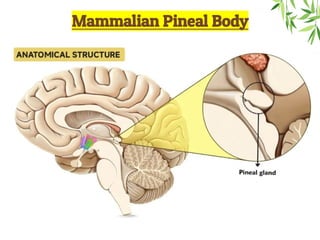
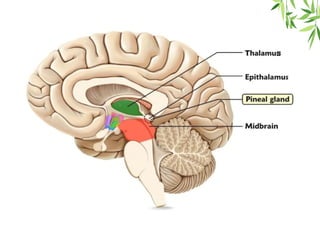
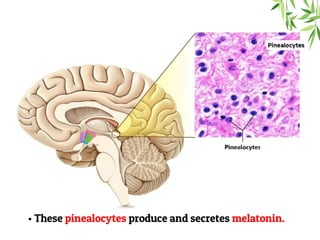
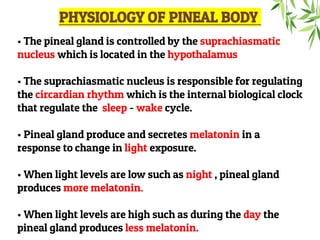
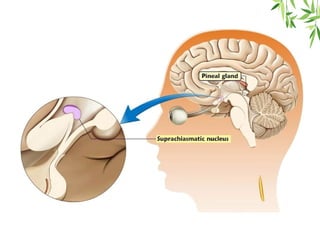
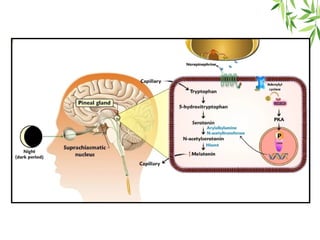
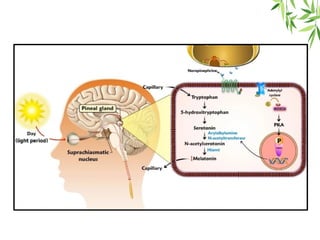
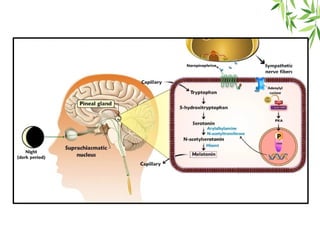
The document presents a detailed overview of the mammalian pineal gland, its structure, and the significance of its hormone, melatonin, in regulating circadian rhythms, seasonal reproduction, and various physiological processes. It highlights the role of the pineal body as an endocrine gland that produces melatonin in response to light exposure and discusses its effects on sleep-wake cycles, immune modulation, and neuroprotection. Additionally, it addresses potential clinical applications of melatonin in treating sleep disorders and other health conditions.