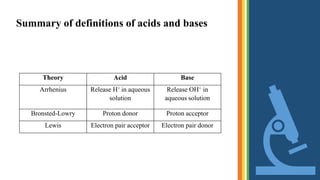
This document defines acids, bases, and salts according to three theories:
1) Arrhenius defines acids as substances that yield hydrogen ions in water and bases as substances that yield hydroxide ions in water. Neutralization produces salt and water.
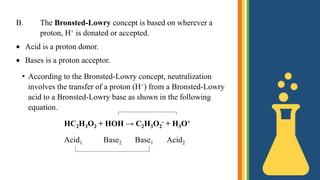
2) Bronsted-Lowry defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. Neutralization involves the transfer of a proton from an acid to a base.
3) Lewis defines acids as electron pair acceptors and bases as electron pair donors. Neutralization involves the sharing of an electron pair between an acid and base.







![C. The Lewis concept is based on the shared electron pair.
Acid is an electron pair acceptor.
Base is an electron pair donor.
Example of Lewis acids are Ag+, BF3, AlCl3 while NH3
(ammonia) and RNH2 (amines) are classified as Lewis bases.
: NH3 + HCl → [H: NH3]+ Cl-
Base Acid Salt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidsbasesandsalt-181016233053/85/Acids-bases-and-salt-9-320.jpg)