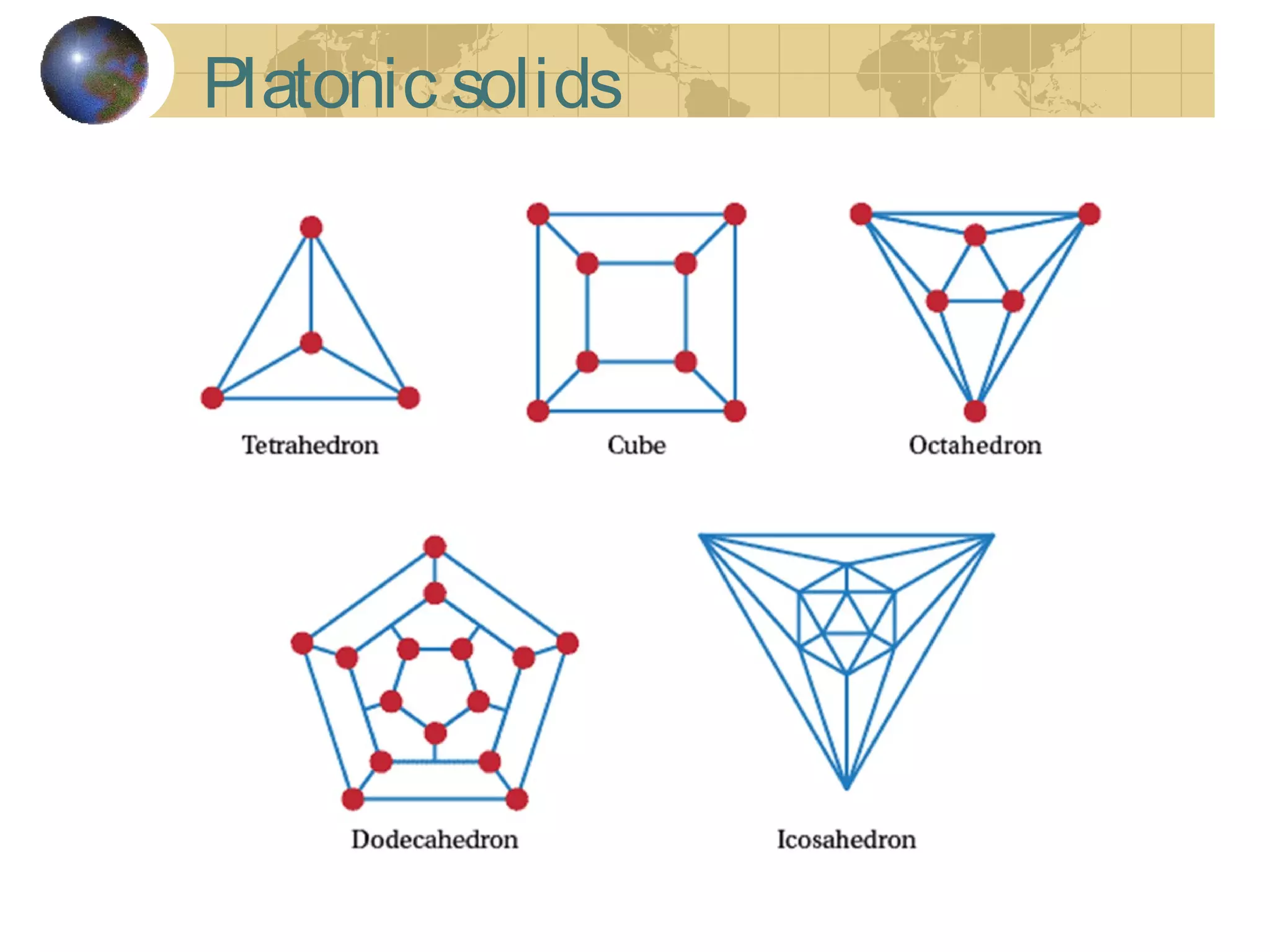
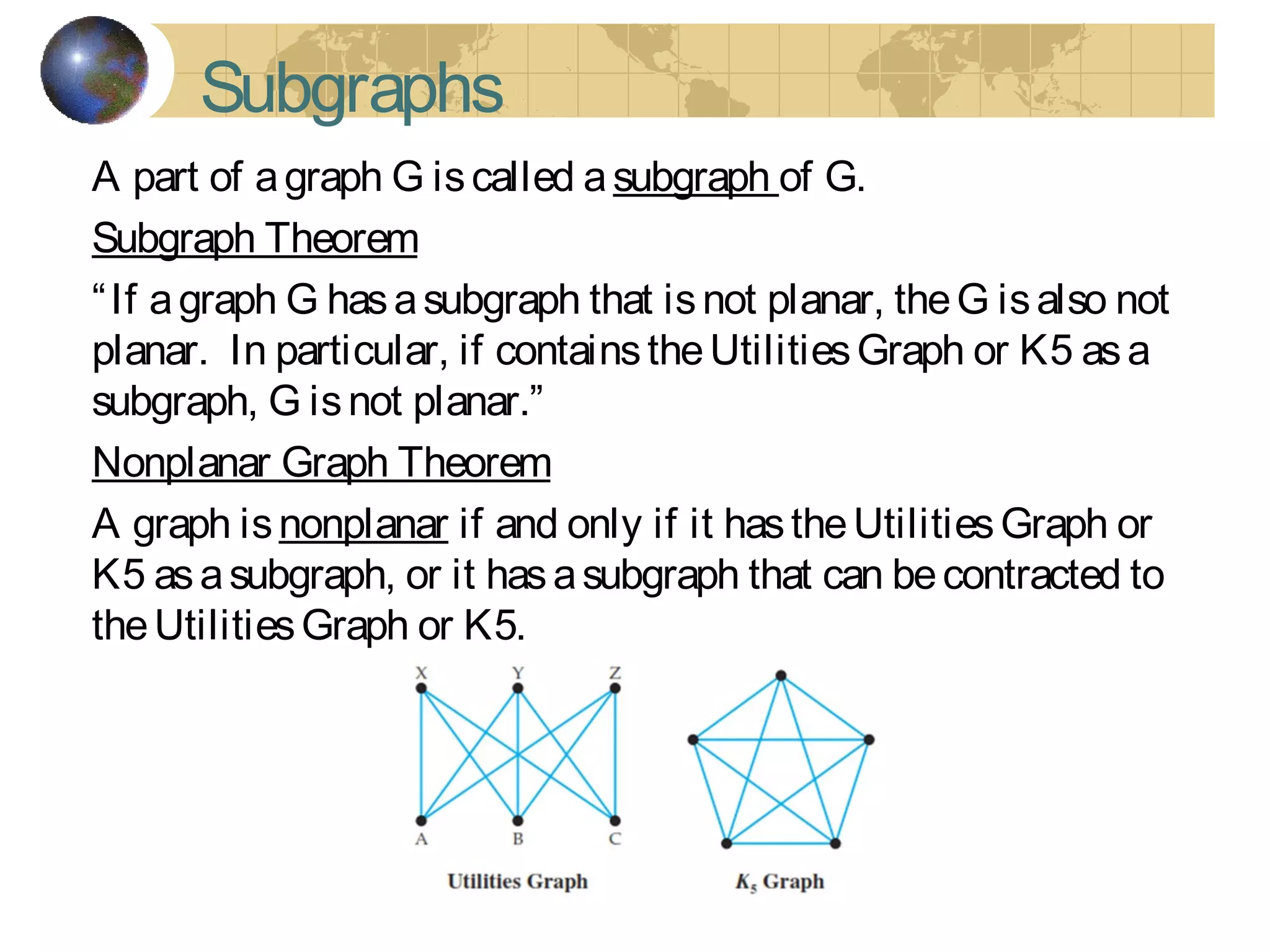
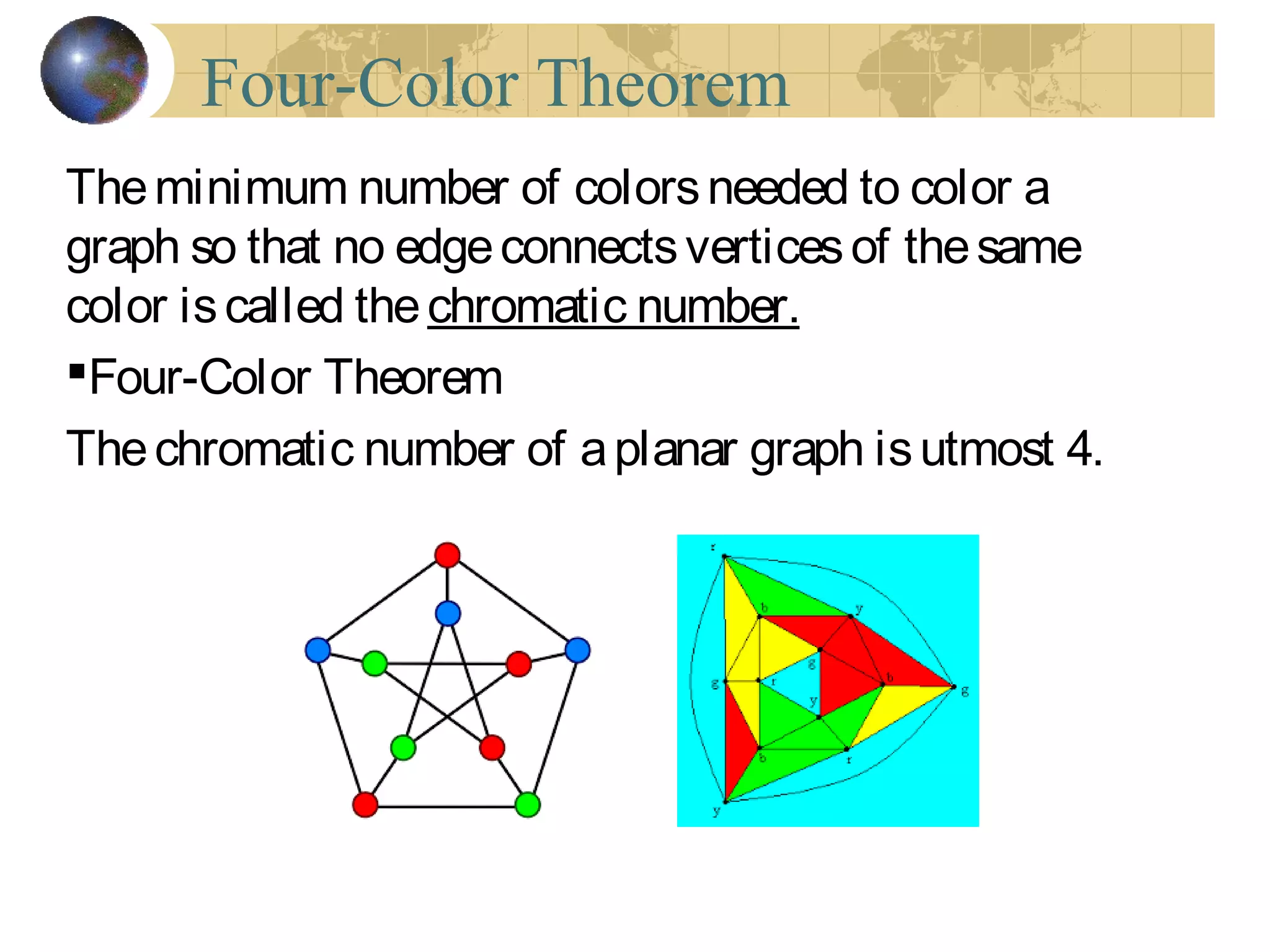
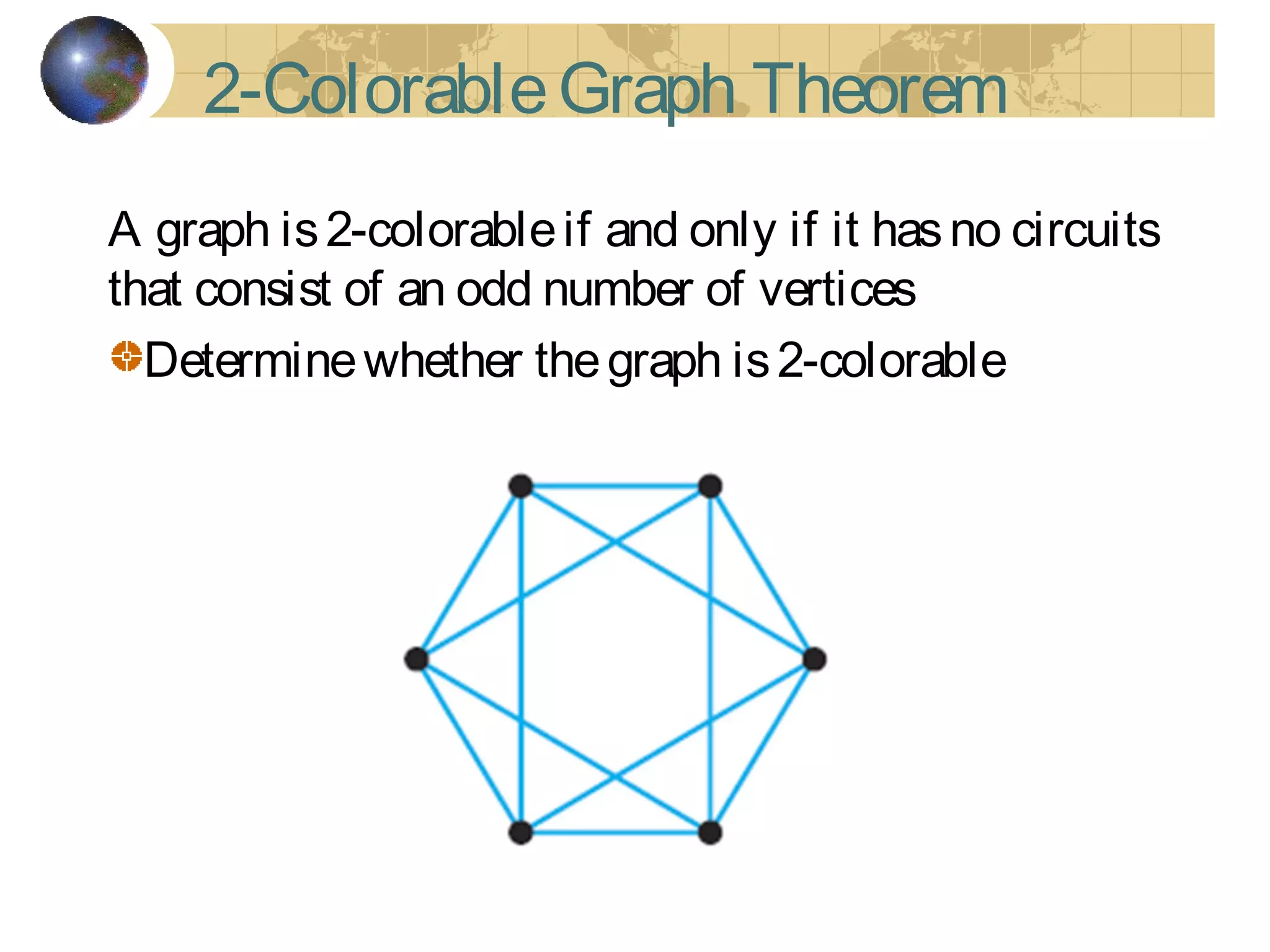
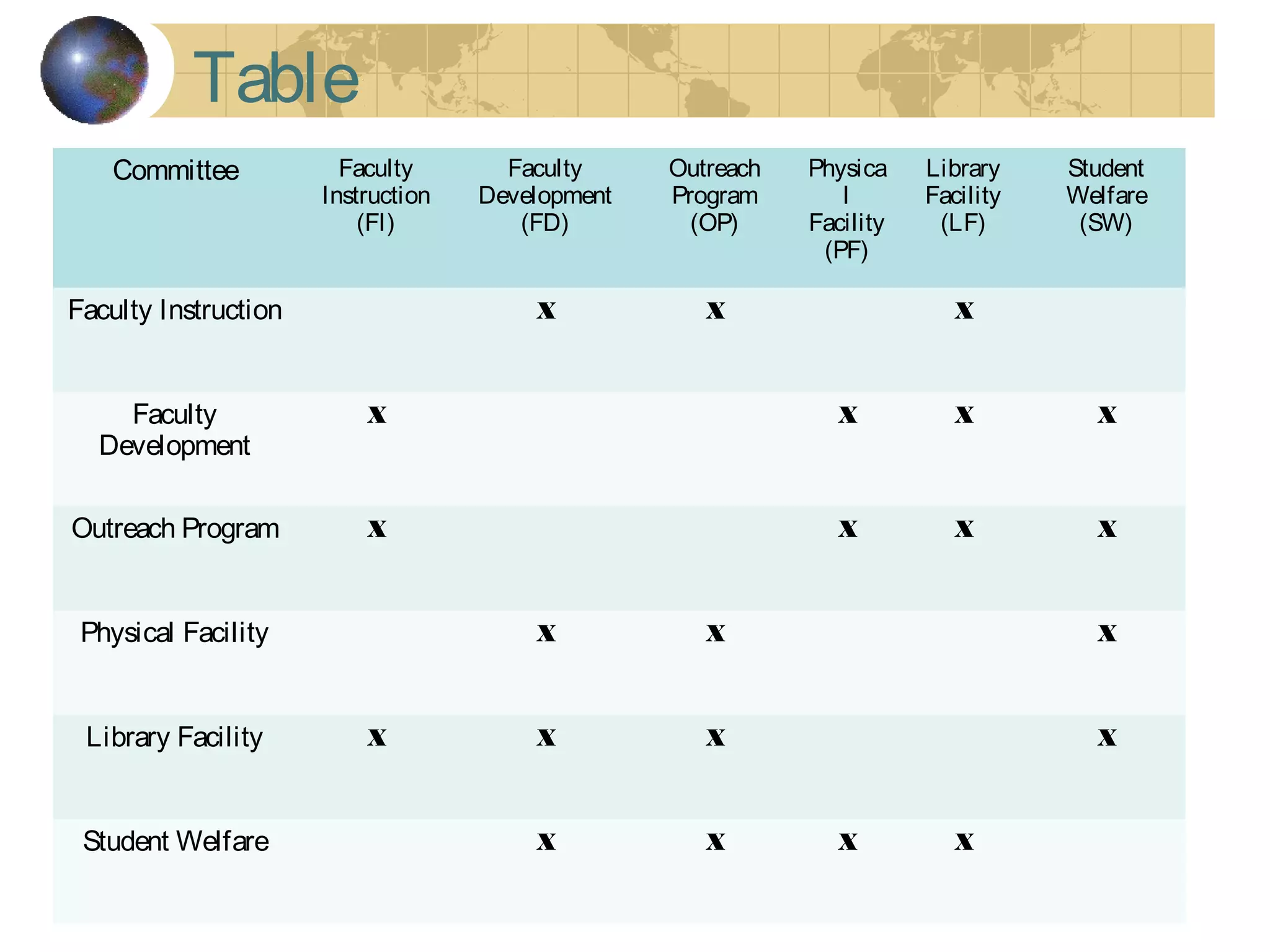
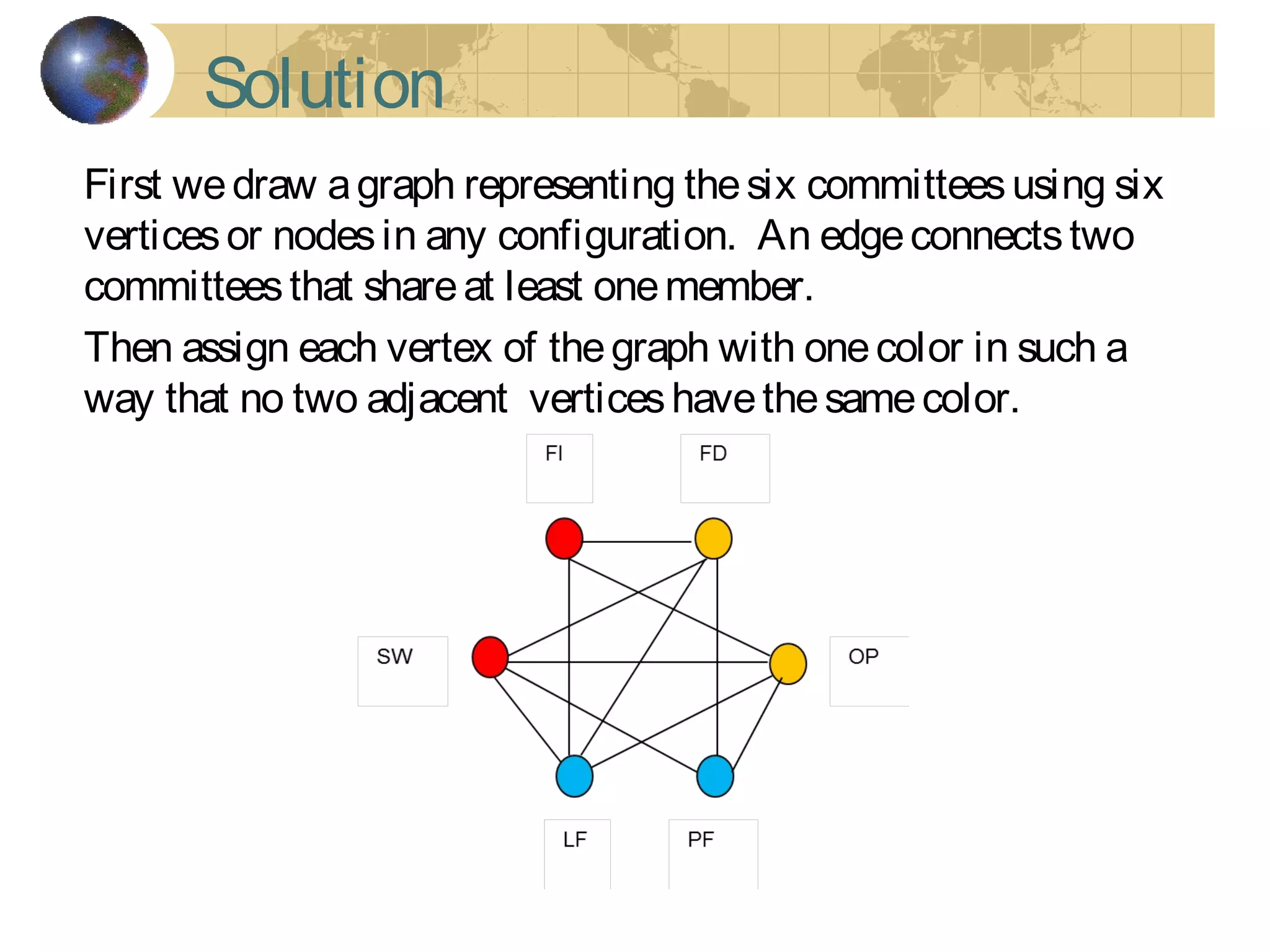
The document discusses Hamiltonian paths and circuits, defined as paths that visit each vertex exactly once, noting the lack of straightforward criteria for determining Hamiltonian circuits compared to Euler circuits. Dirac's theorem is introduced, which provides a condition for a graph to be Hamiltonian, along with examples such as applications in airline flight graphs and the Traveling Salesman Problem. Various algorithms, including greedy and edge-picking algorithms, are mentioned for finding Hamiltonian circuits, leading to practical applications in scheduling and network design.