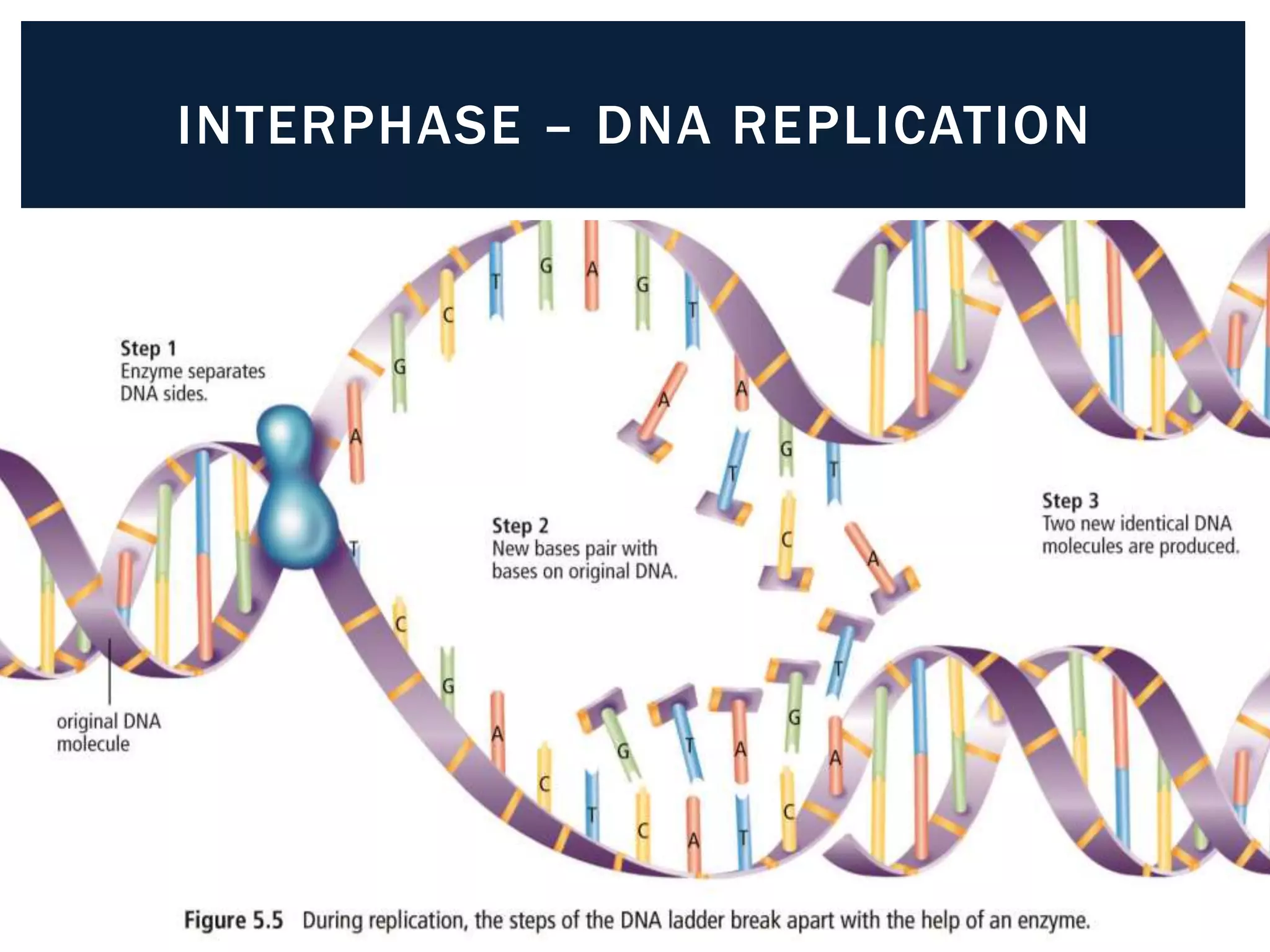
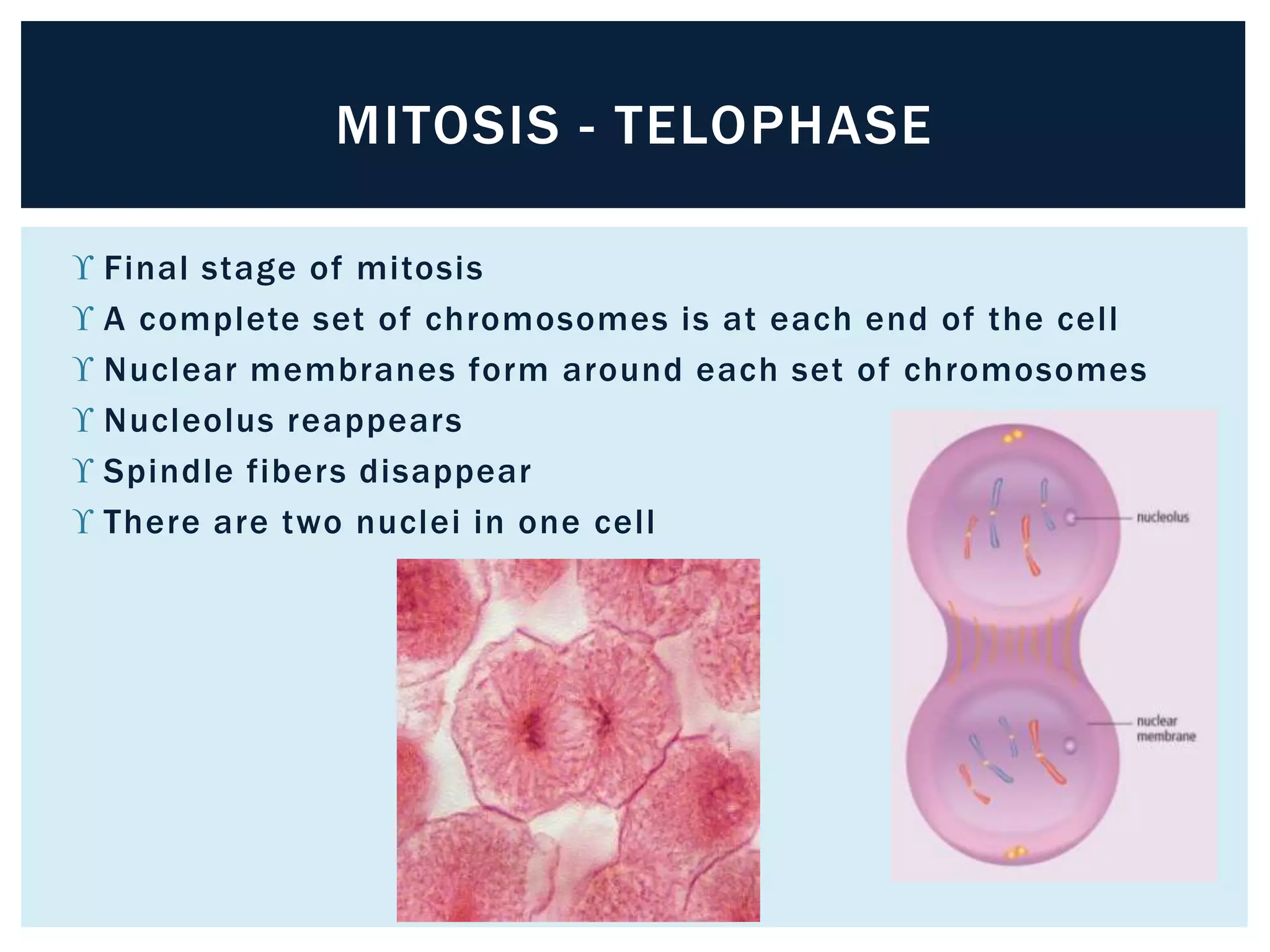
The cell cycle describes the life of a cell and is divided into three main stages: interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows and DNA is replicated. Mitosis involves the duplication and separation of chromosomes, dividing the nucleus. Cytokinesis then splits the cell into two identical daughter cells. The stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, during which the chromosomes align and separate. Cytokinesis differs between plant and animal cells, with plant cells forming a cell plate and animal cells pinching together.