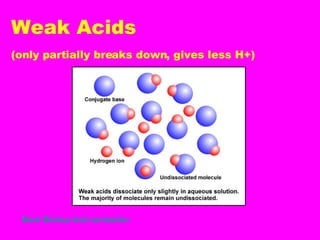
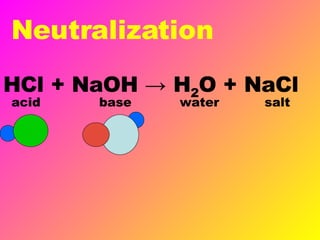
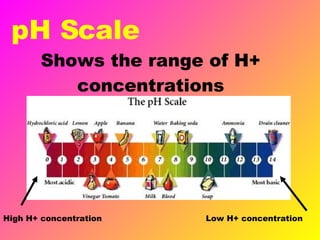
Acids release H+ ions in water and have sour tastes, while bases release OH- ions in water and feel slippery. Strong acids and bases completely ionize in water, while weak acids and bases only partially ionize. Common strong acids include sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, while strong bases include lithium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide. When acids and bases are mixed, they neutralize each other through a reaction that produces water and a salt. Indicators change color depending on whether the solution is acidic or basic, and can be used to measure the pH of a solution.