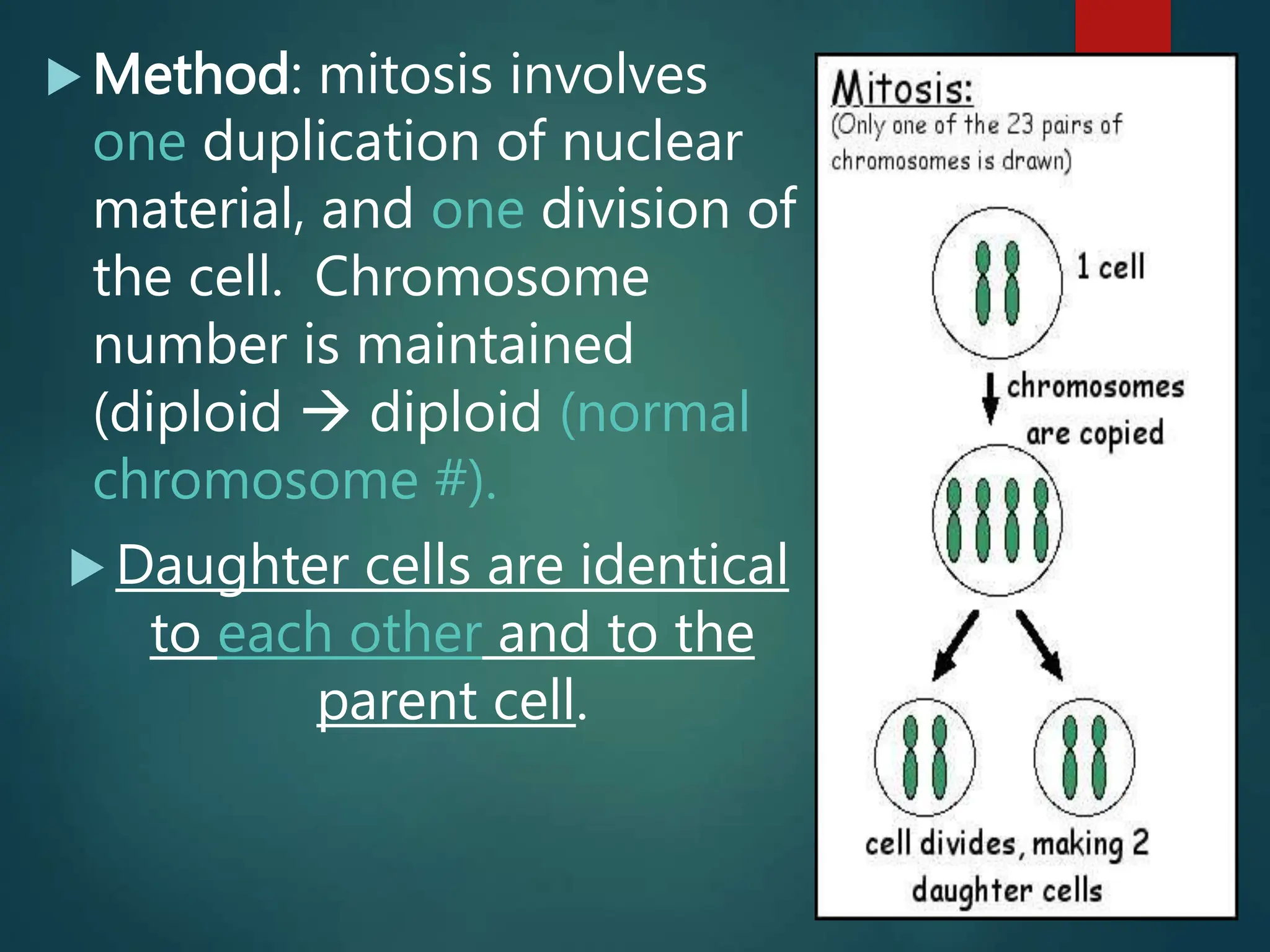
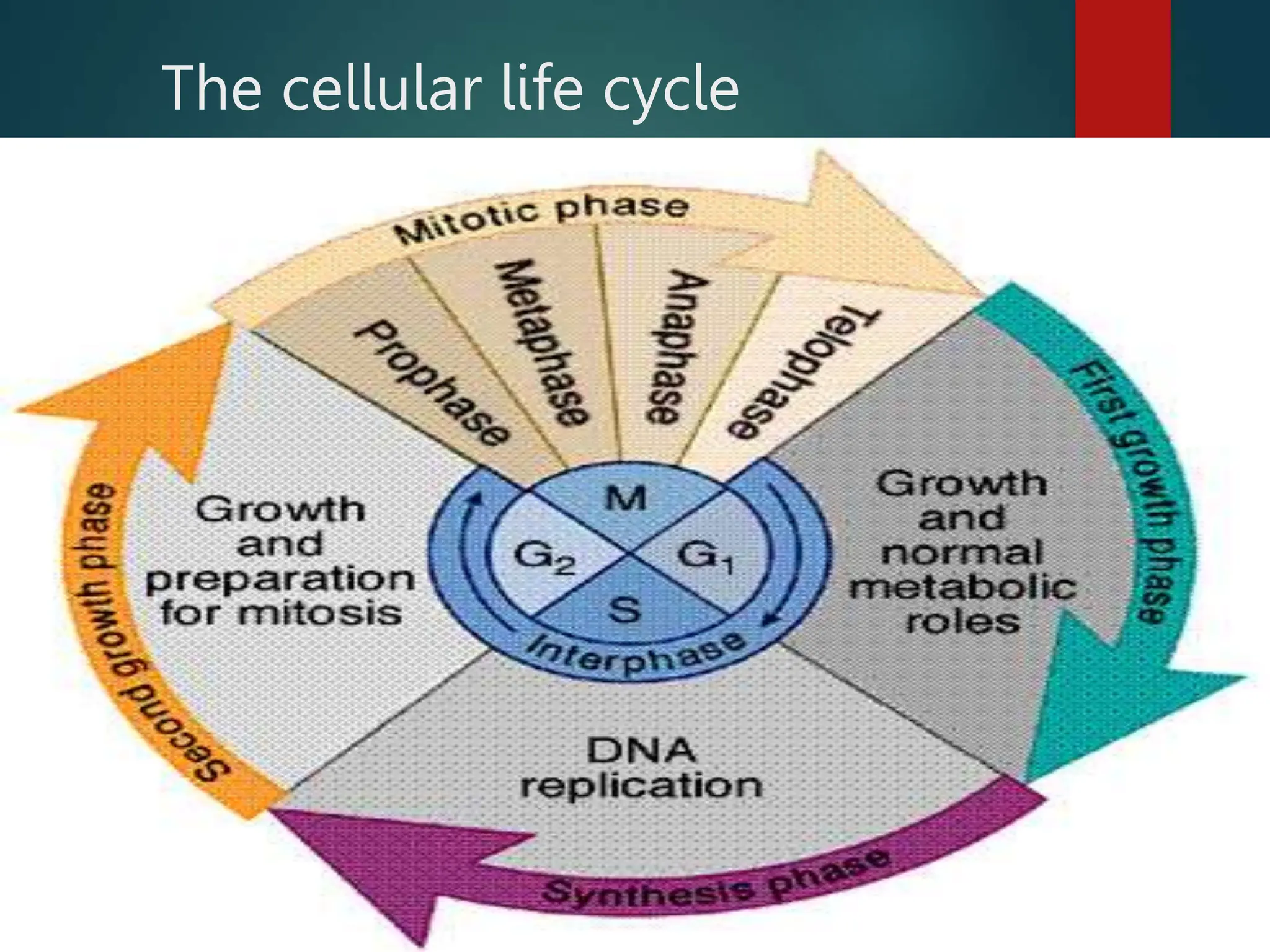
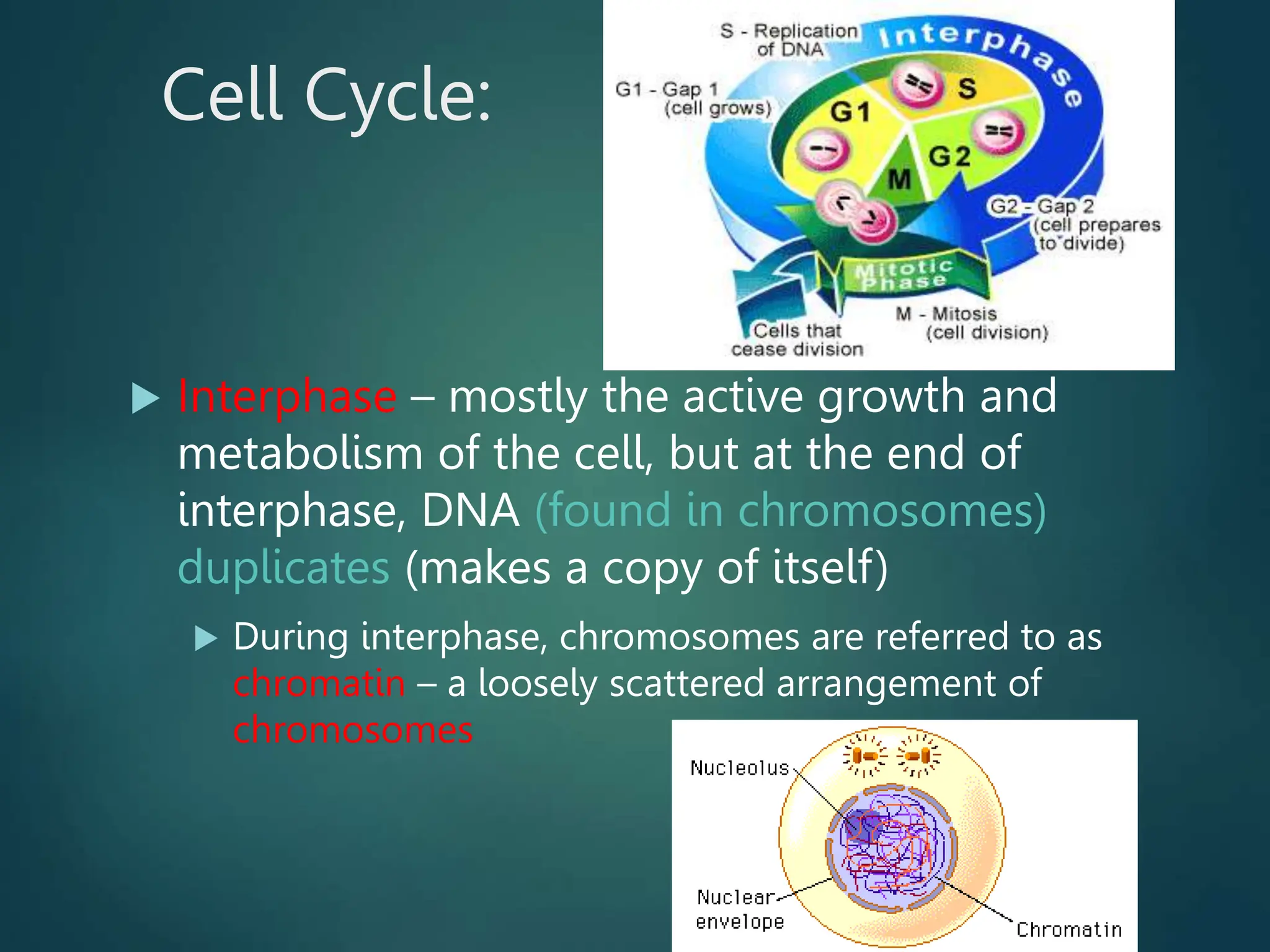
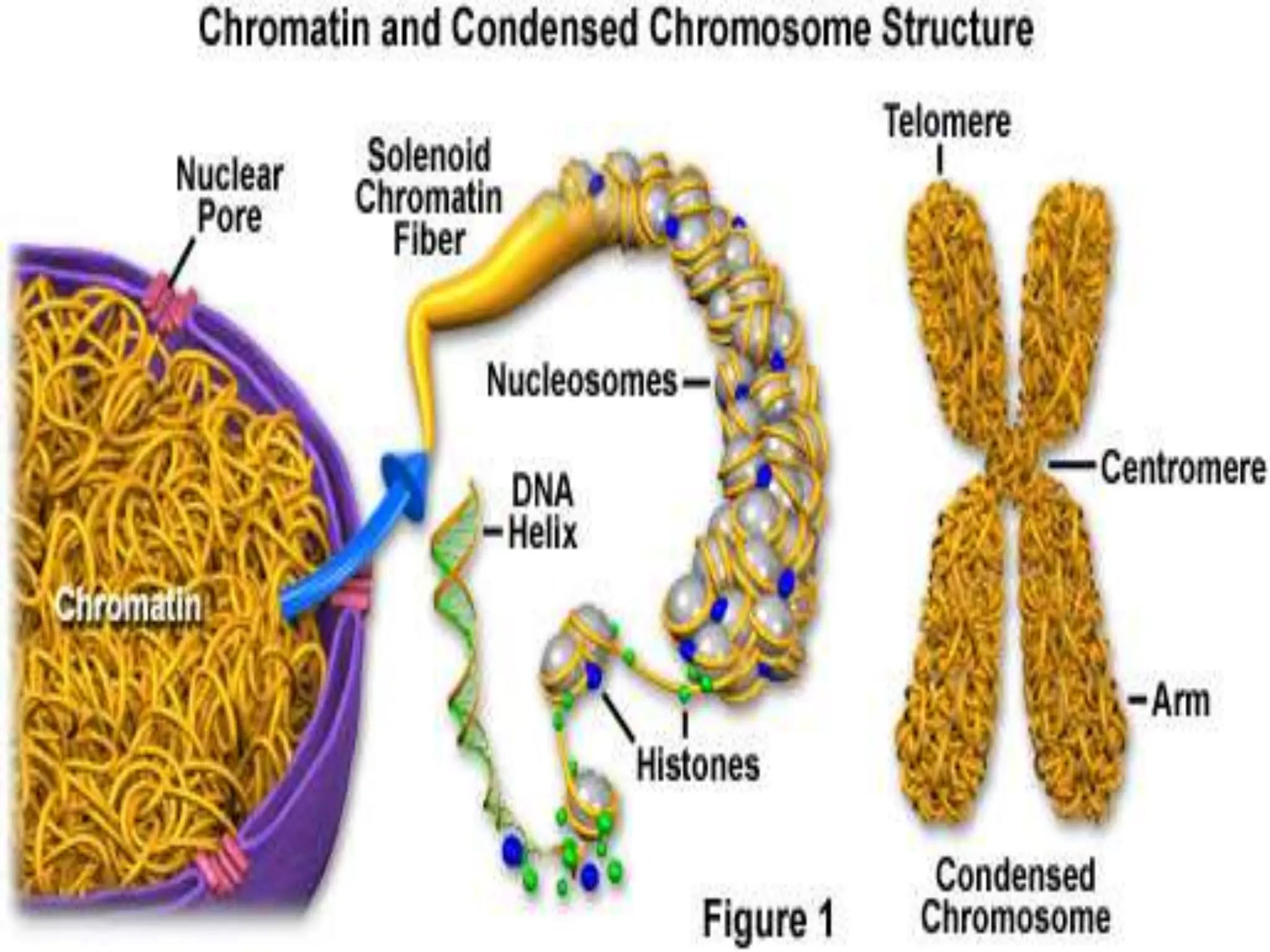
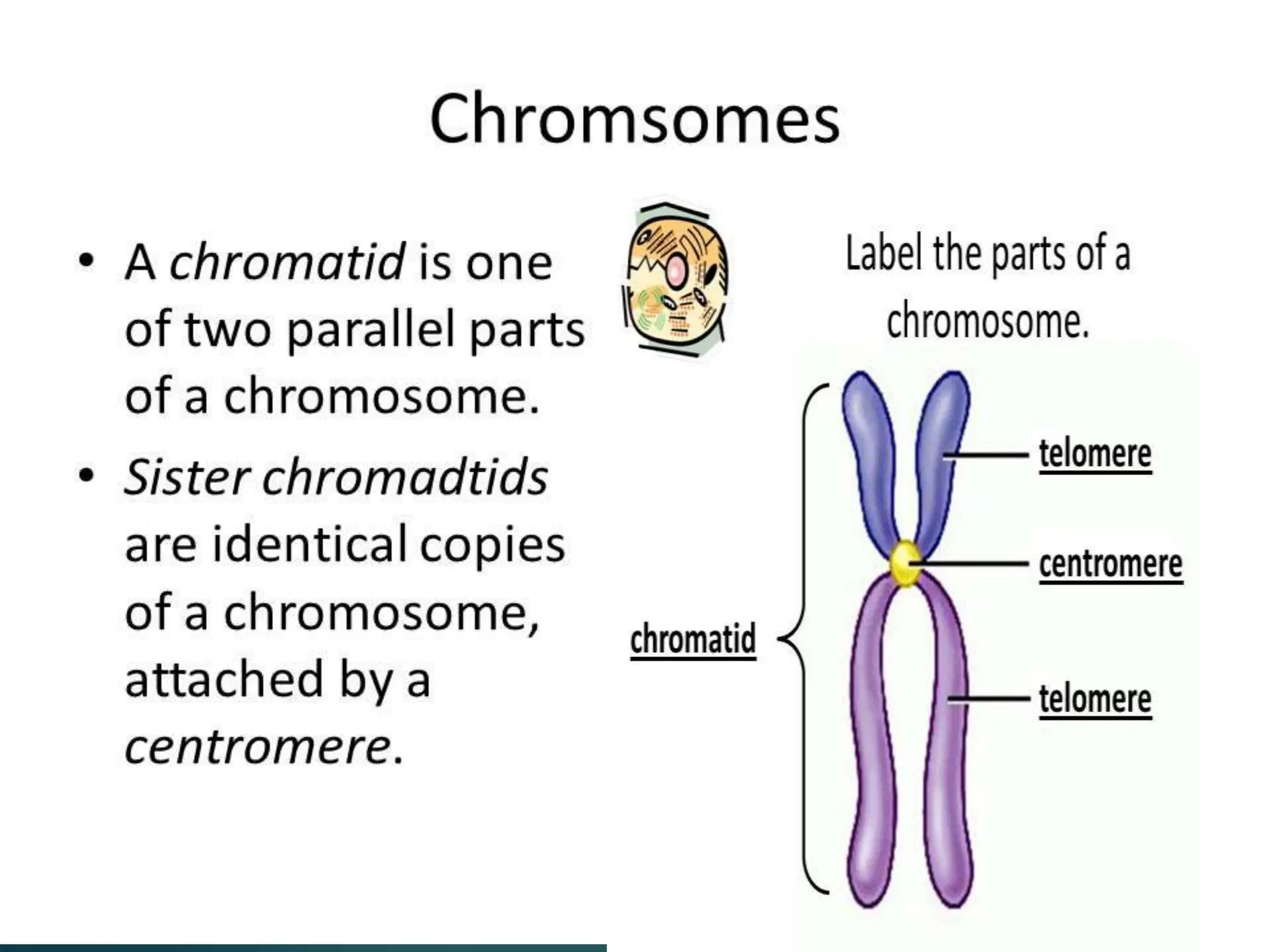
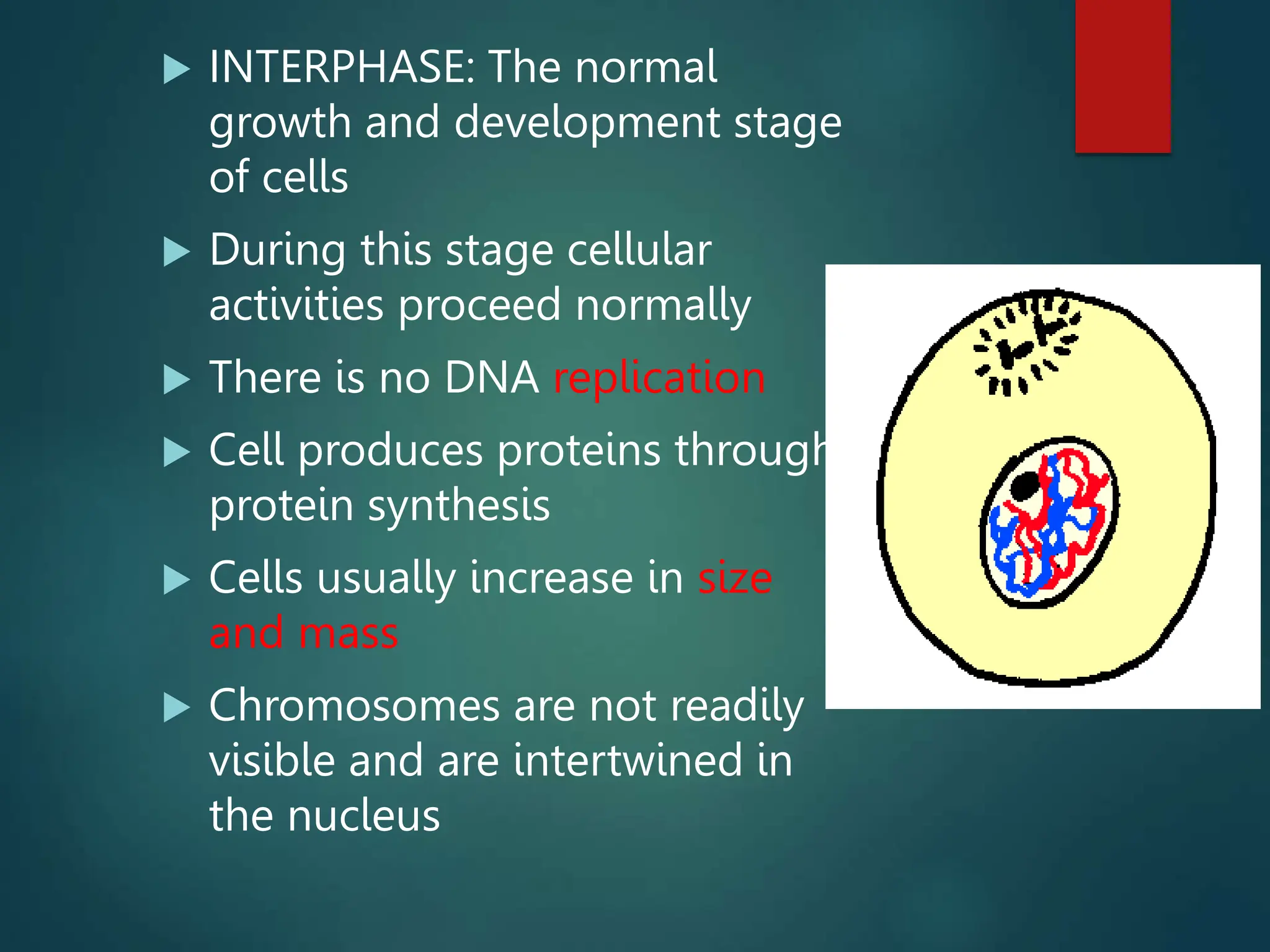
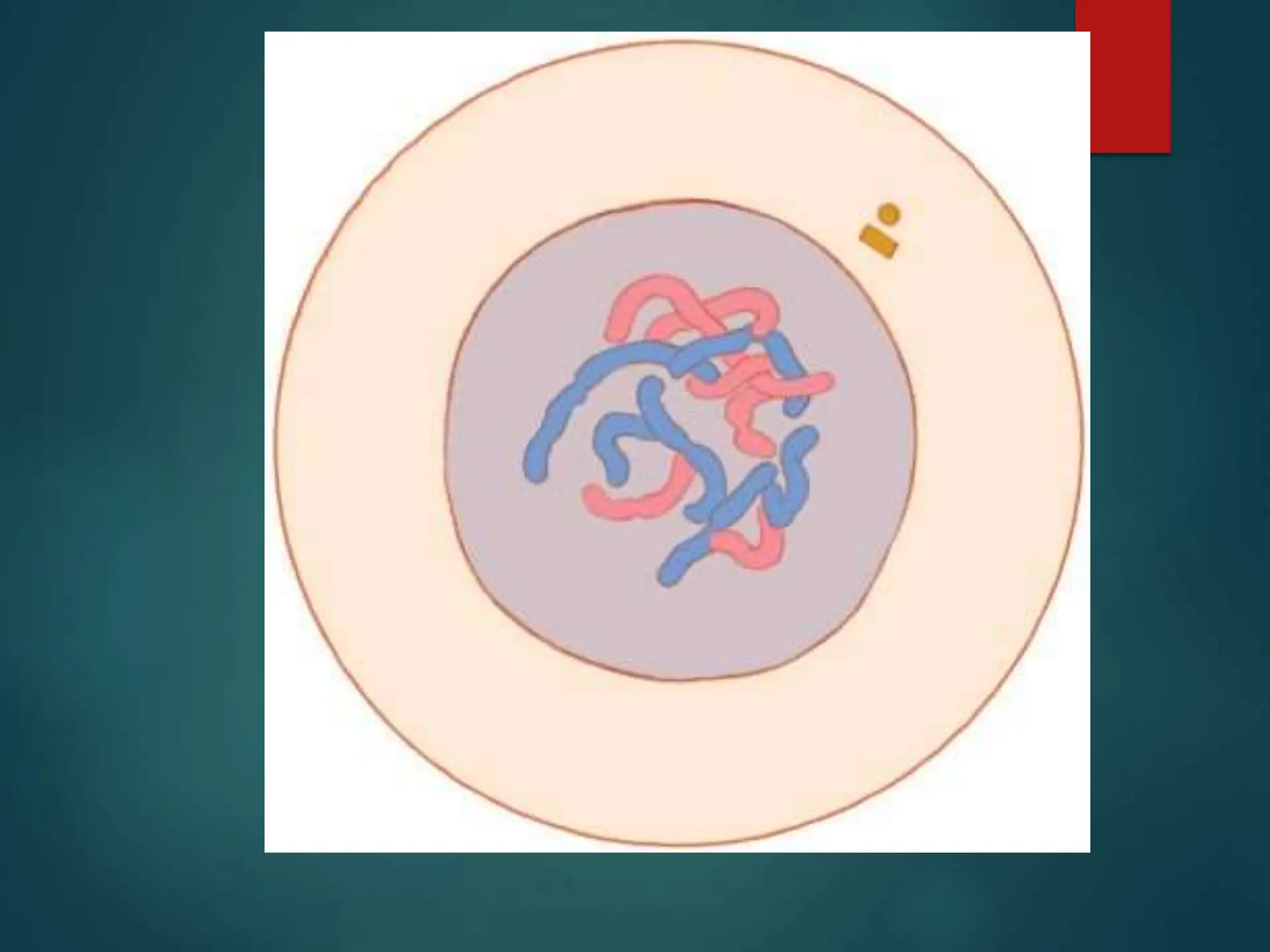
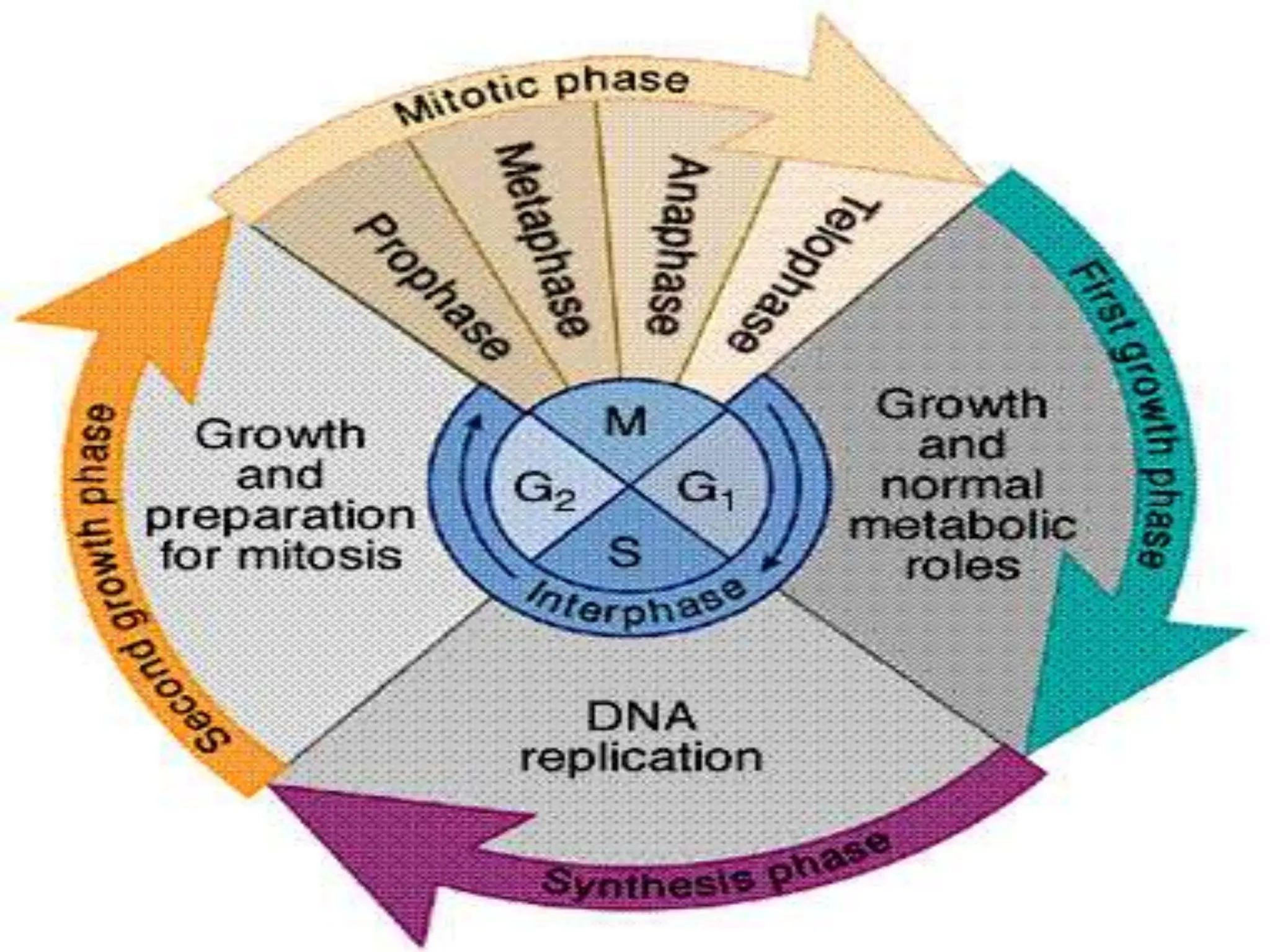
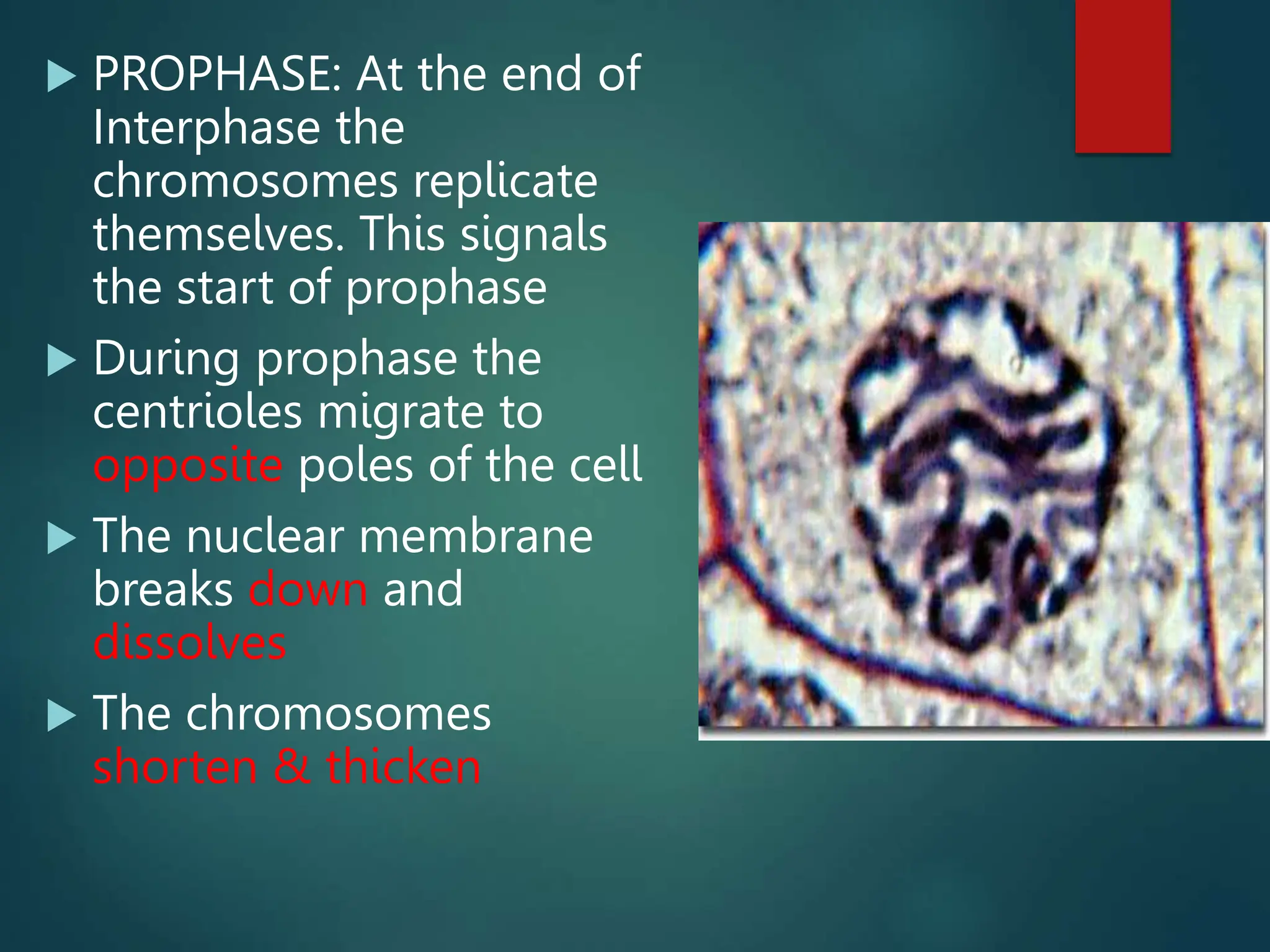
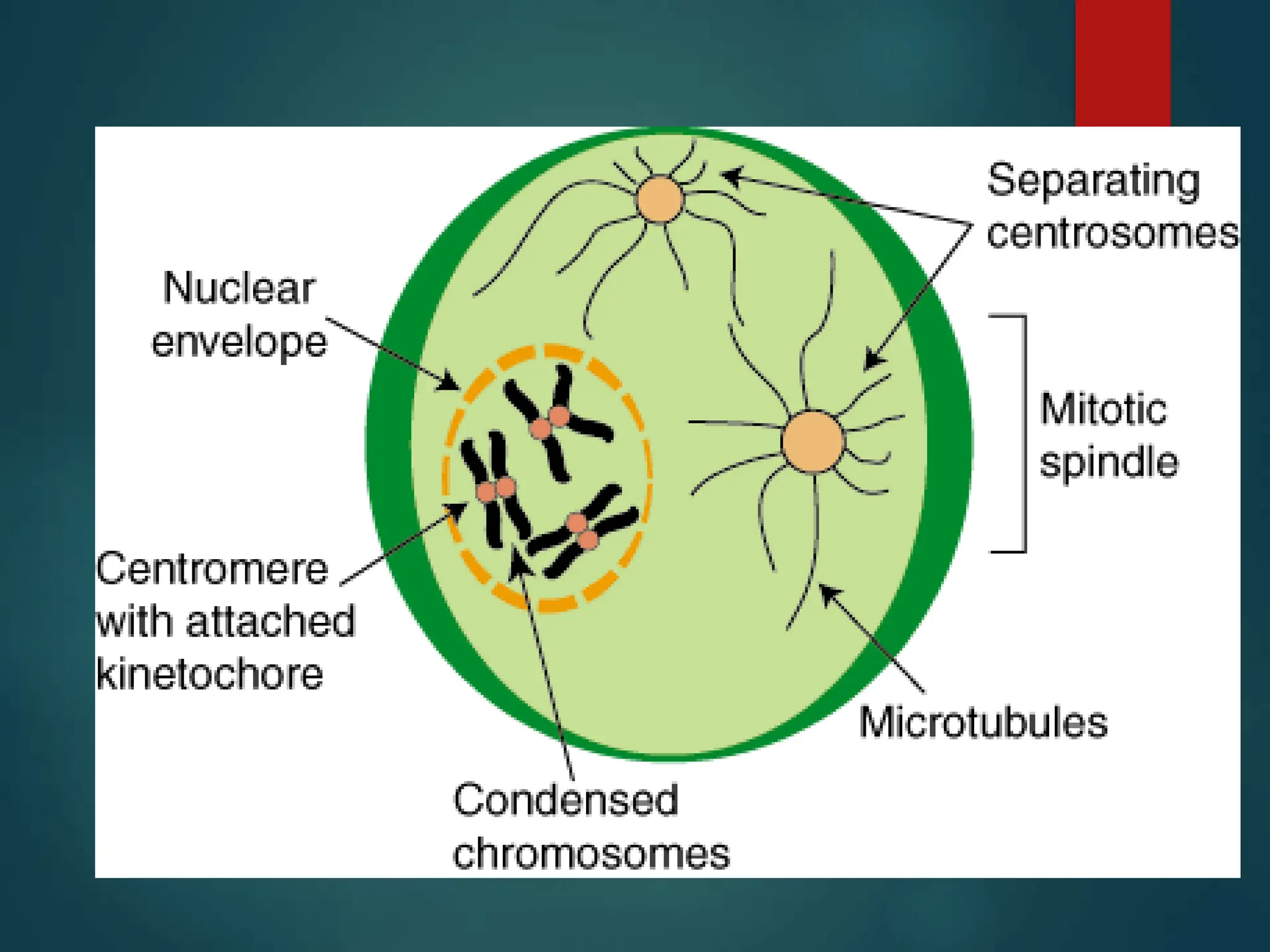
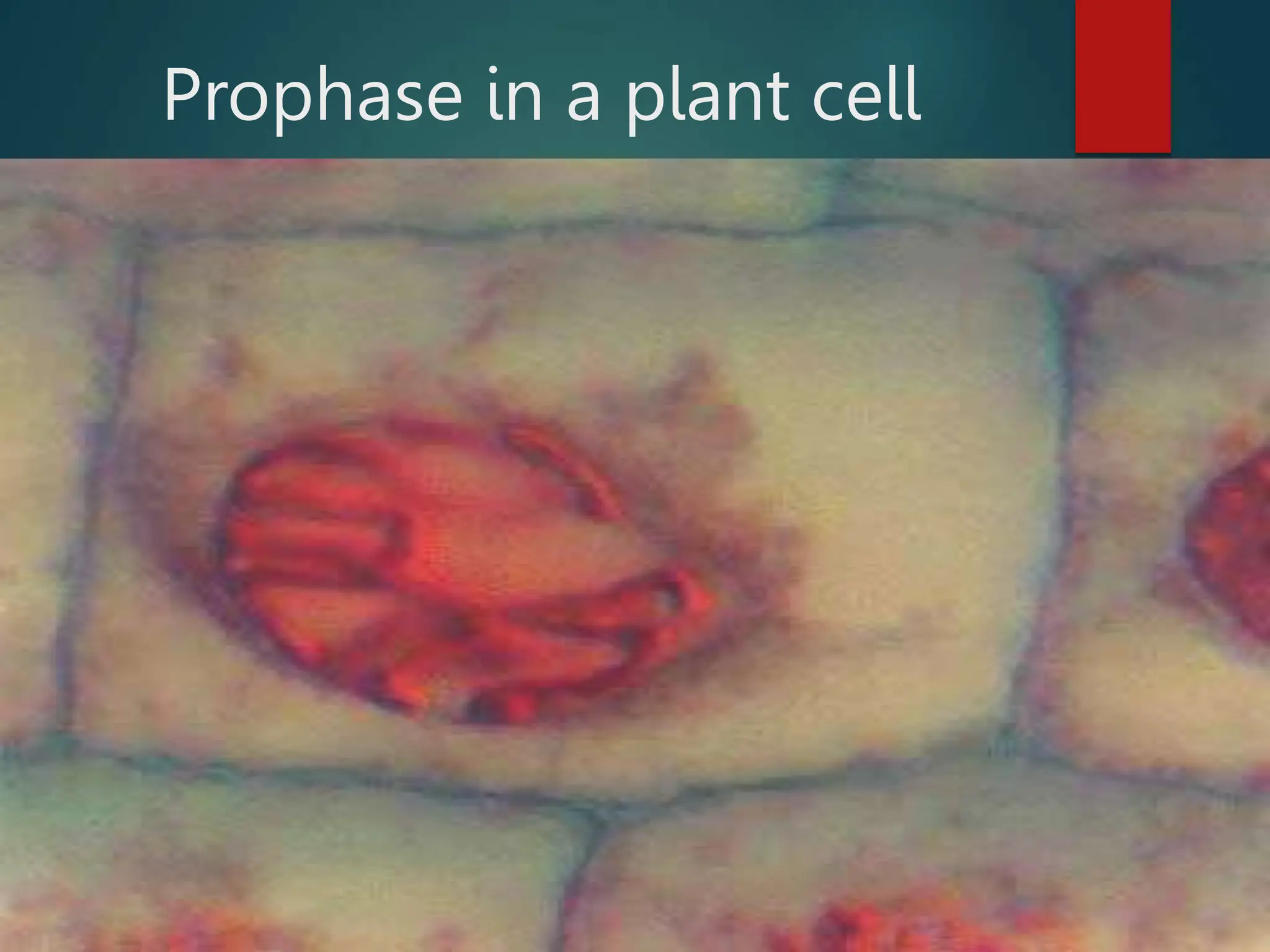
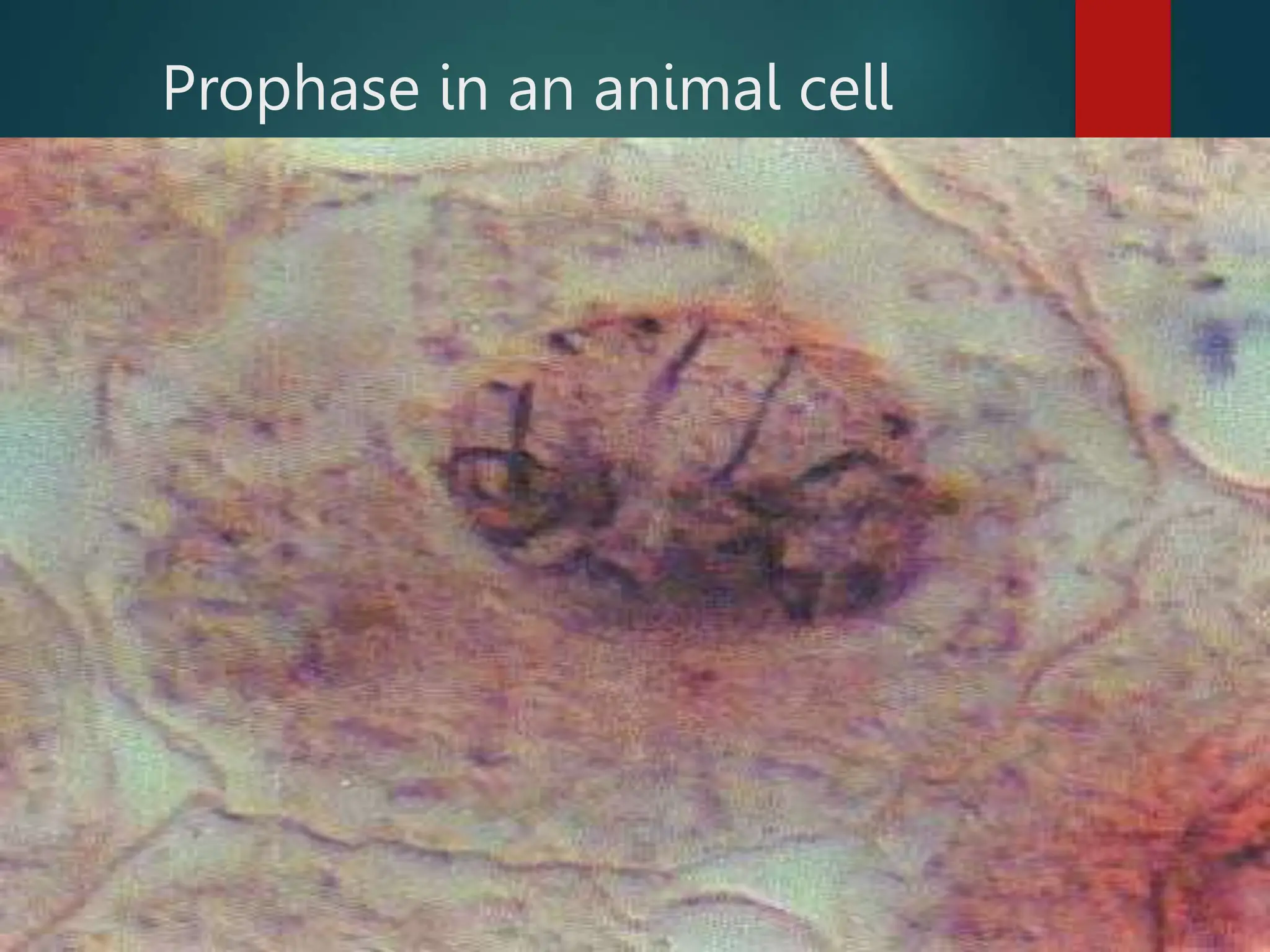
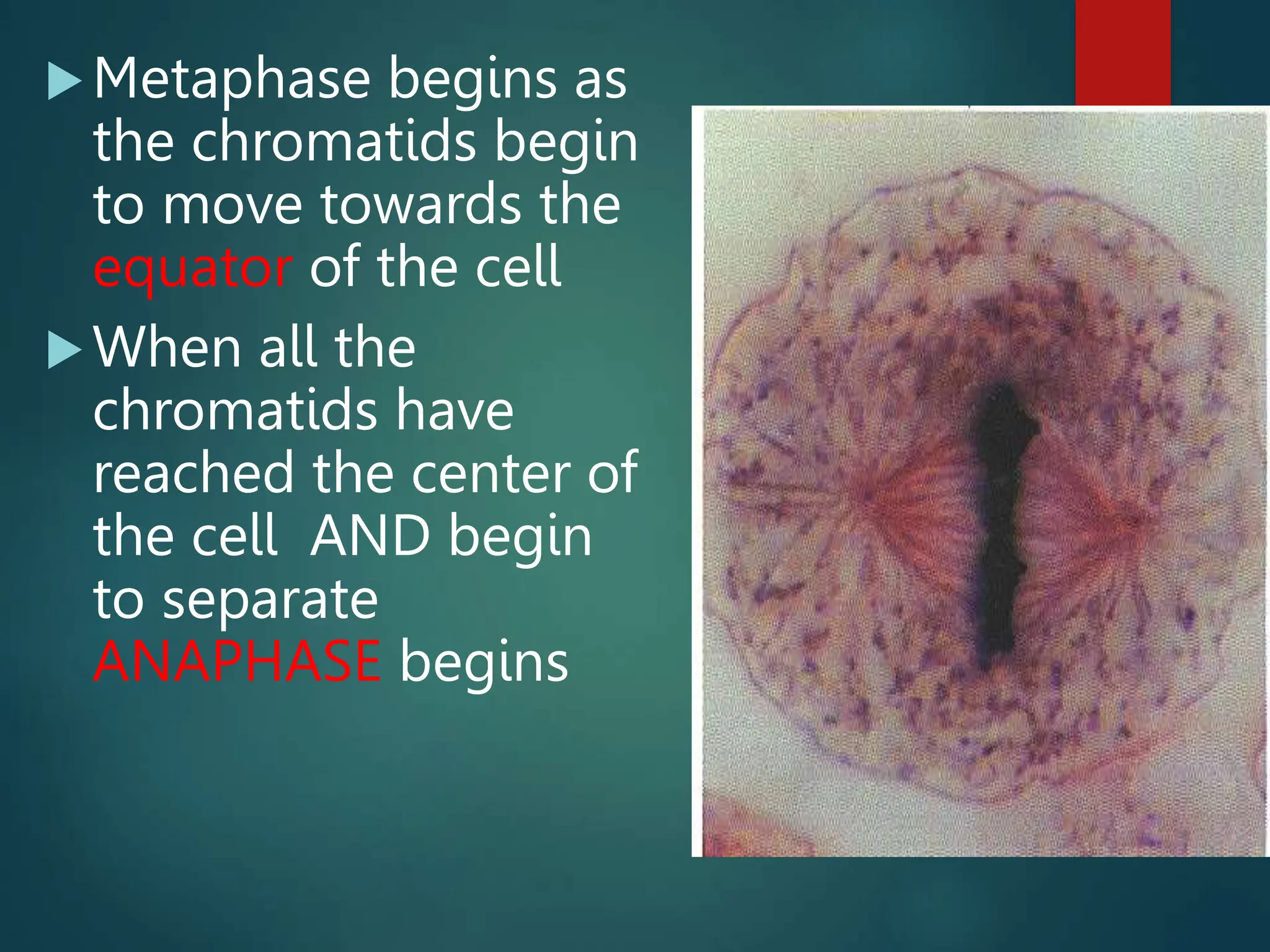
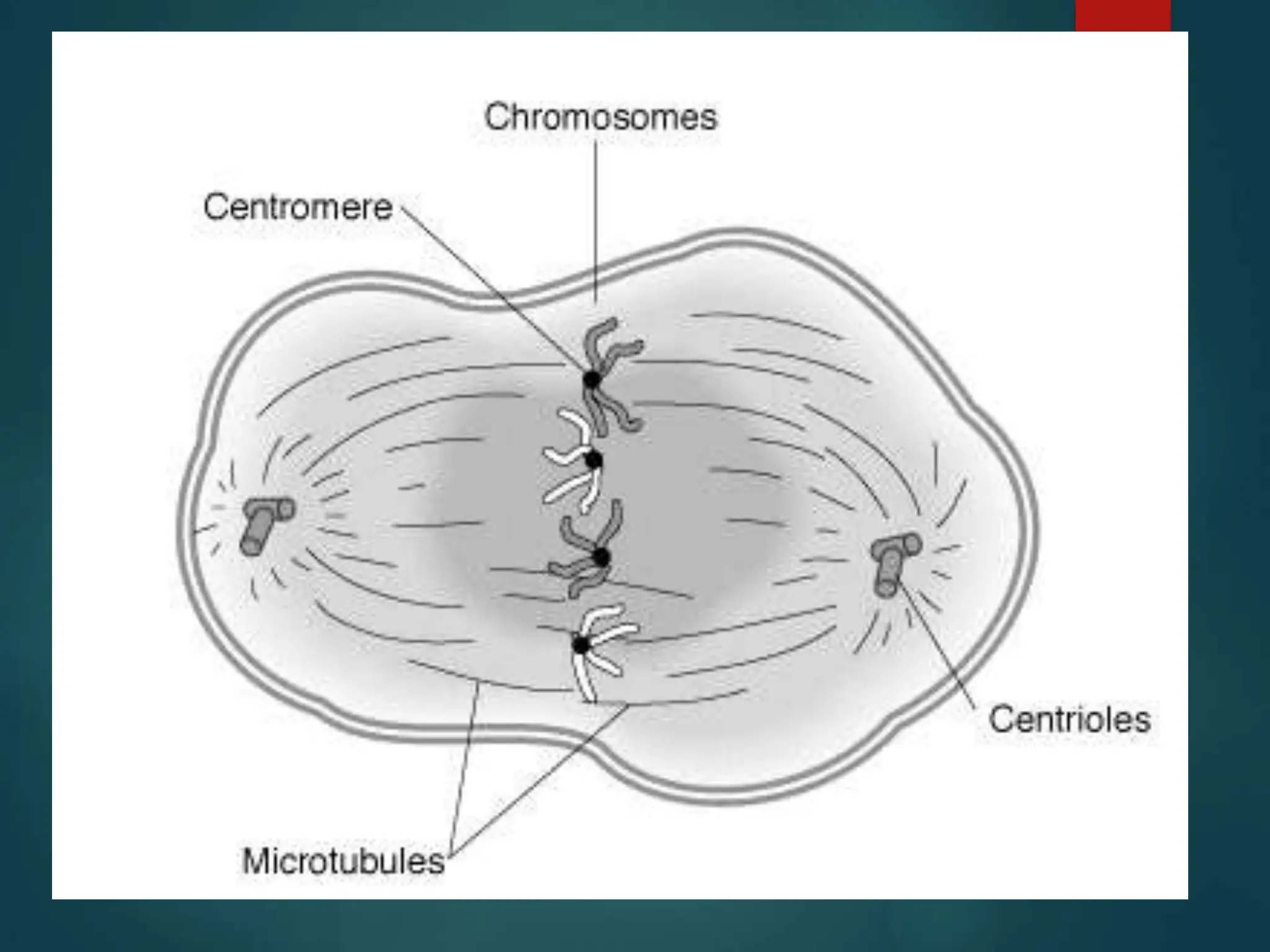
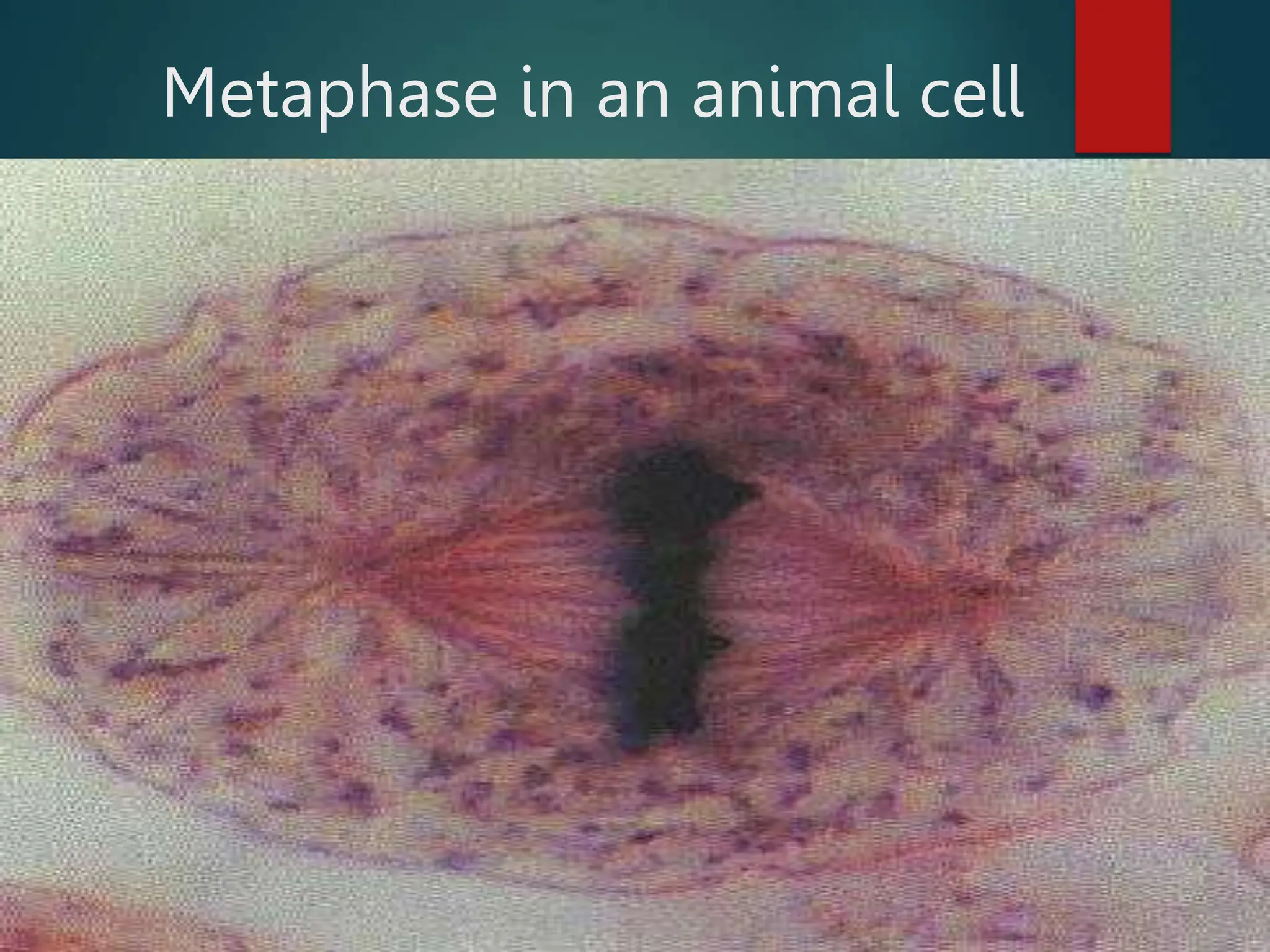
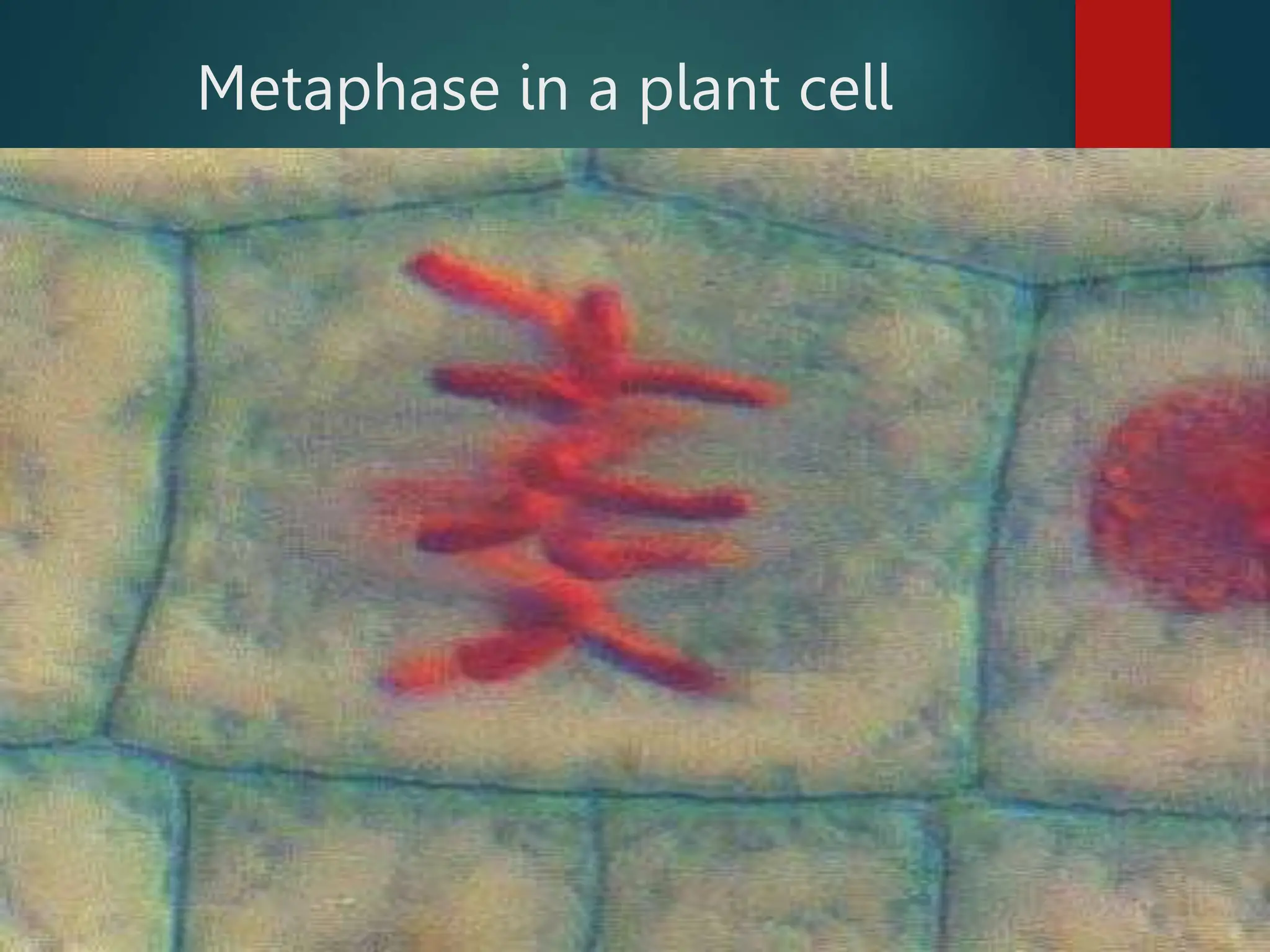
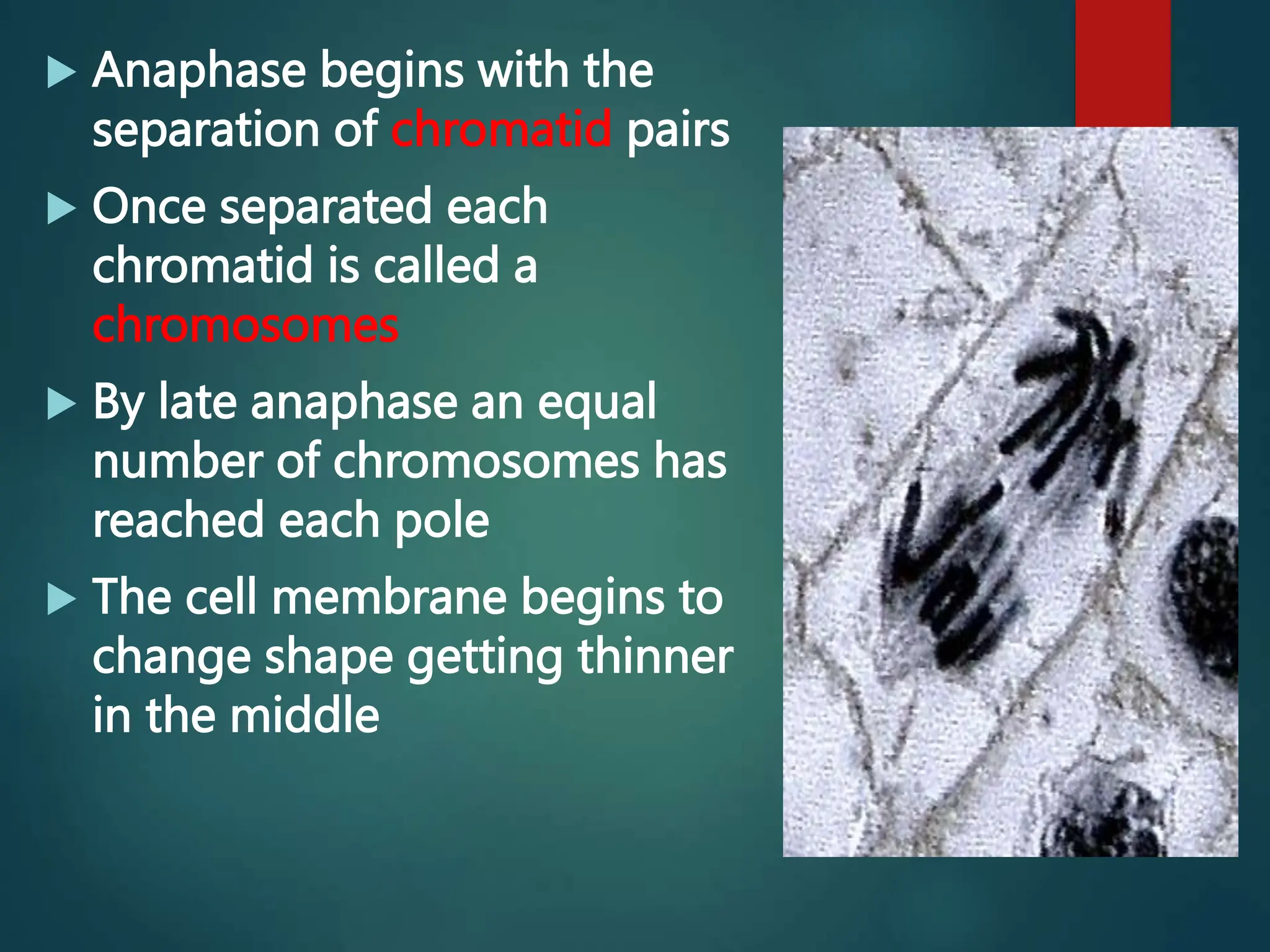
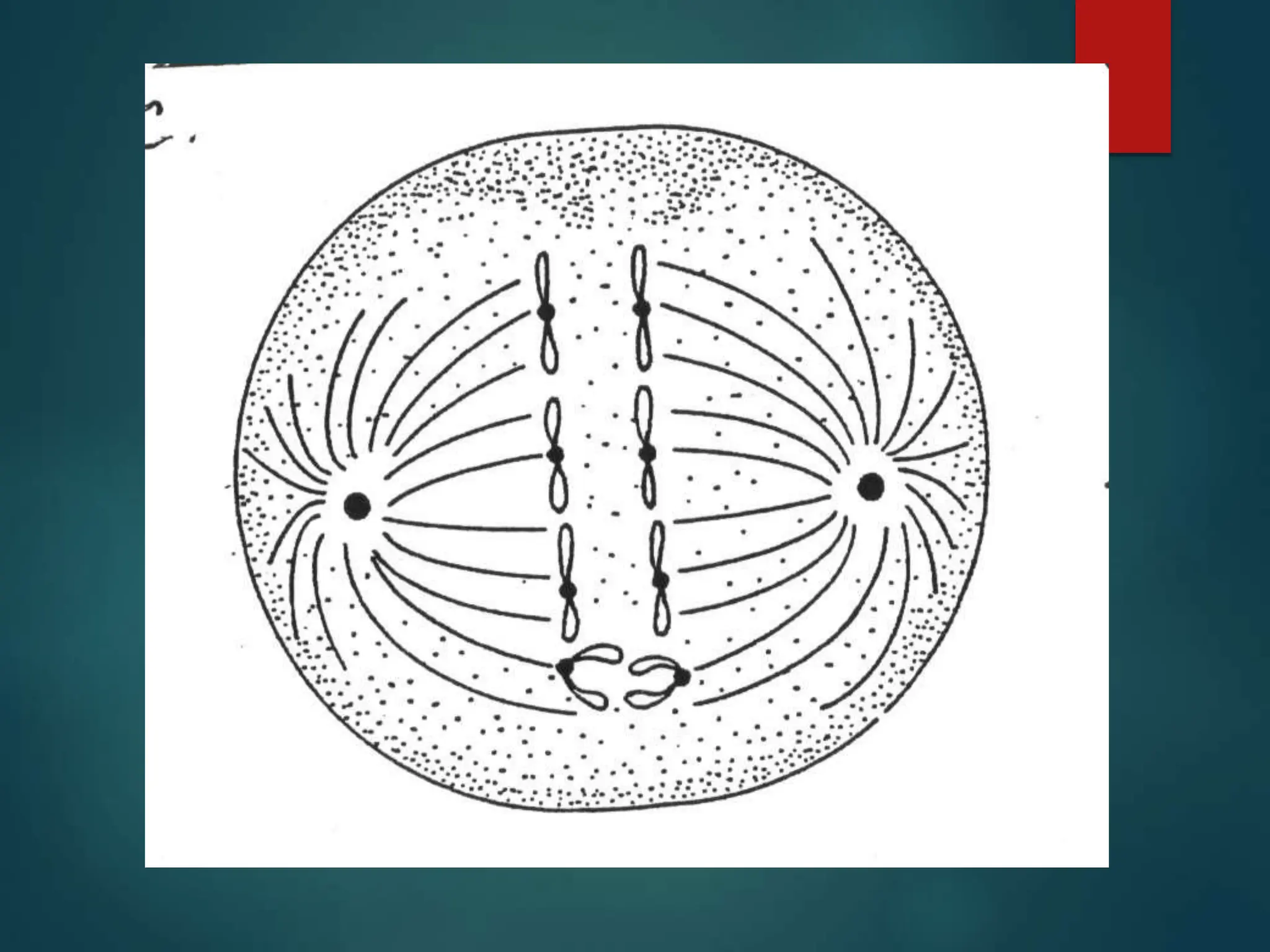
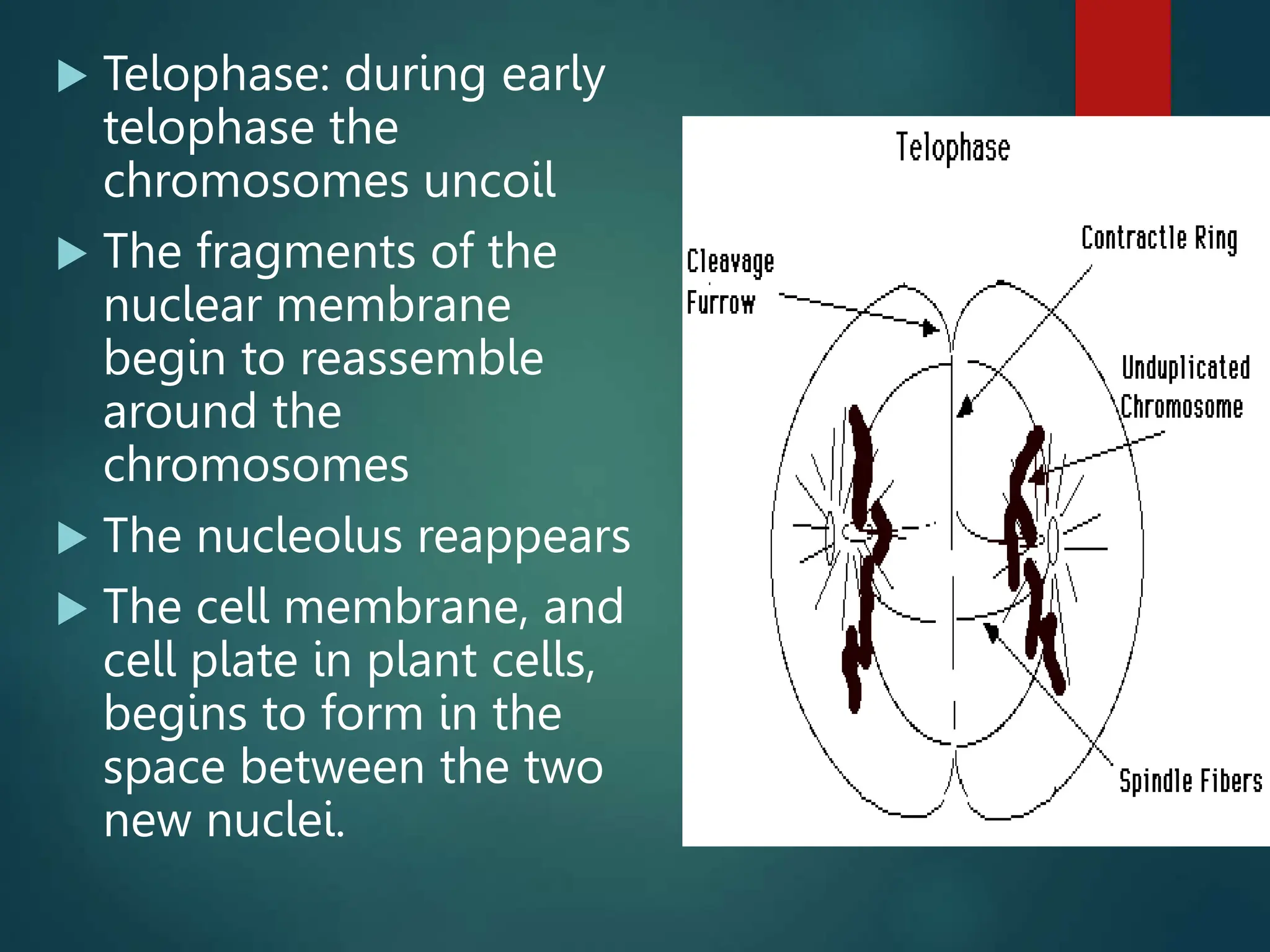
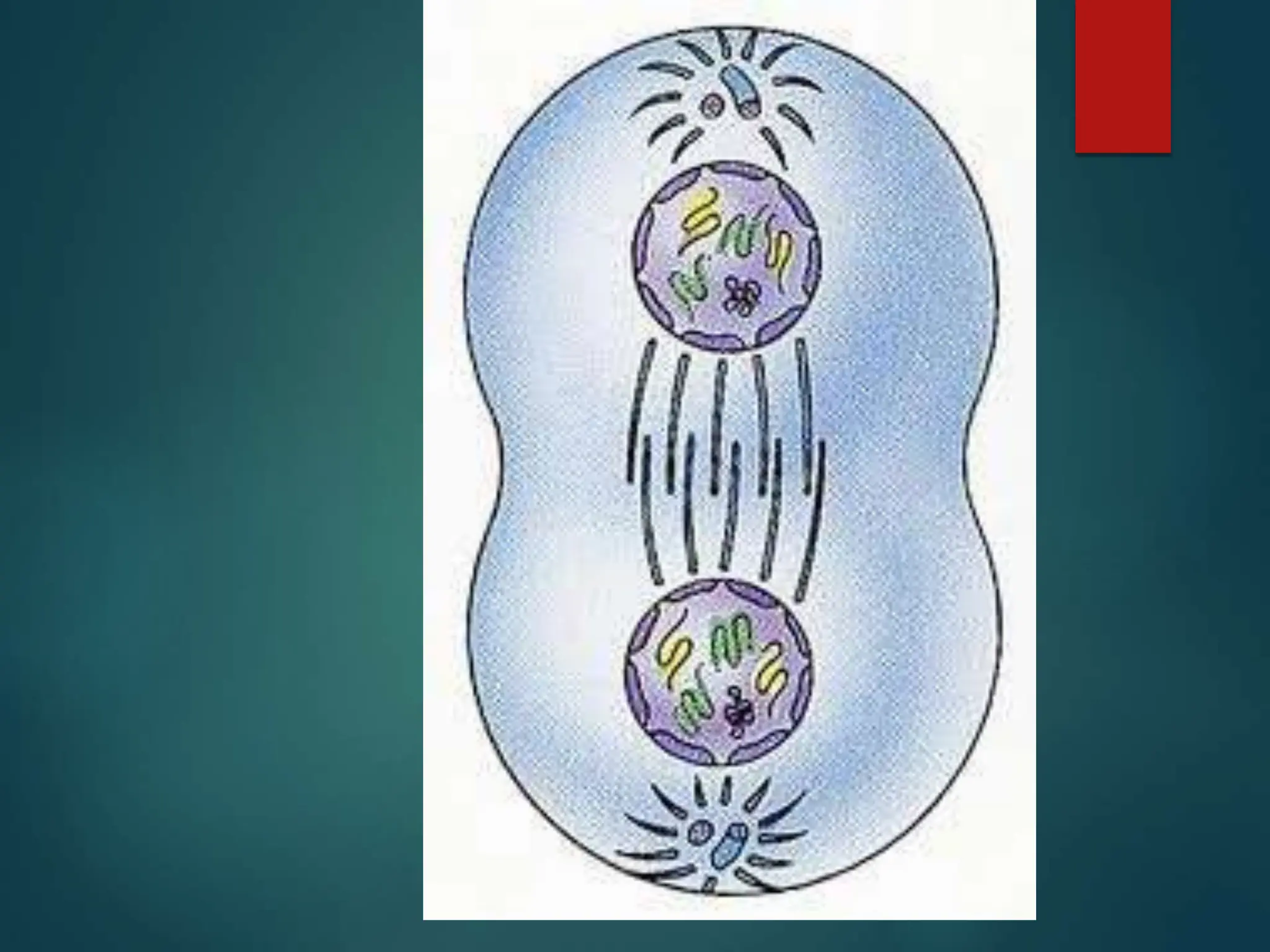
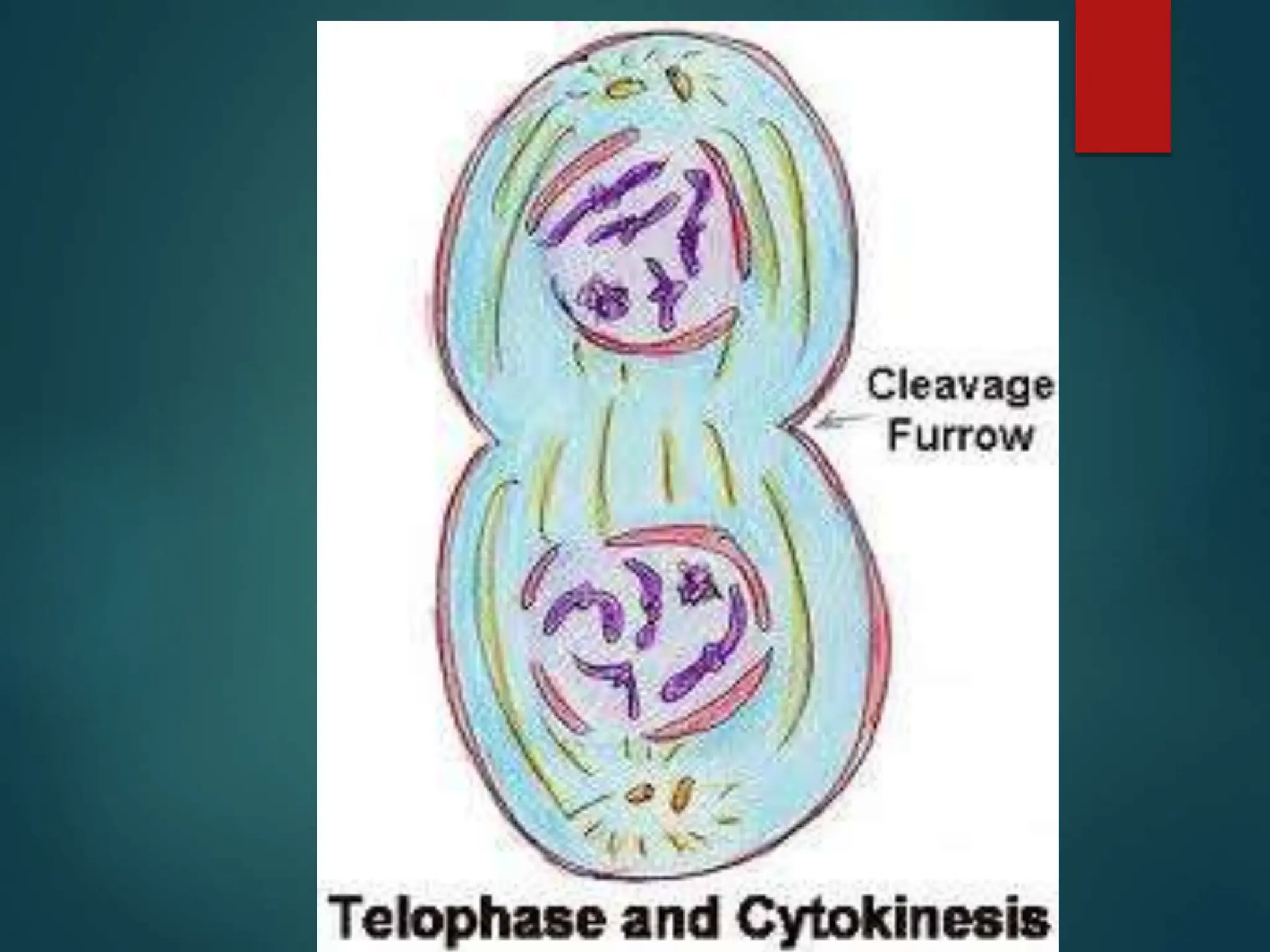
Mitosis is a process of cell division that produces two daughter cells with identical genetic material to the parent cell. It occurs somatically for growth and tissue repair. During interphase, the cell grows and DNA duplicates. Mitosis then begins with prophase, where chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down. In metaphase, chromosomes align at the center. In anaphase, chromatids separate and move to opposite poles. Telophase ends with two identical daughter nuclei forming. Cytokinesis then divides the cytoplasm, completing cell division.