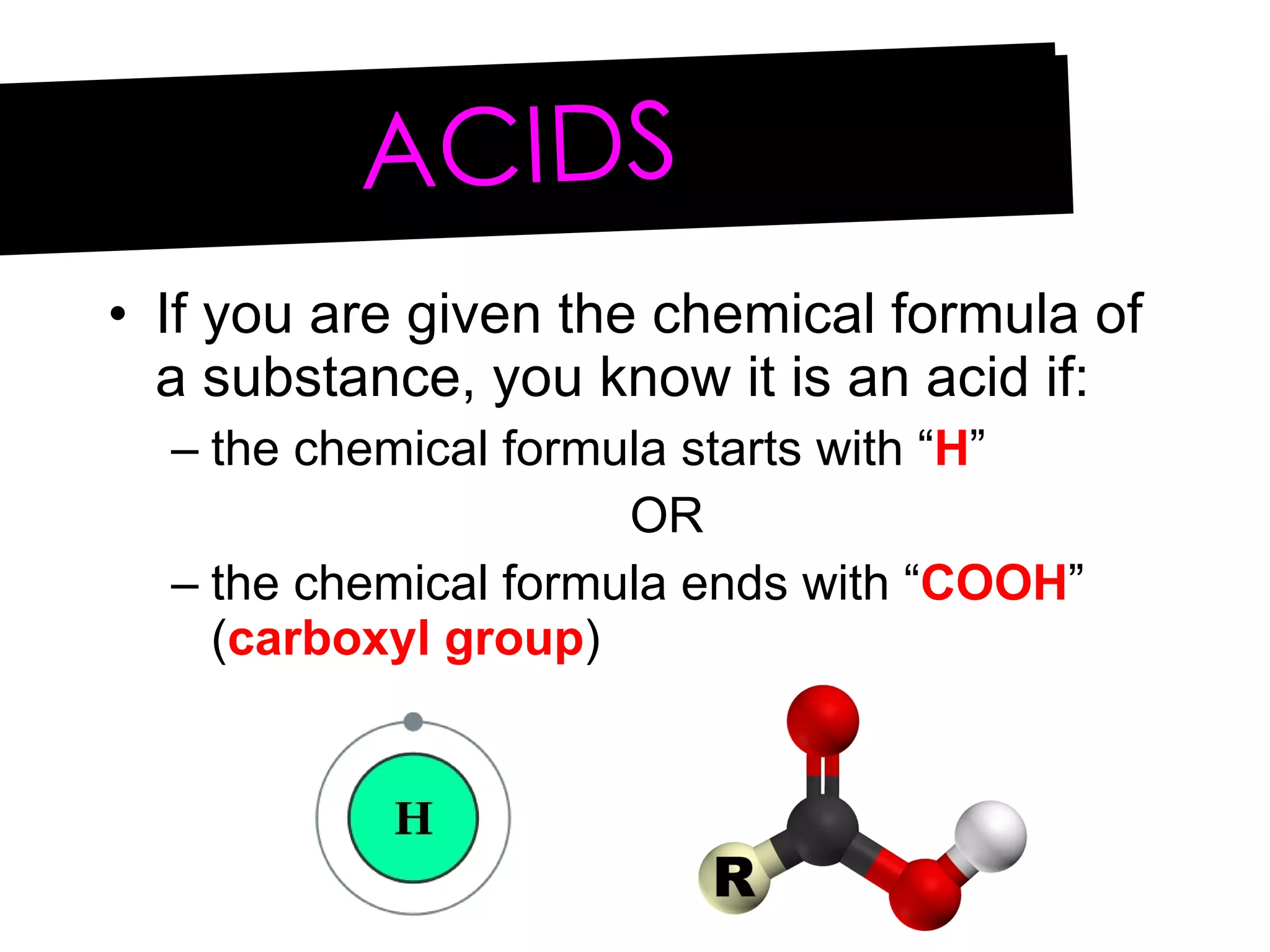
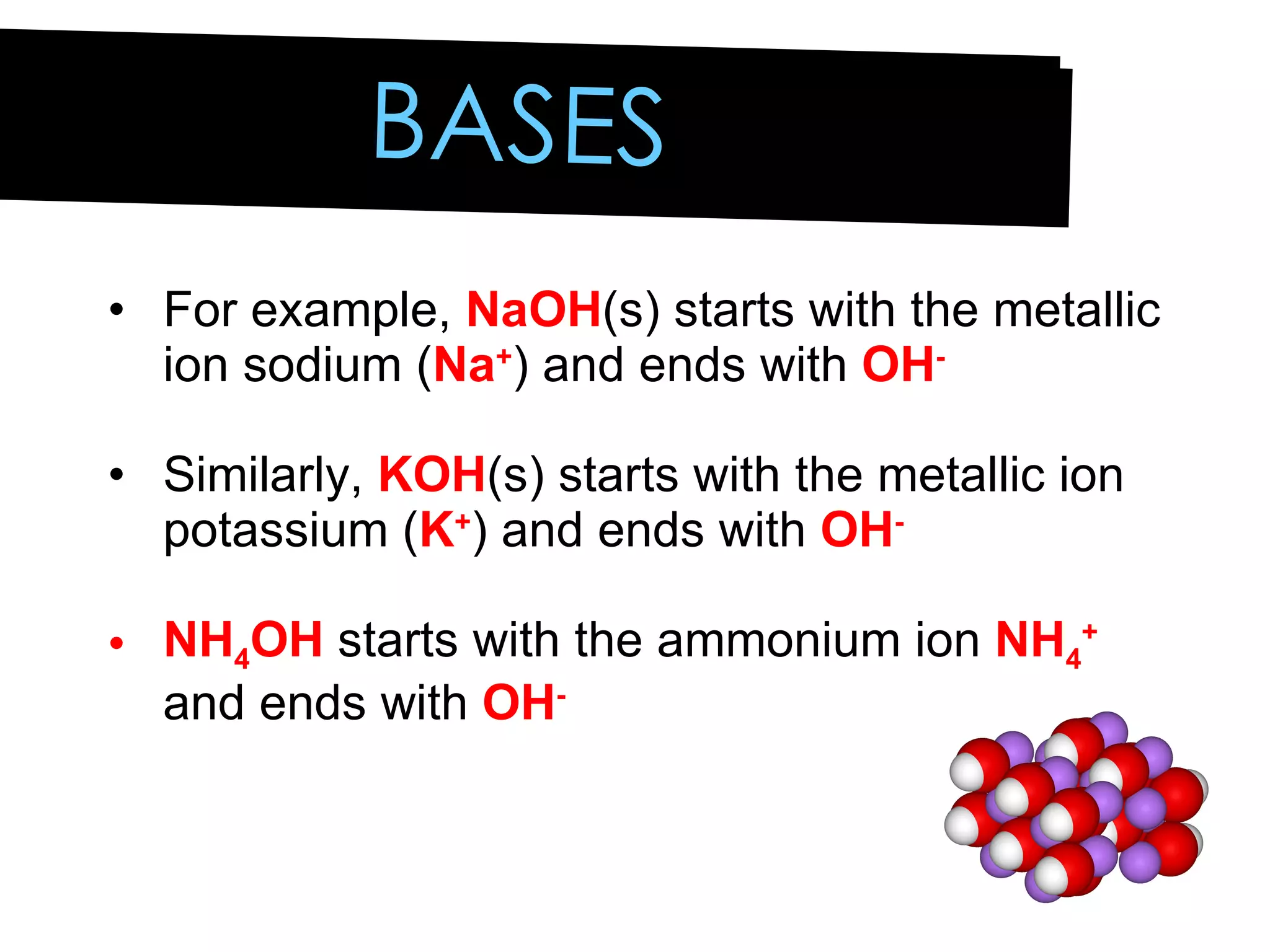
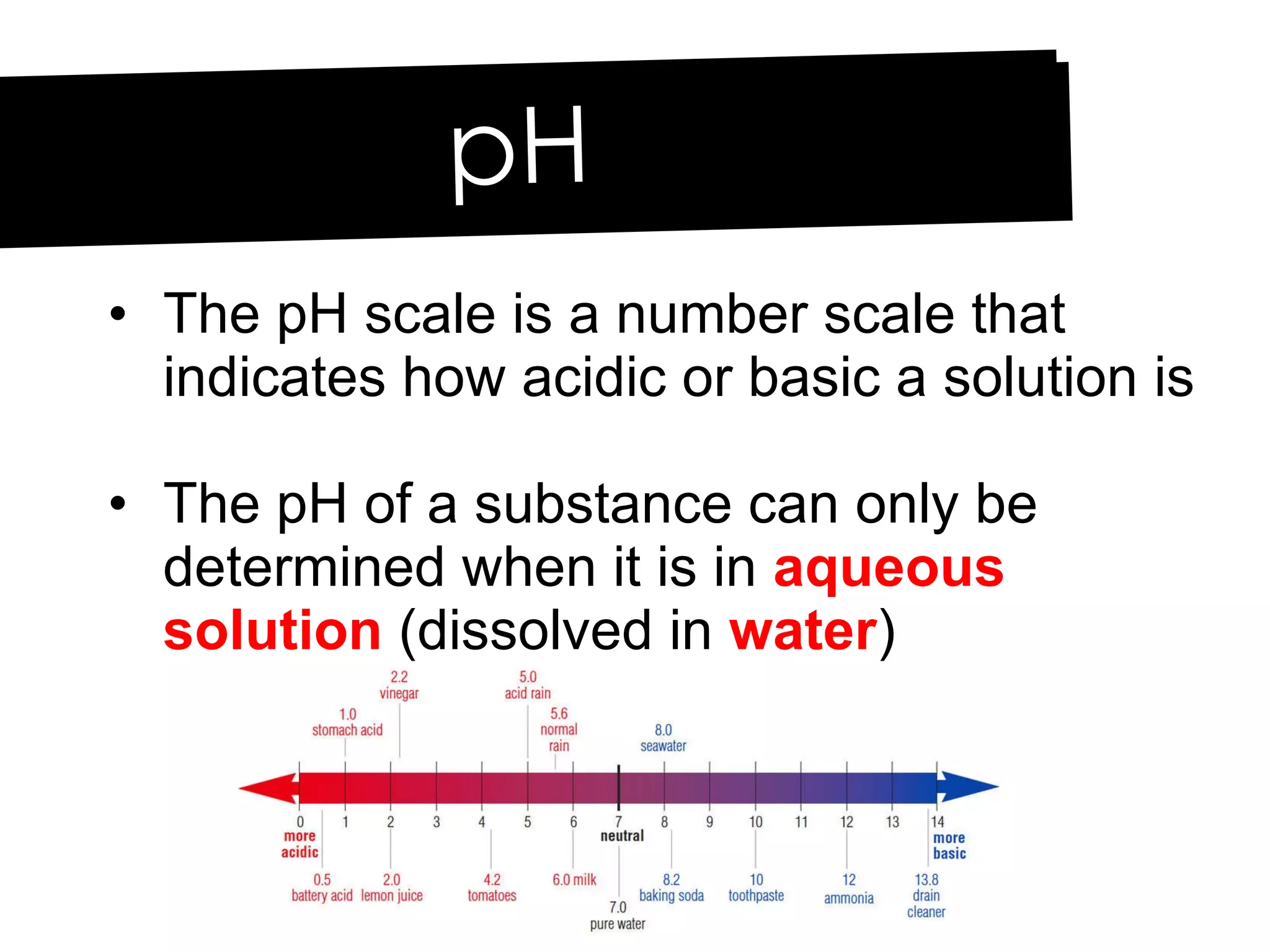
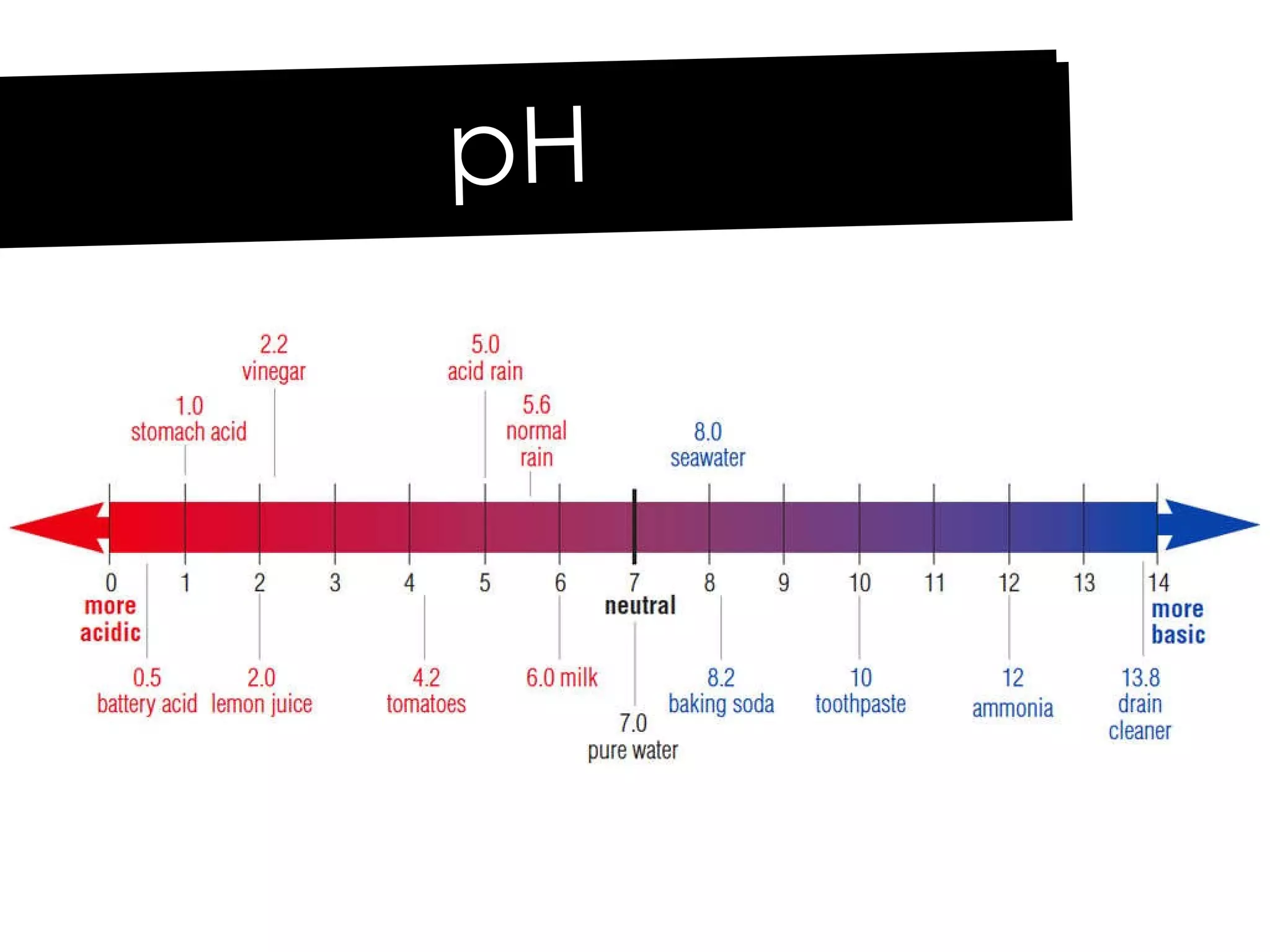
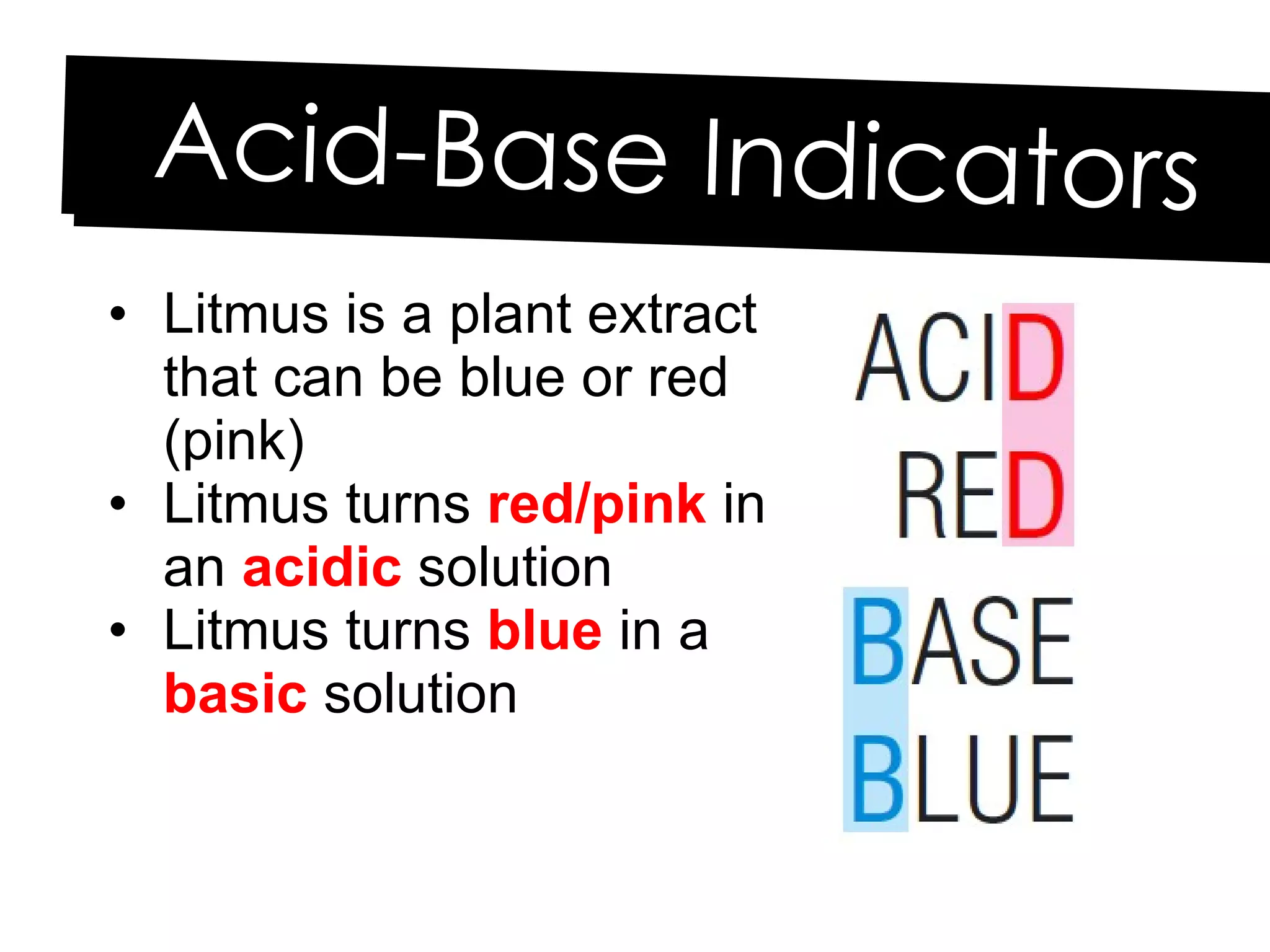
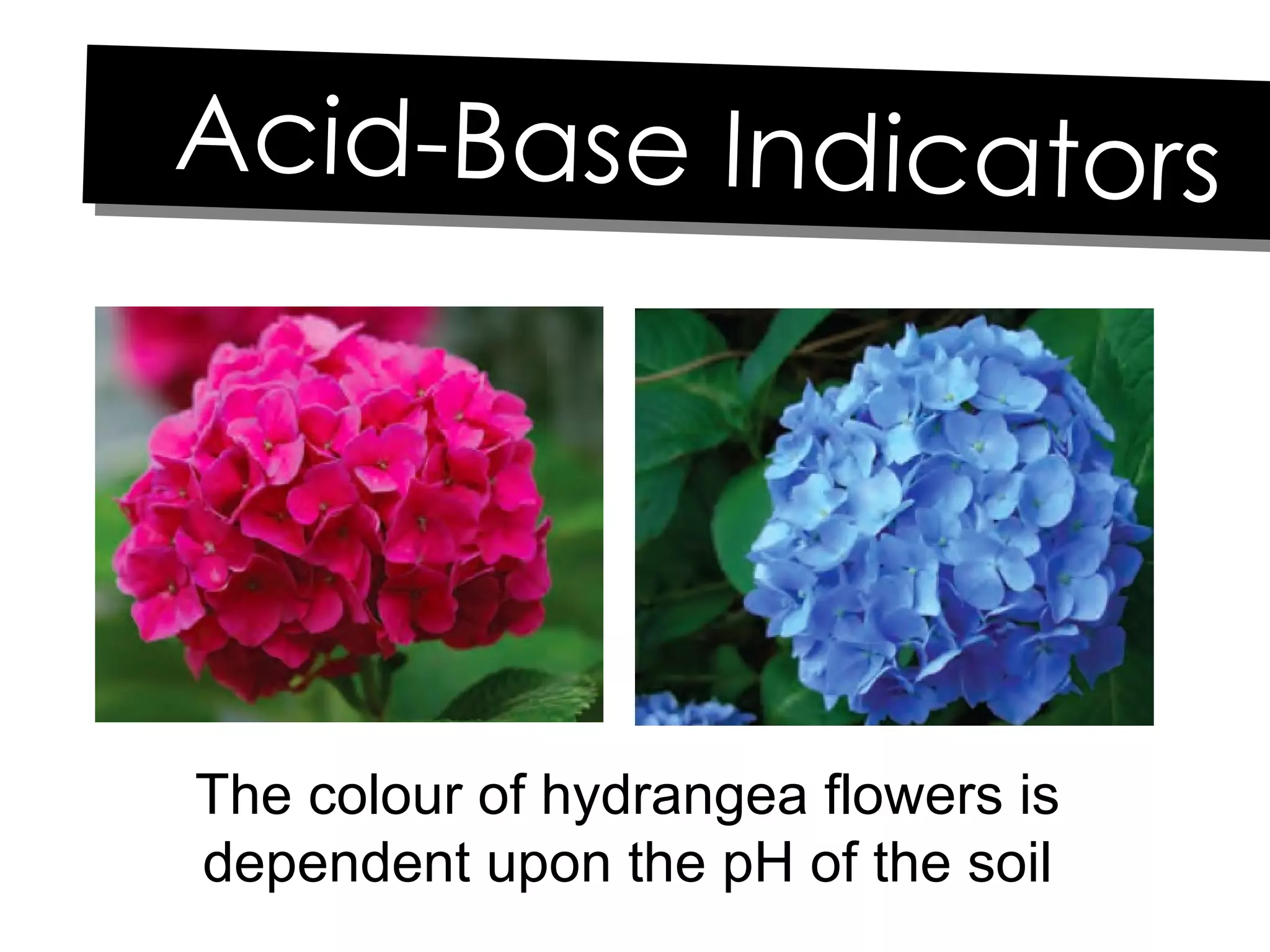
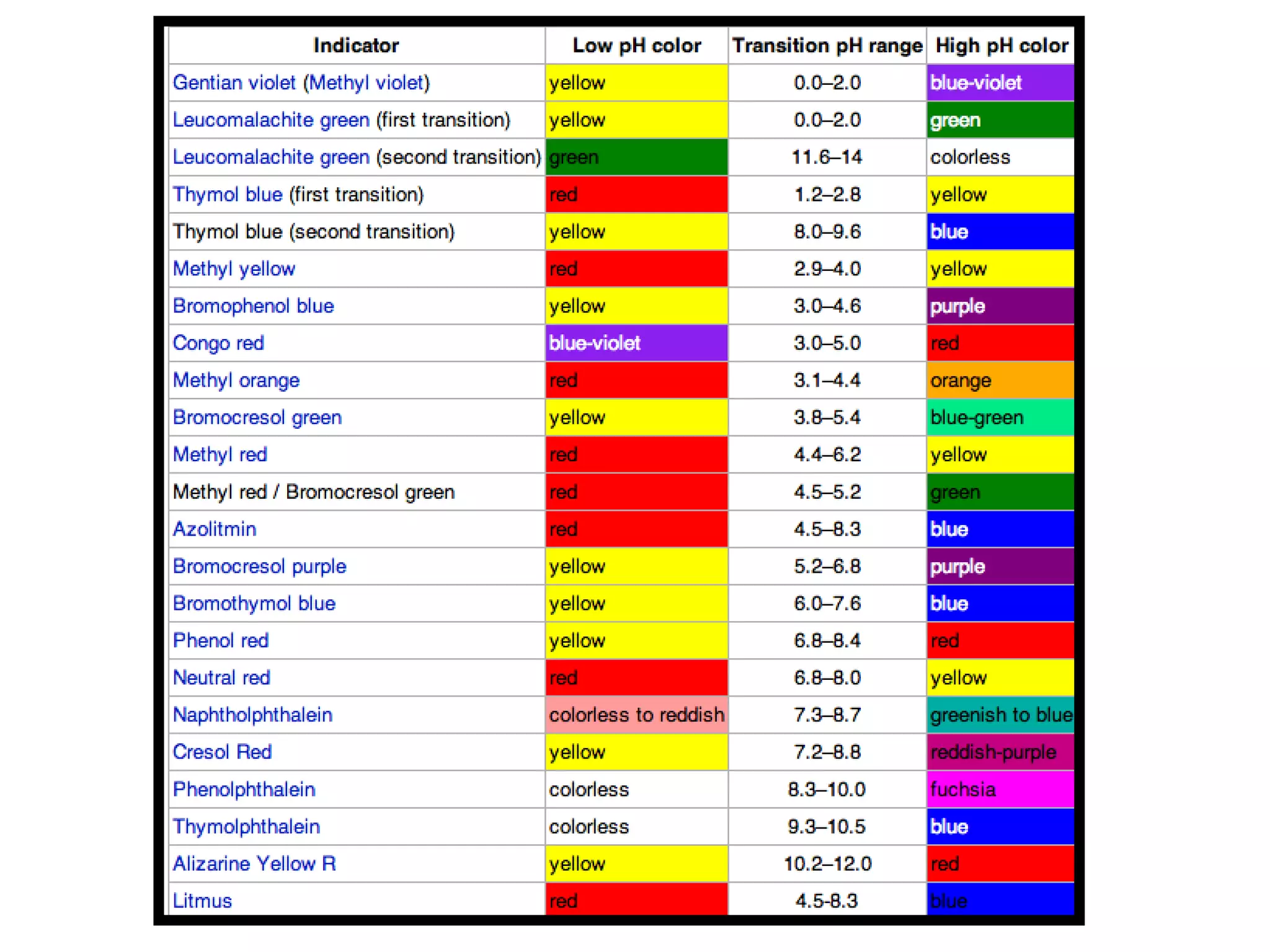
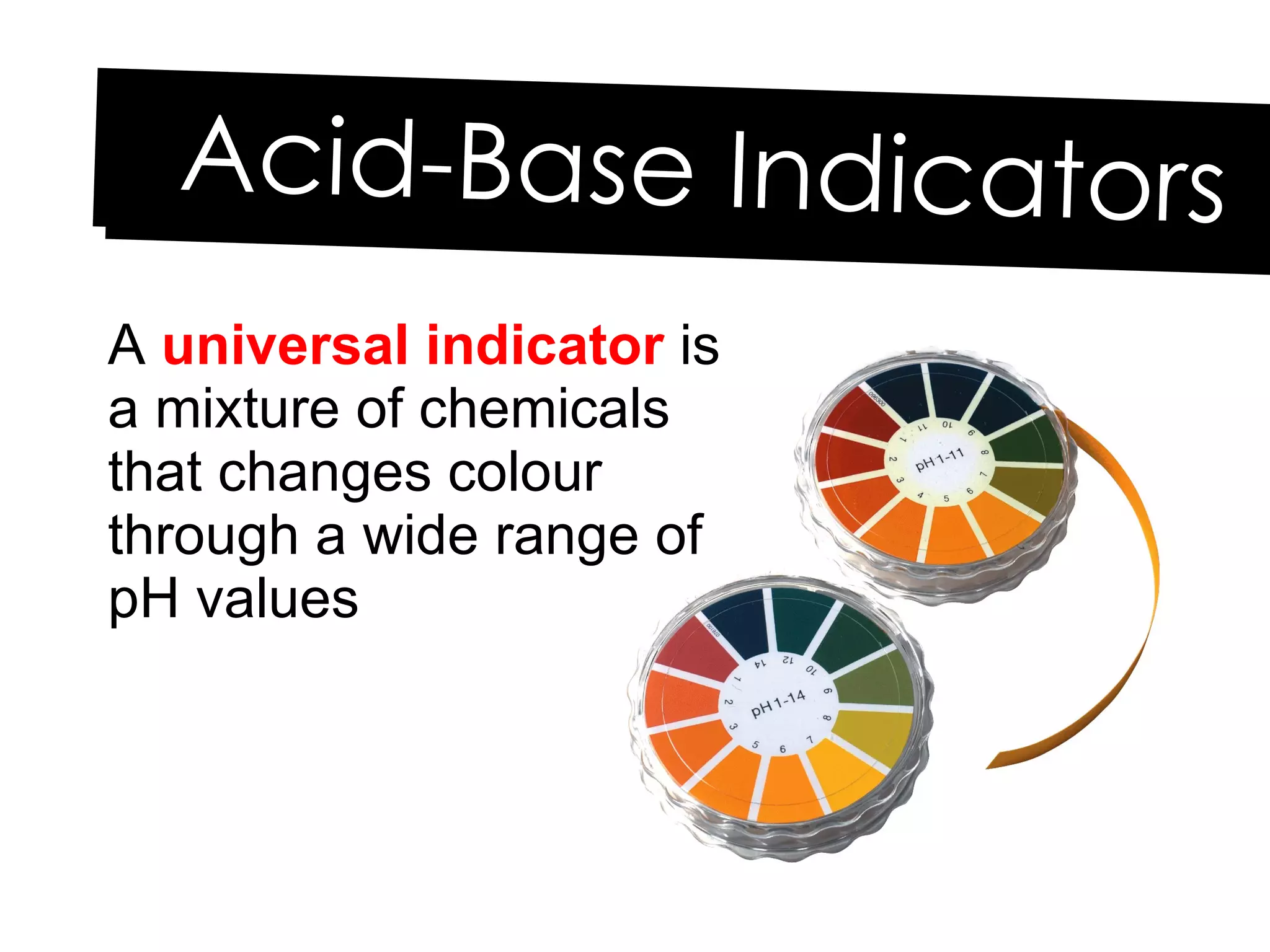
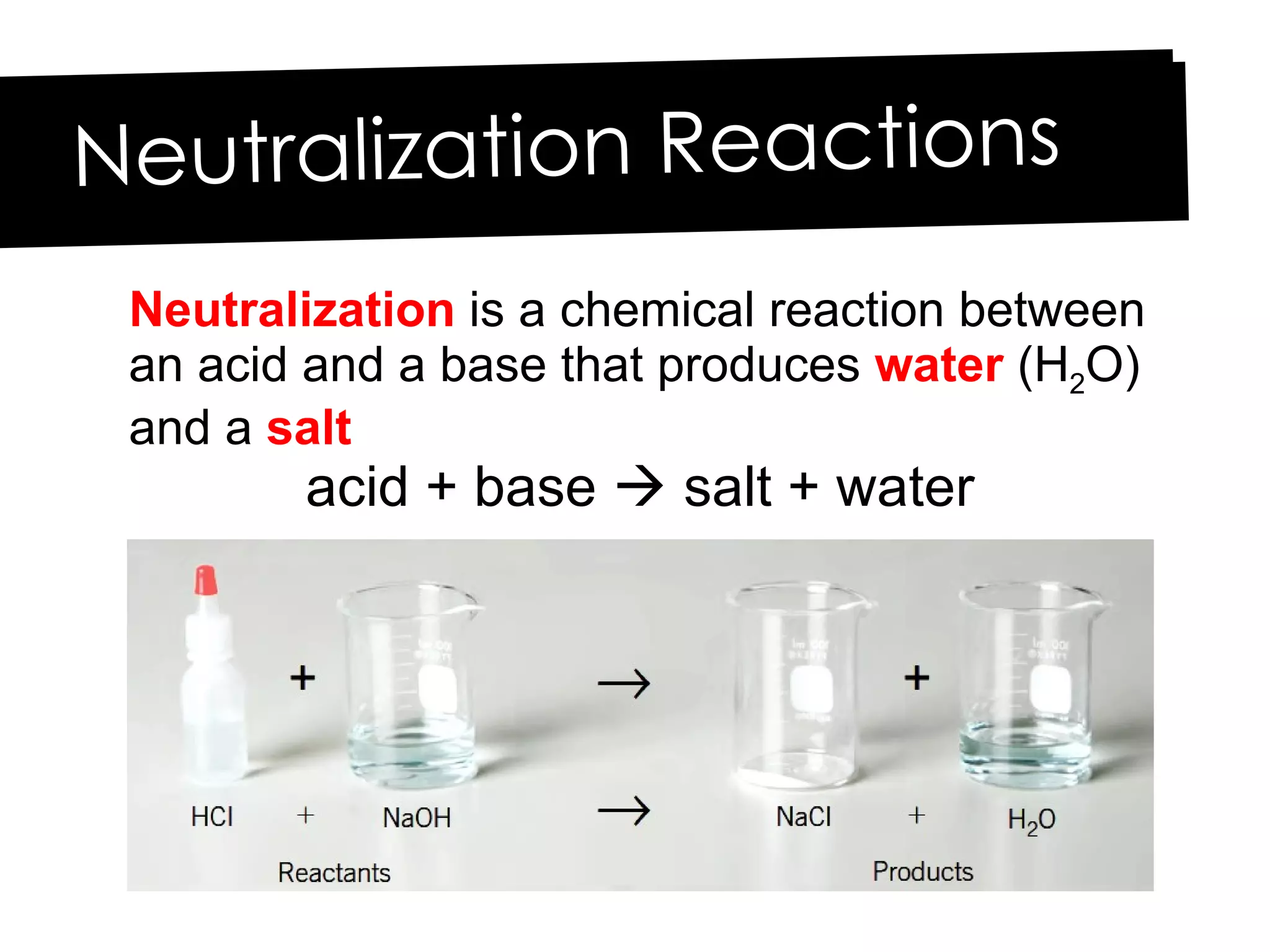
Acids and bases can be identified by their names or chemical formulas. Acids contain hydrogen (H) or a carboxyl group (COOH) and have a pH below 7. Bases contain a metallic or ammonium ion and hydroxide (OH) and have a pH above 7. Acid-base indicators change color at specific pH levels and can be used to determine if a solution is acidic or basic. A neutralization reaction occurs between an acid and base, producing water and a salt.