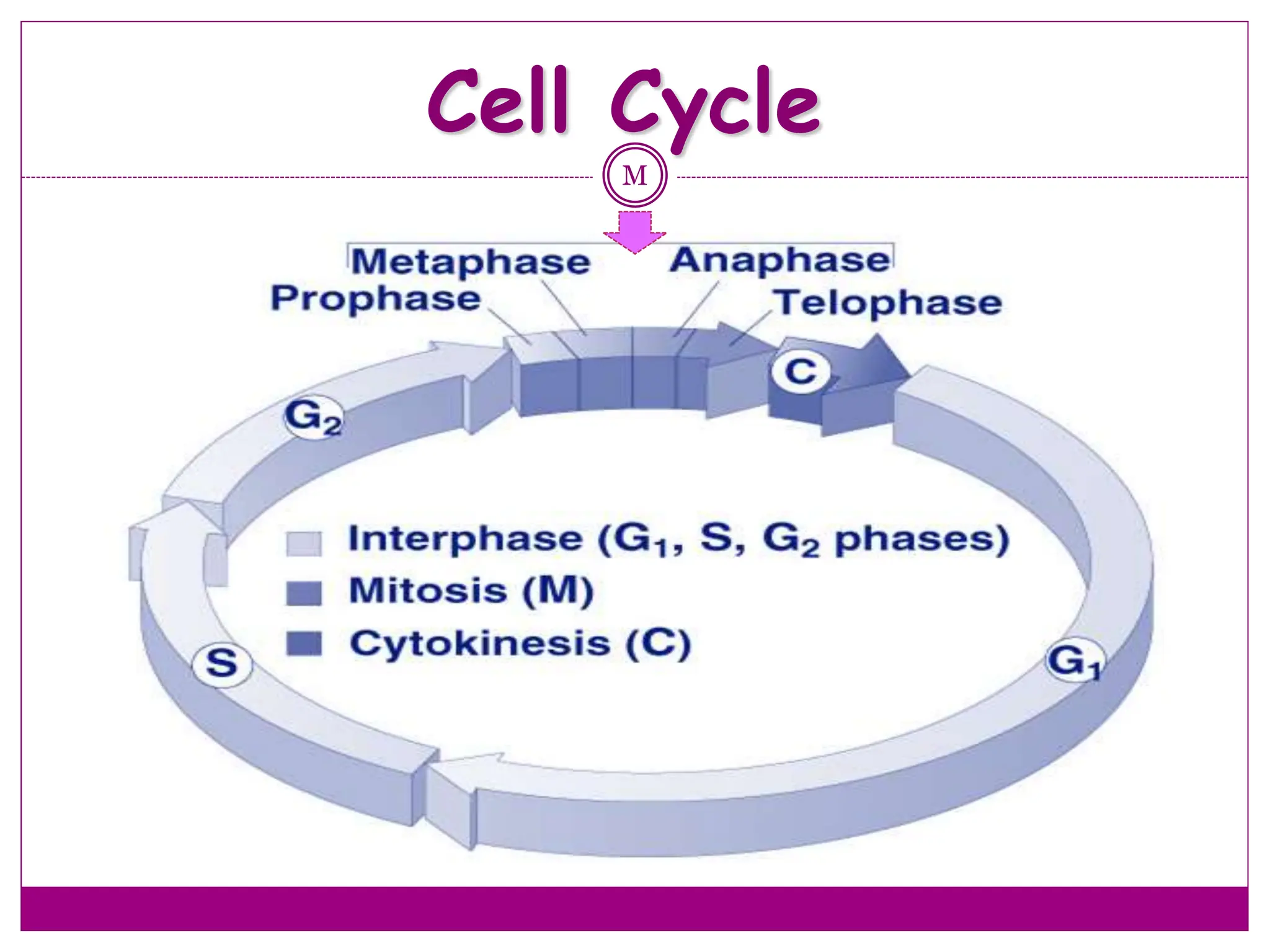
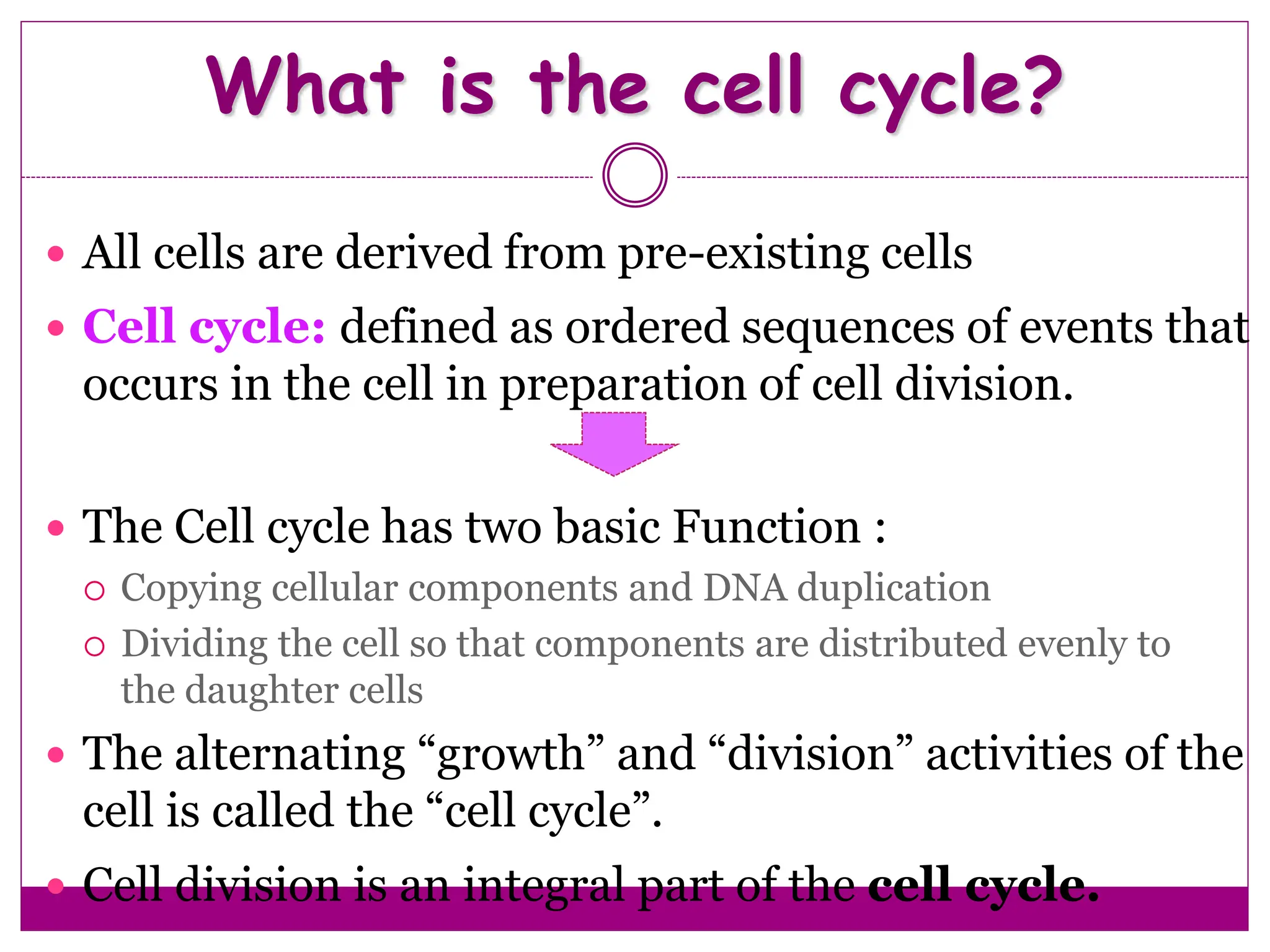
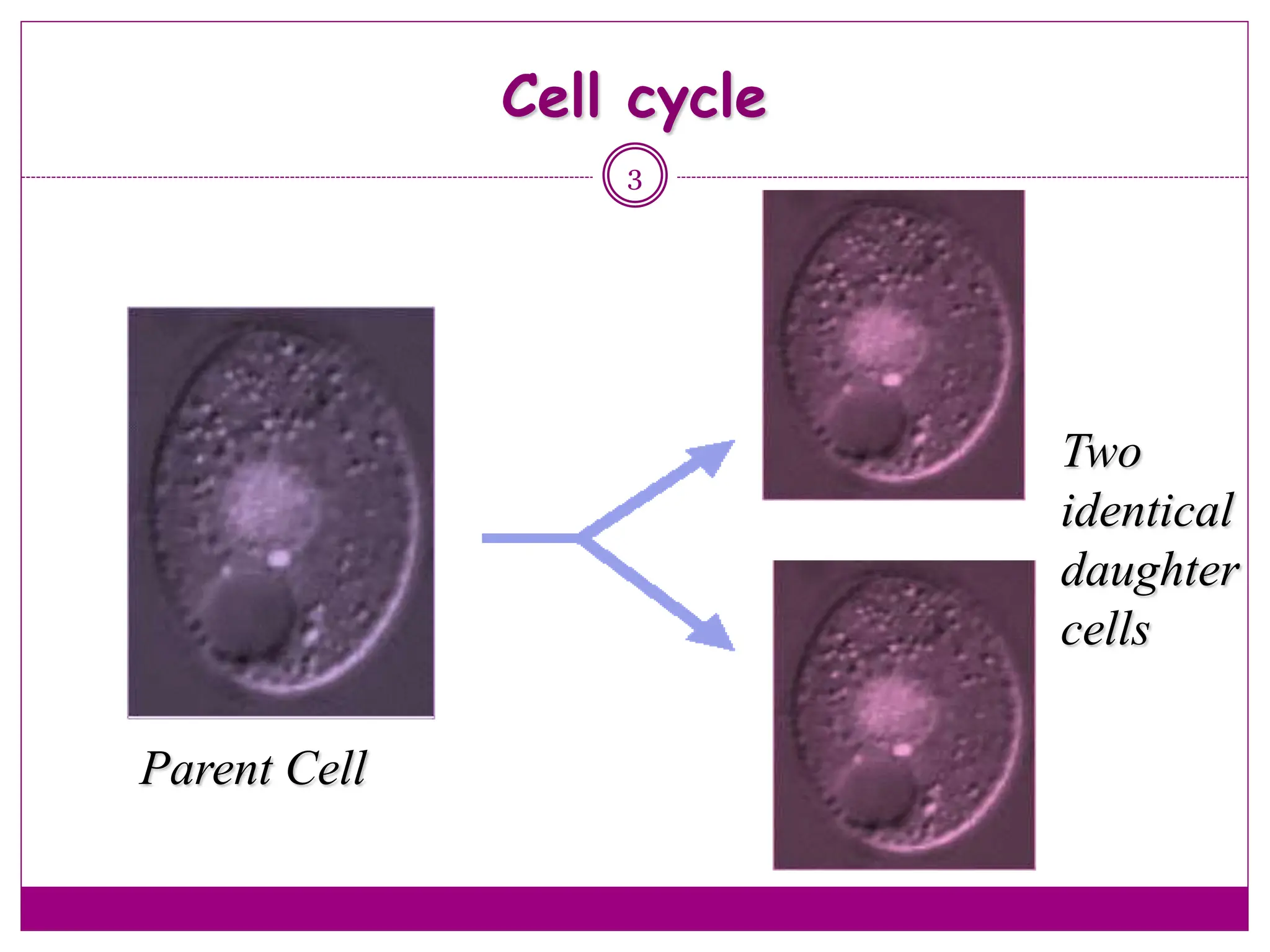
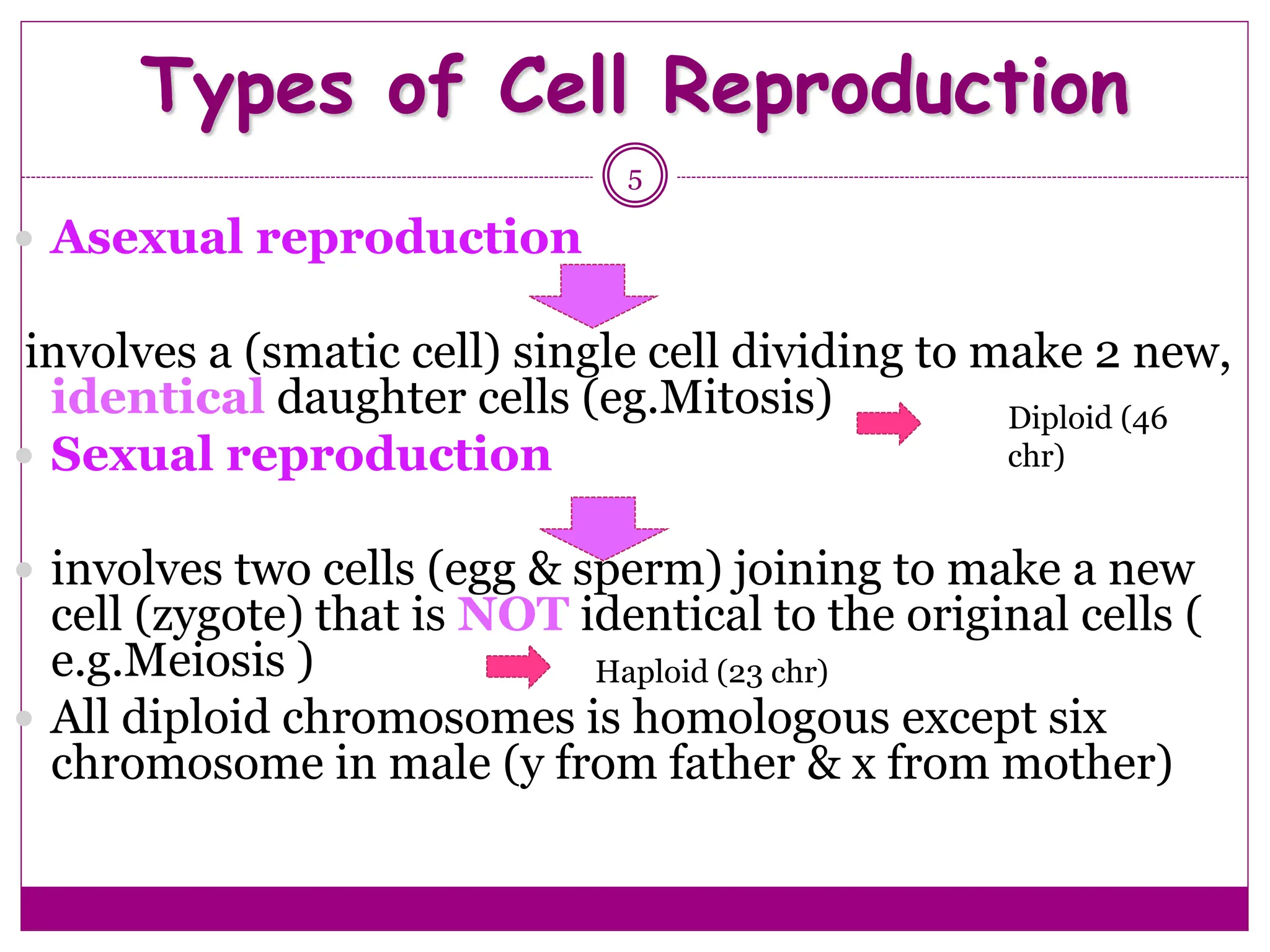
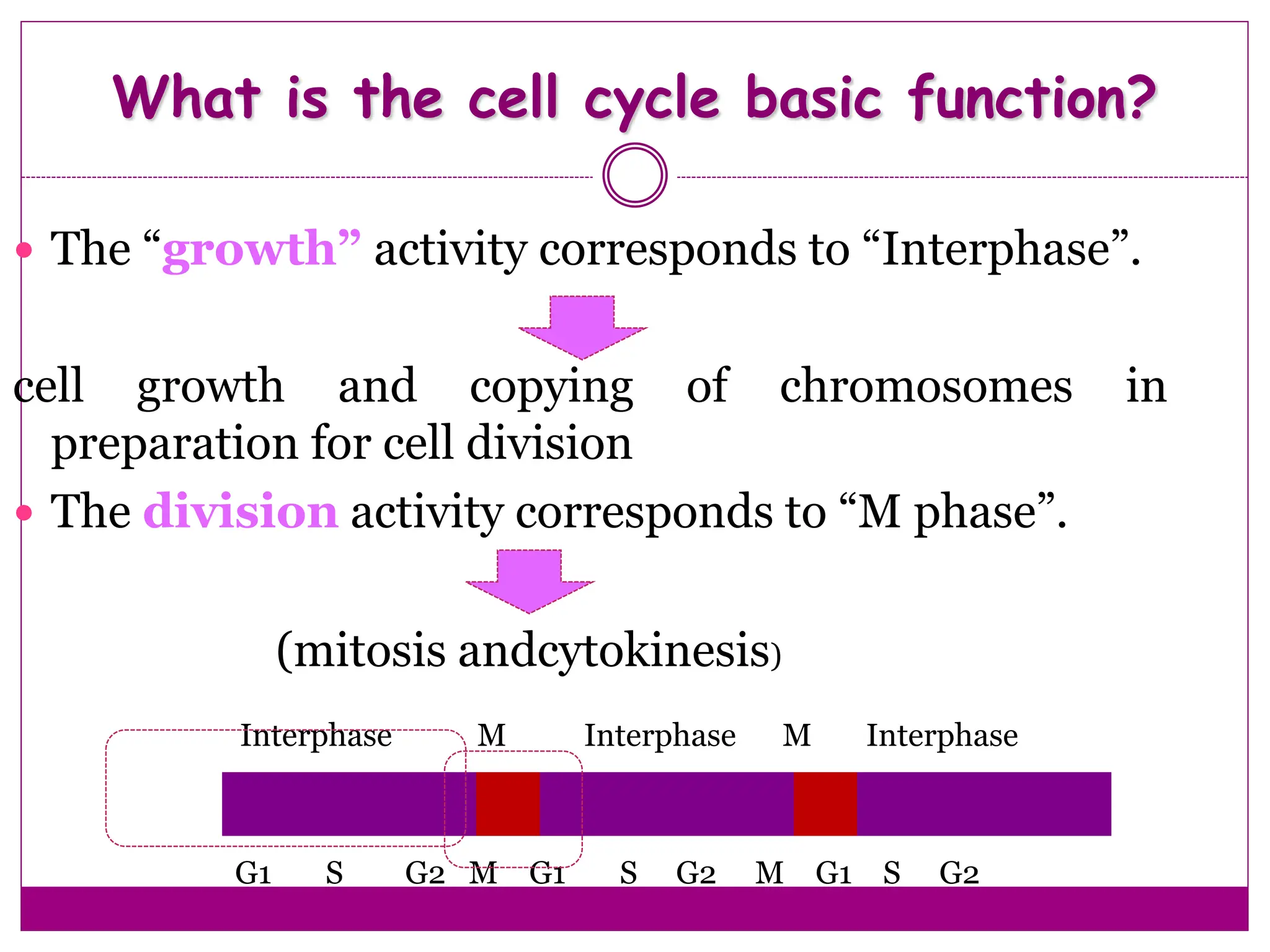
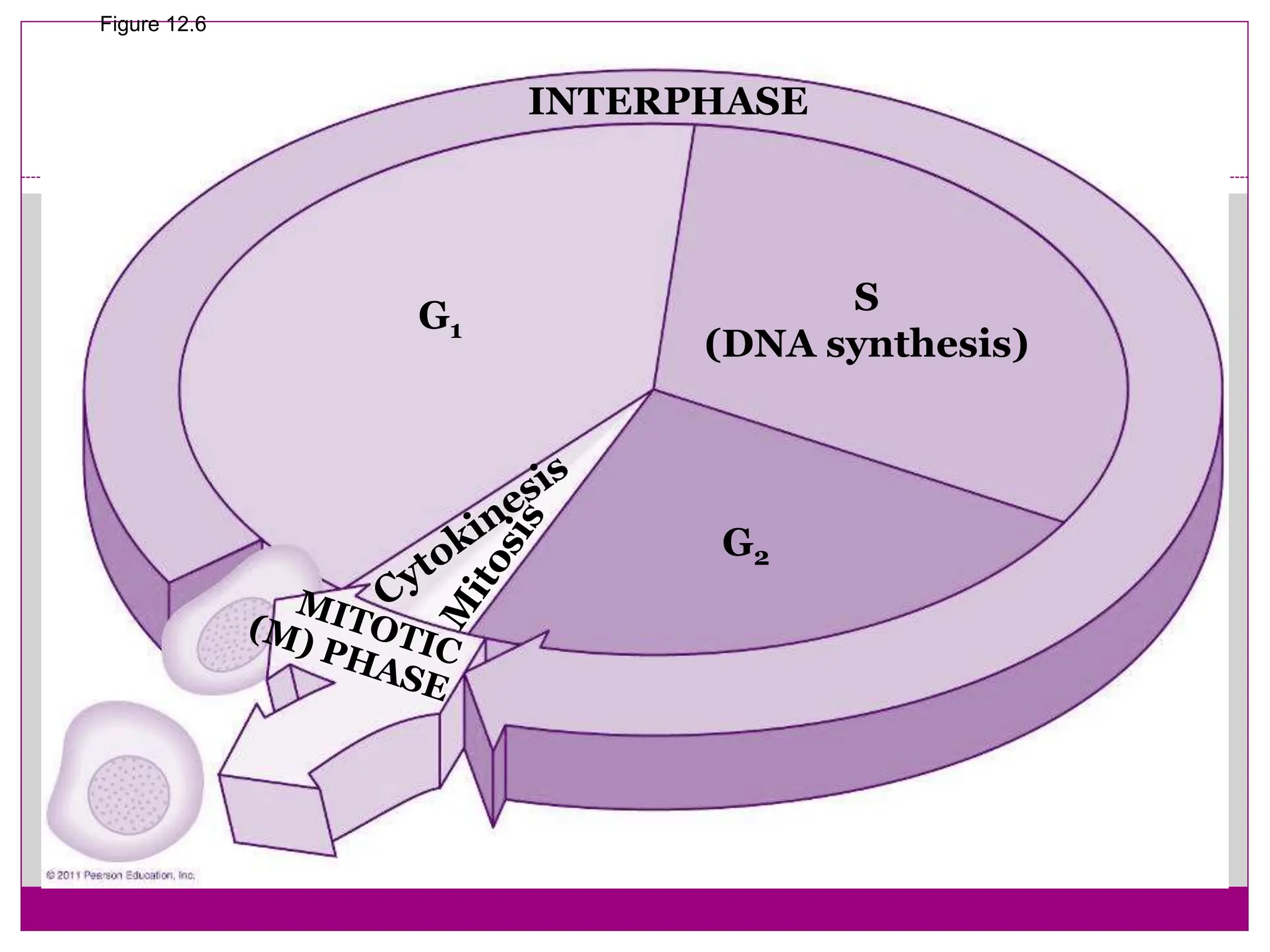
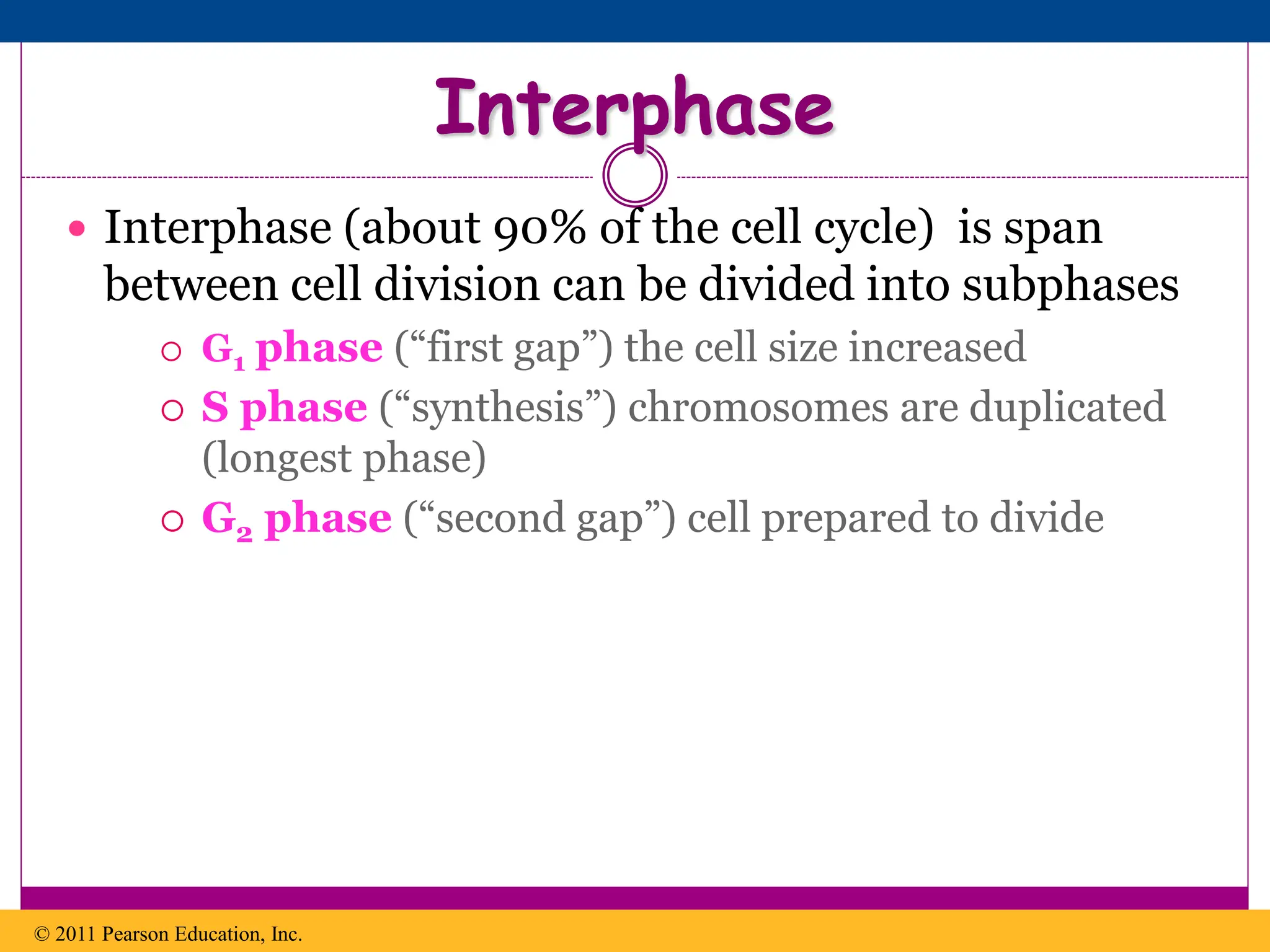
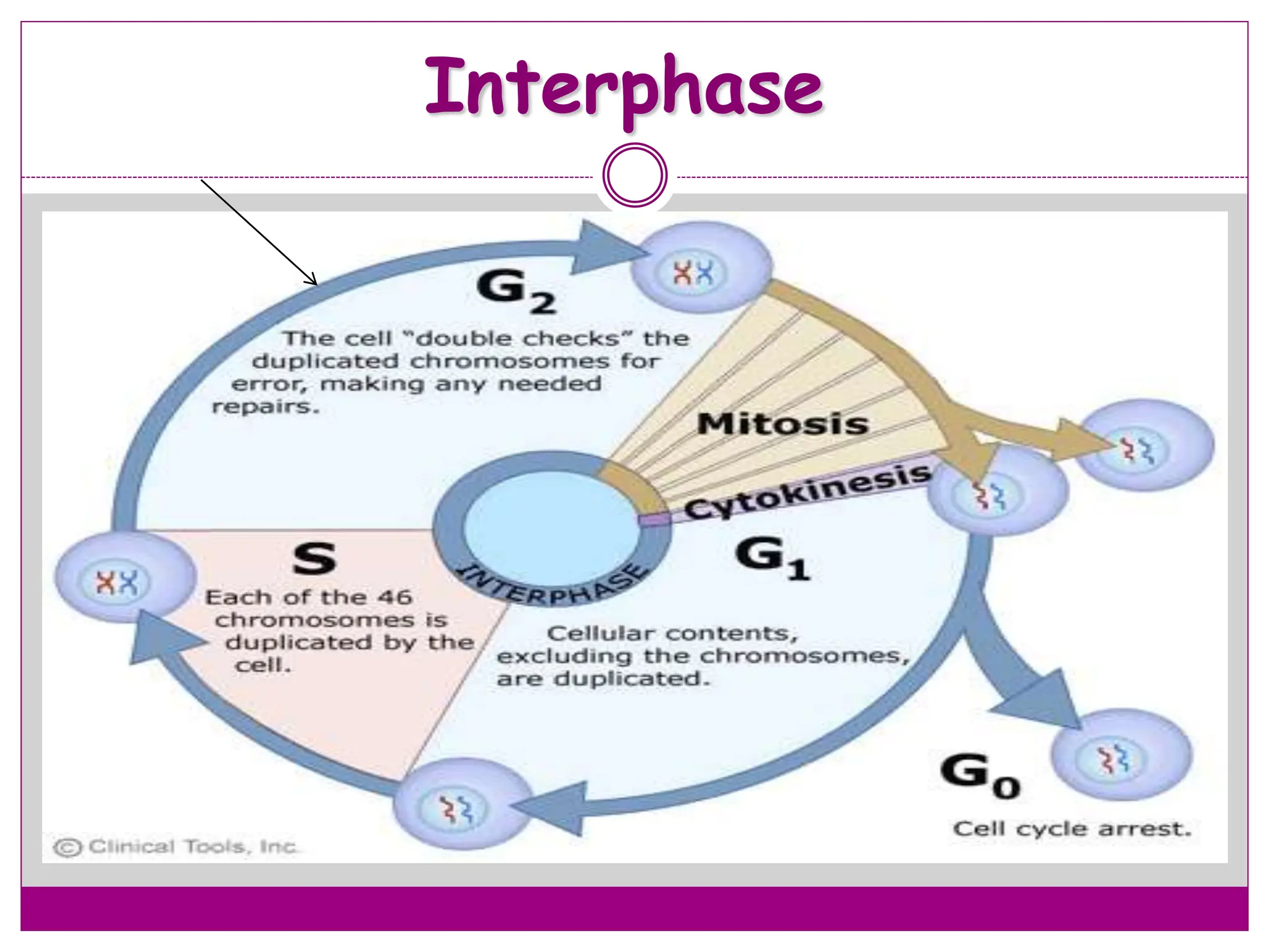
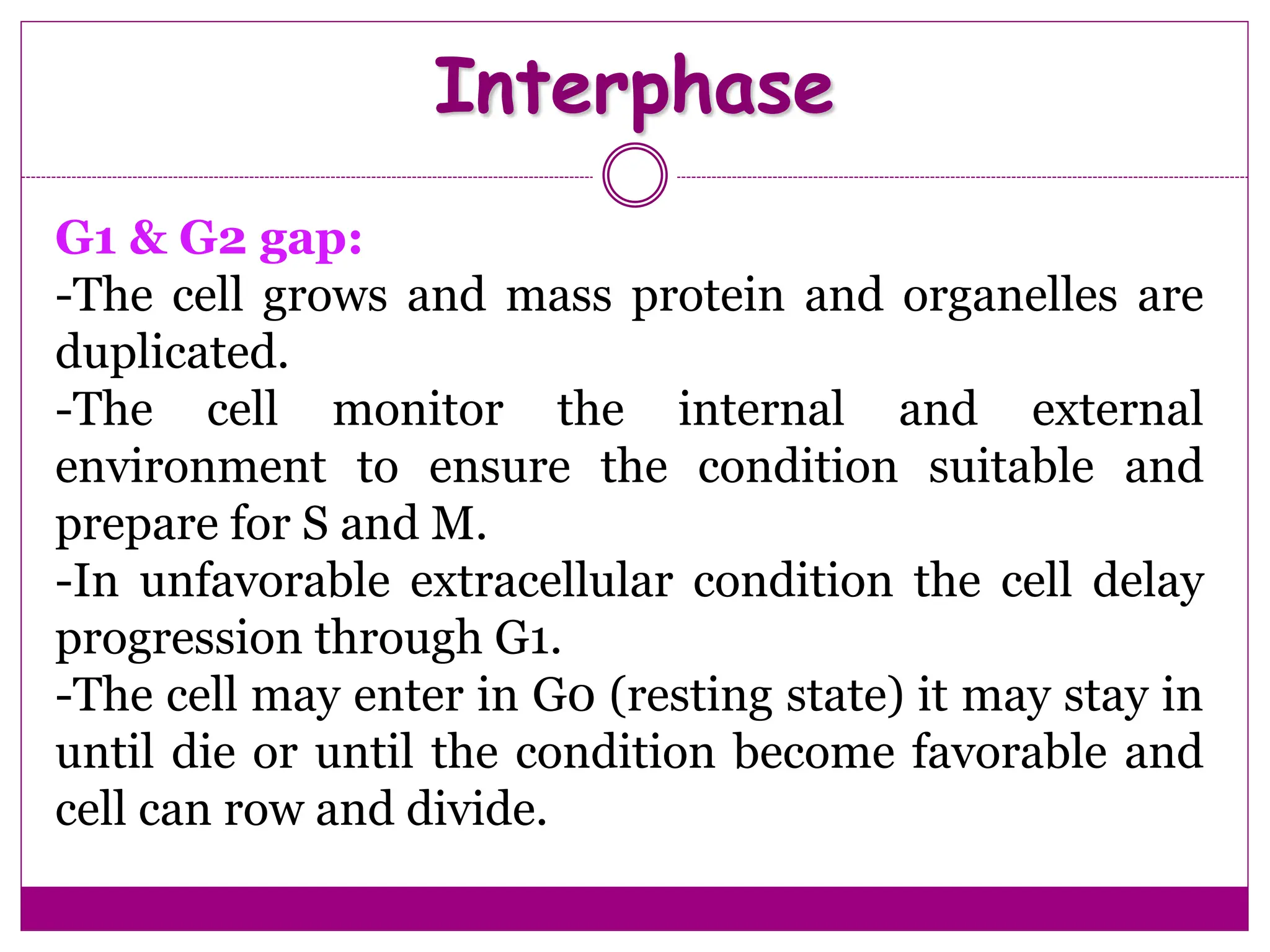
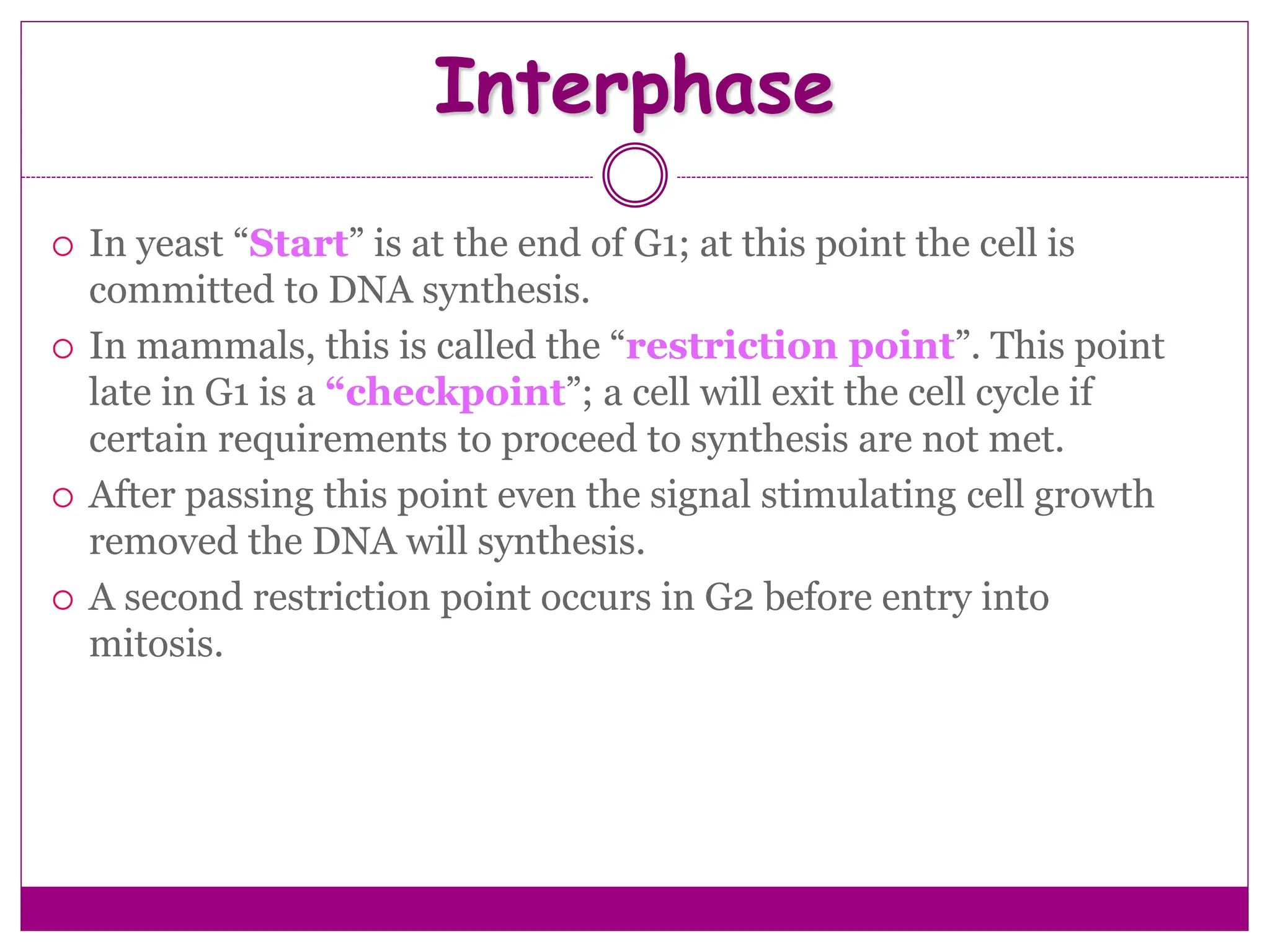
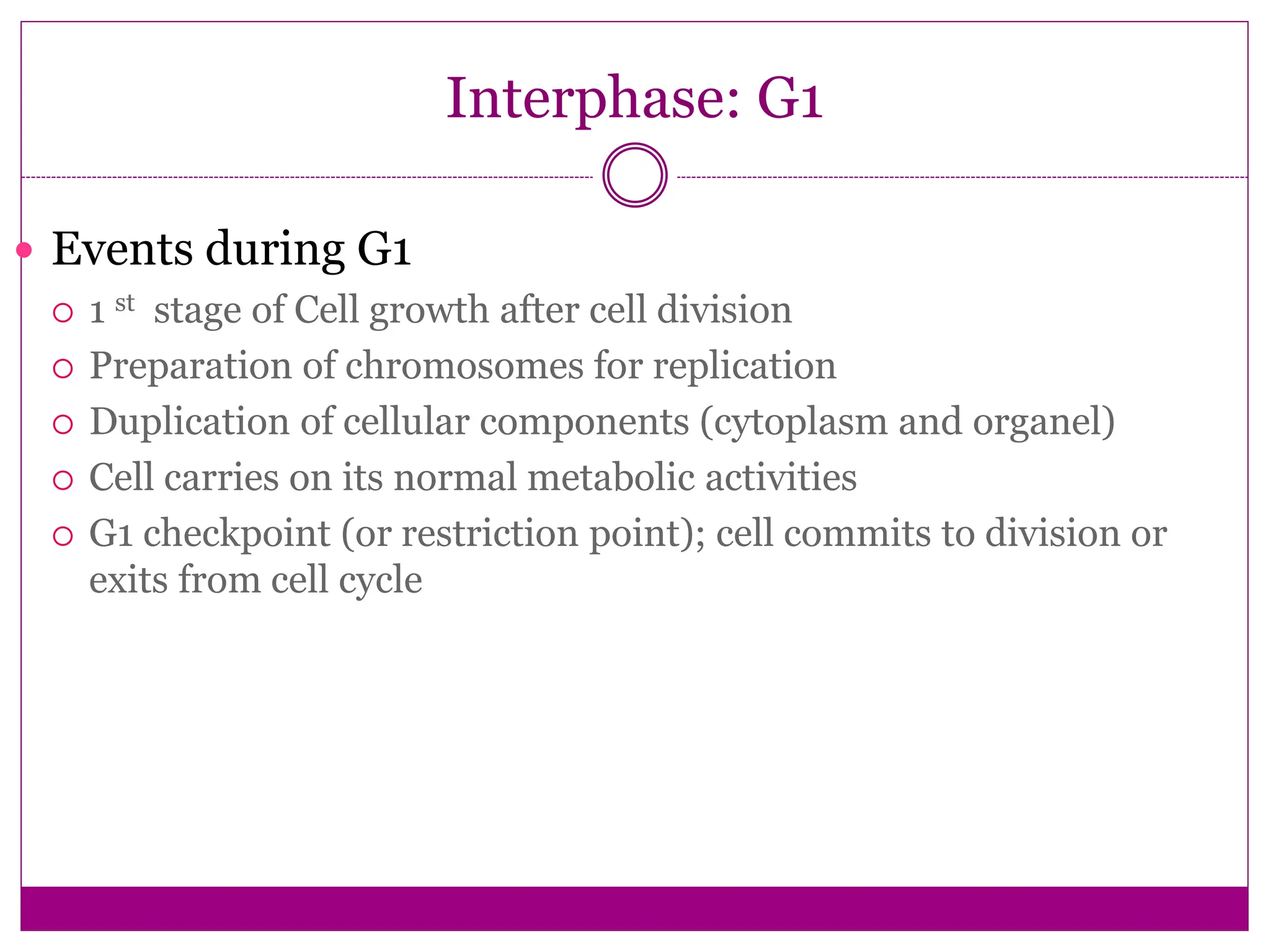
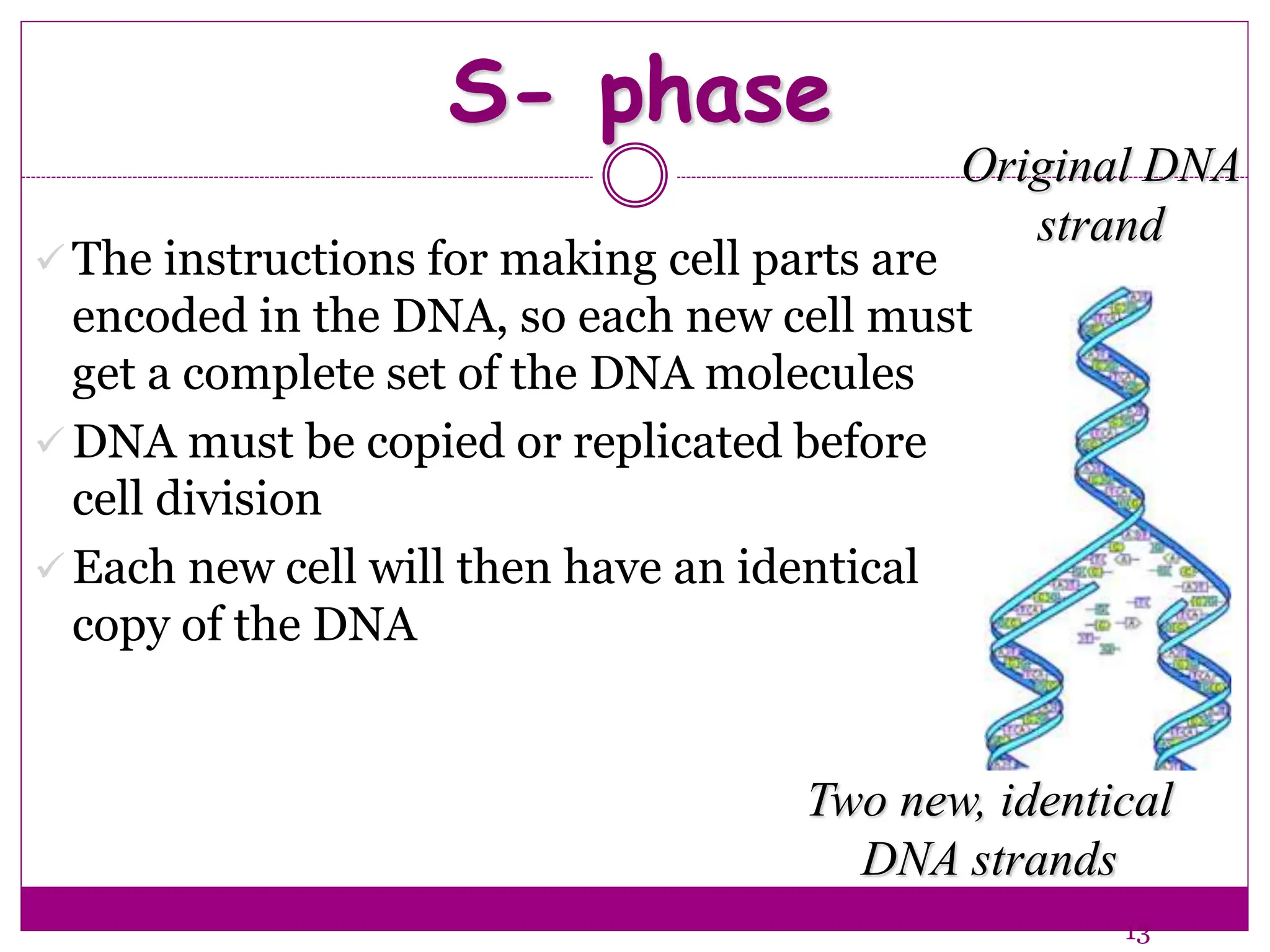
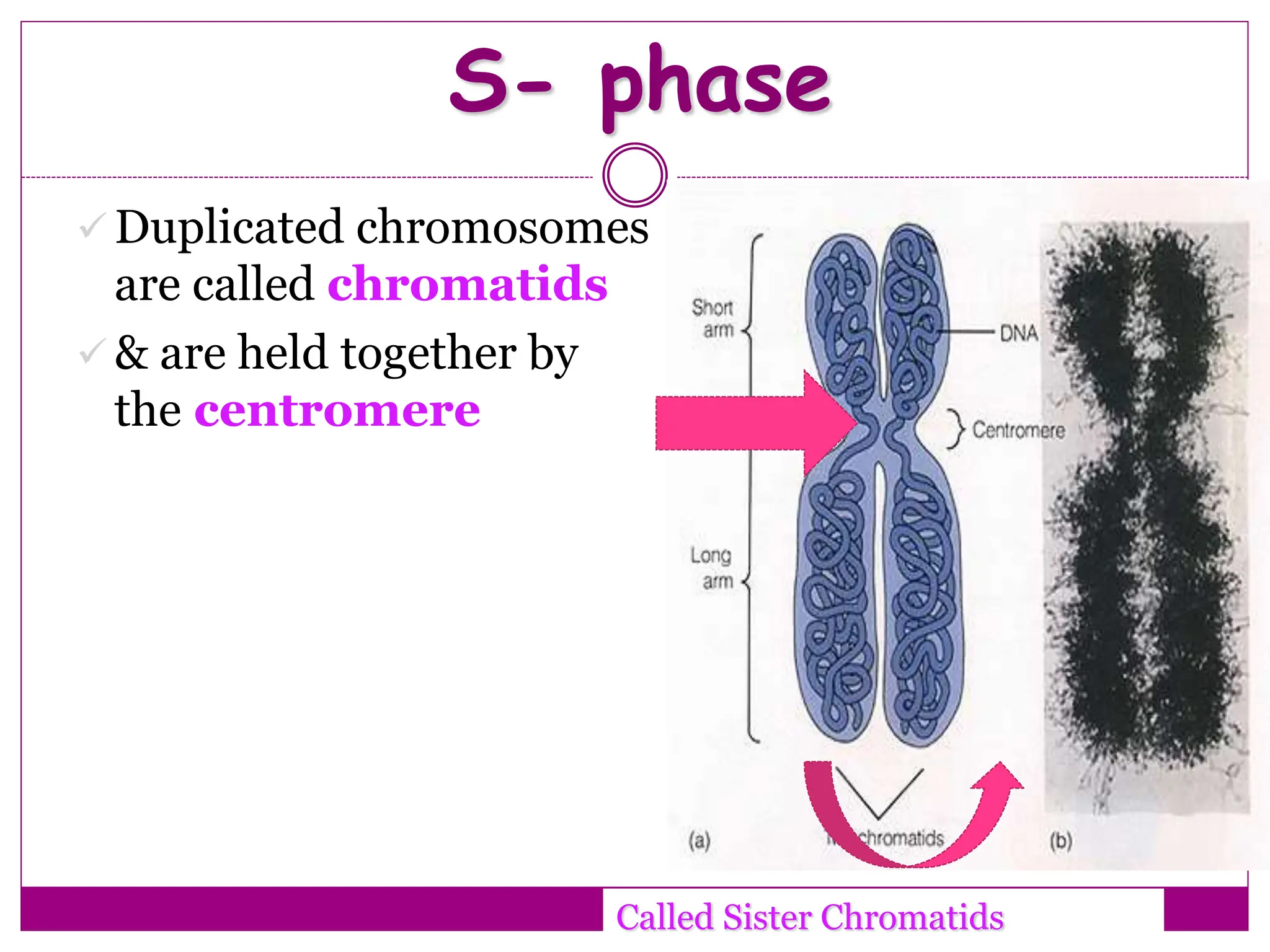
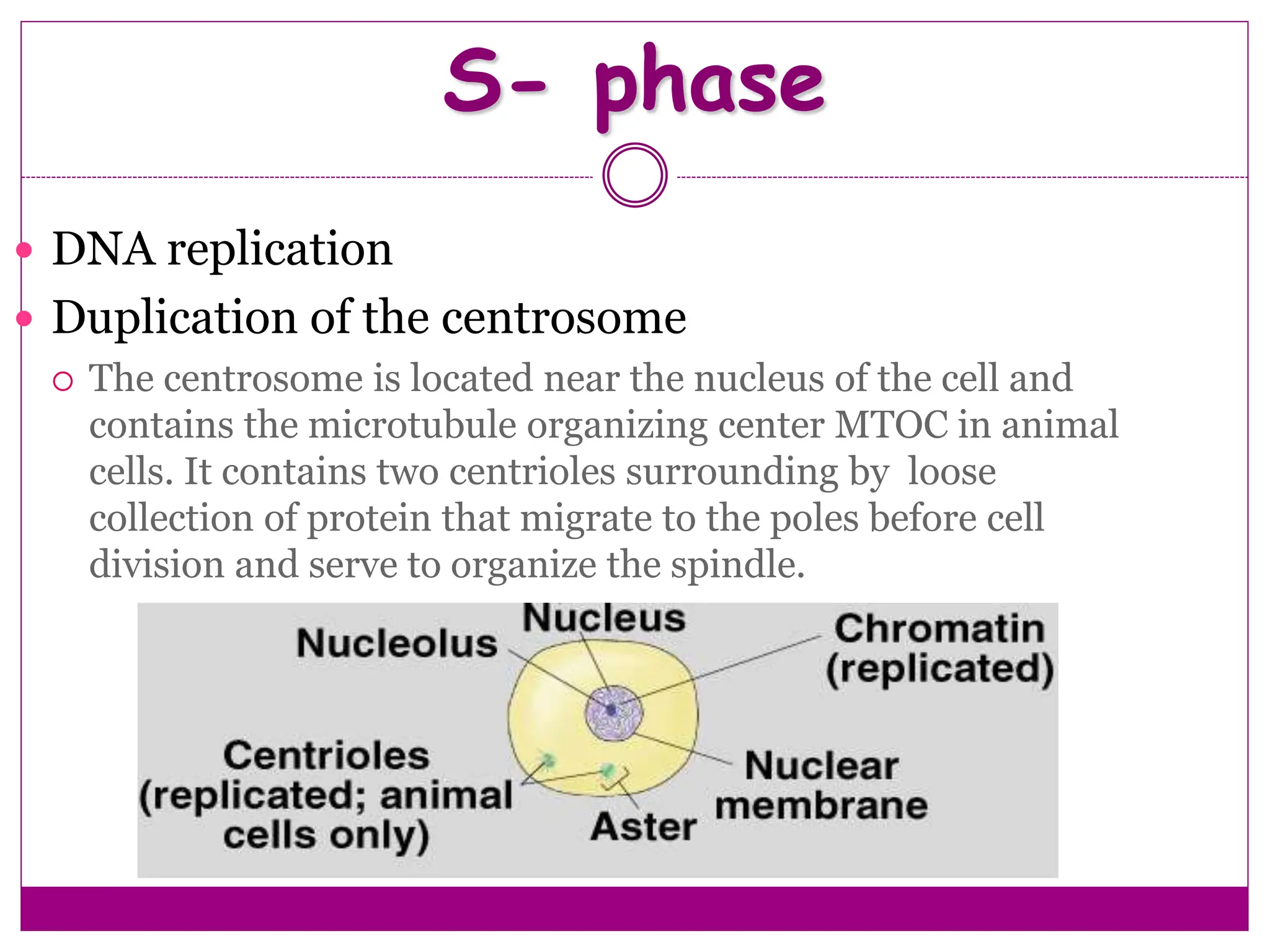
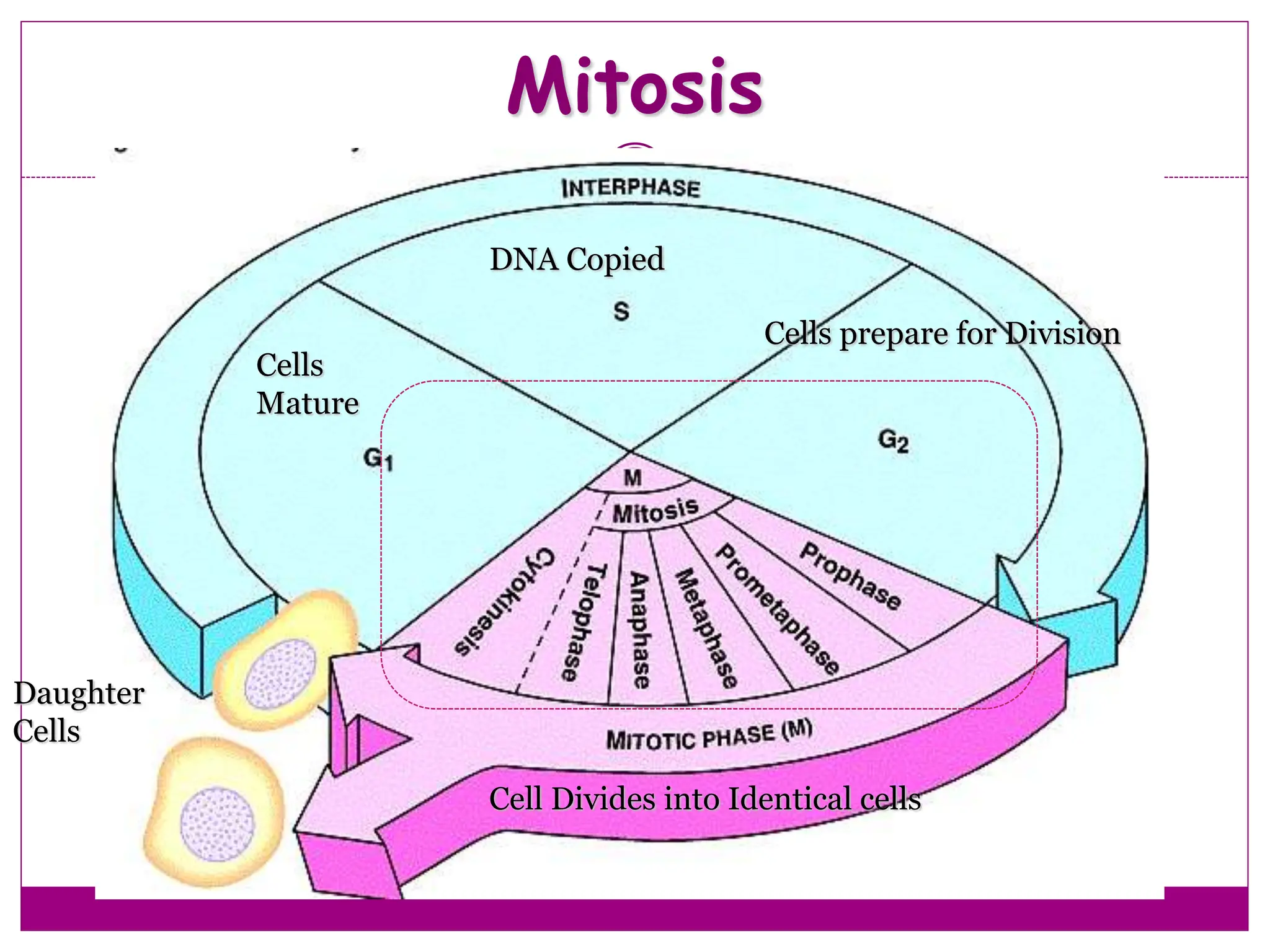
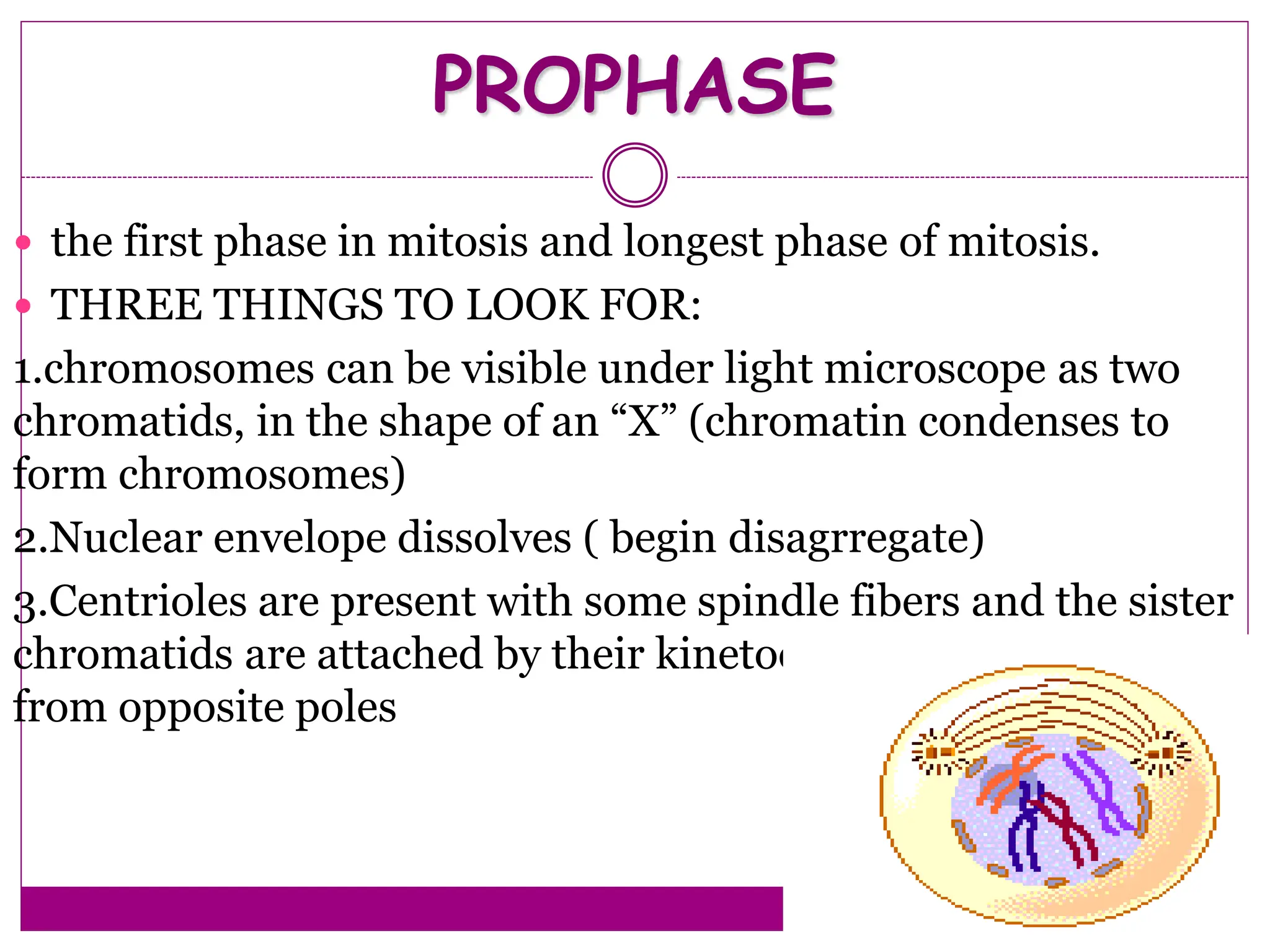
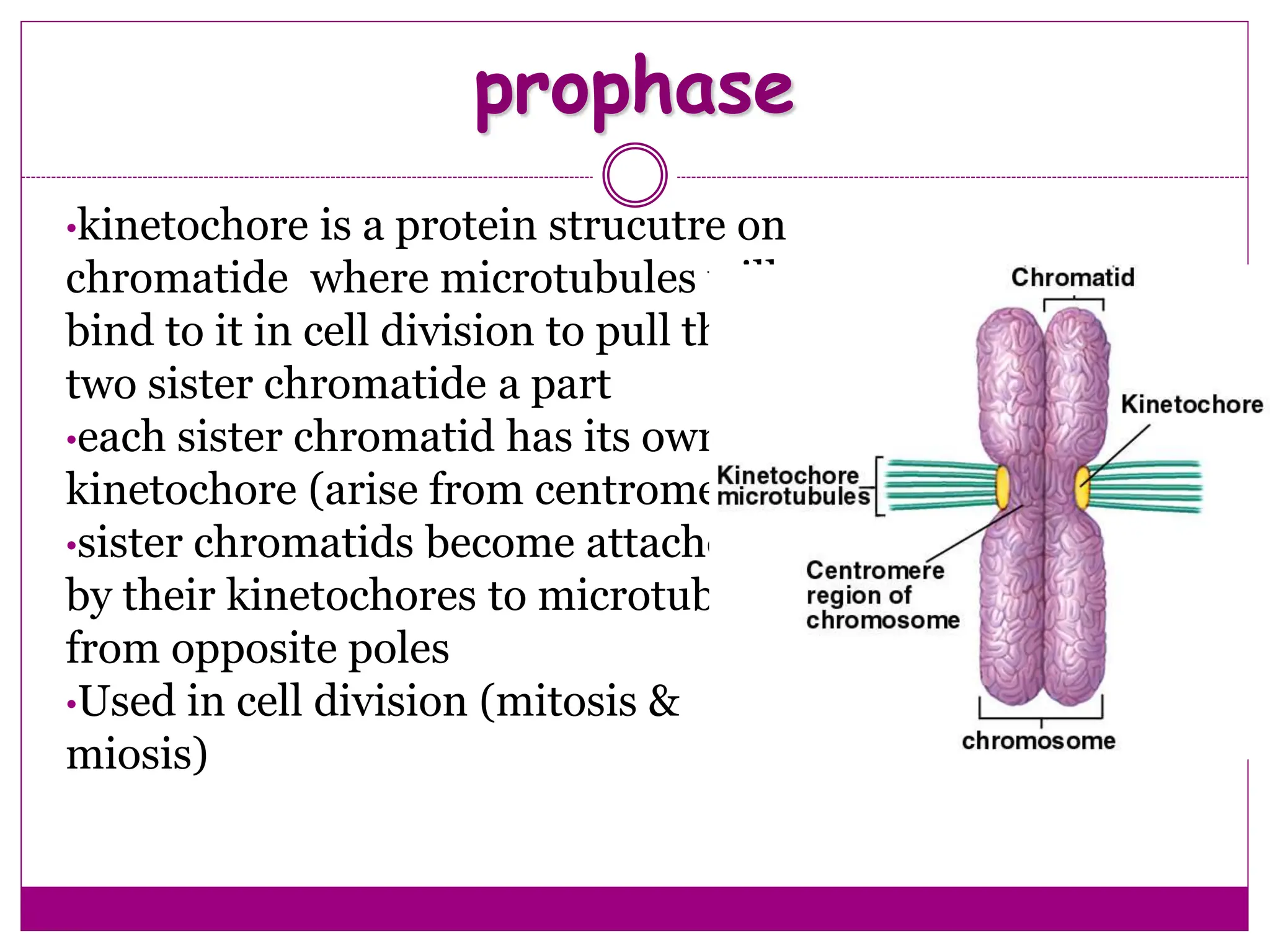
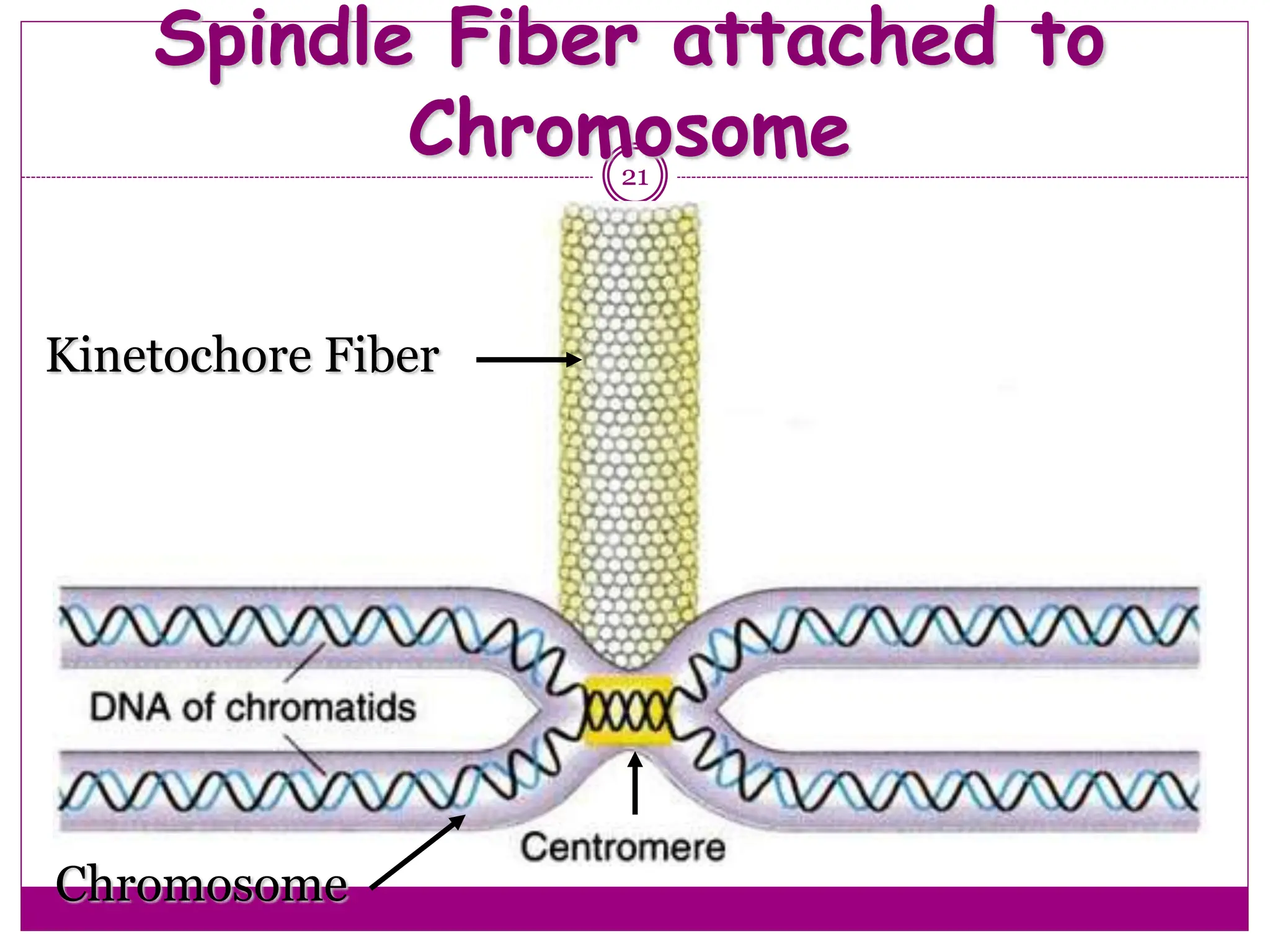
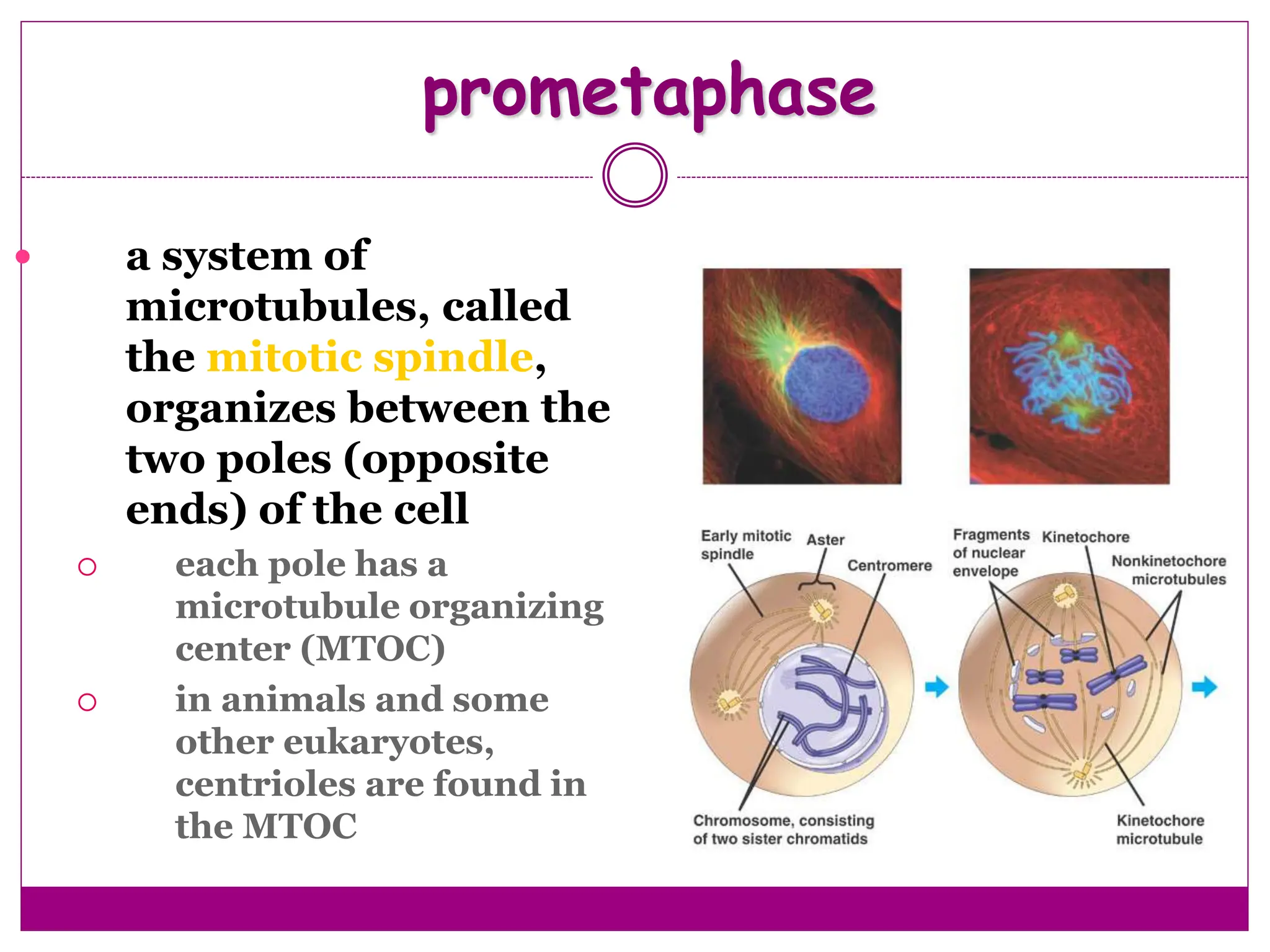
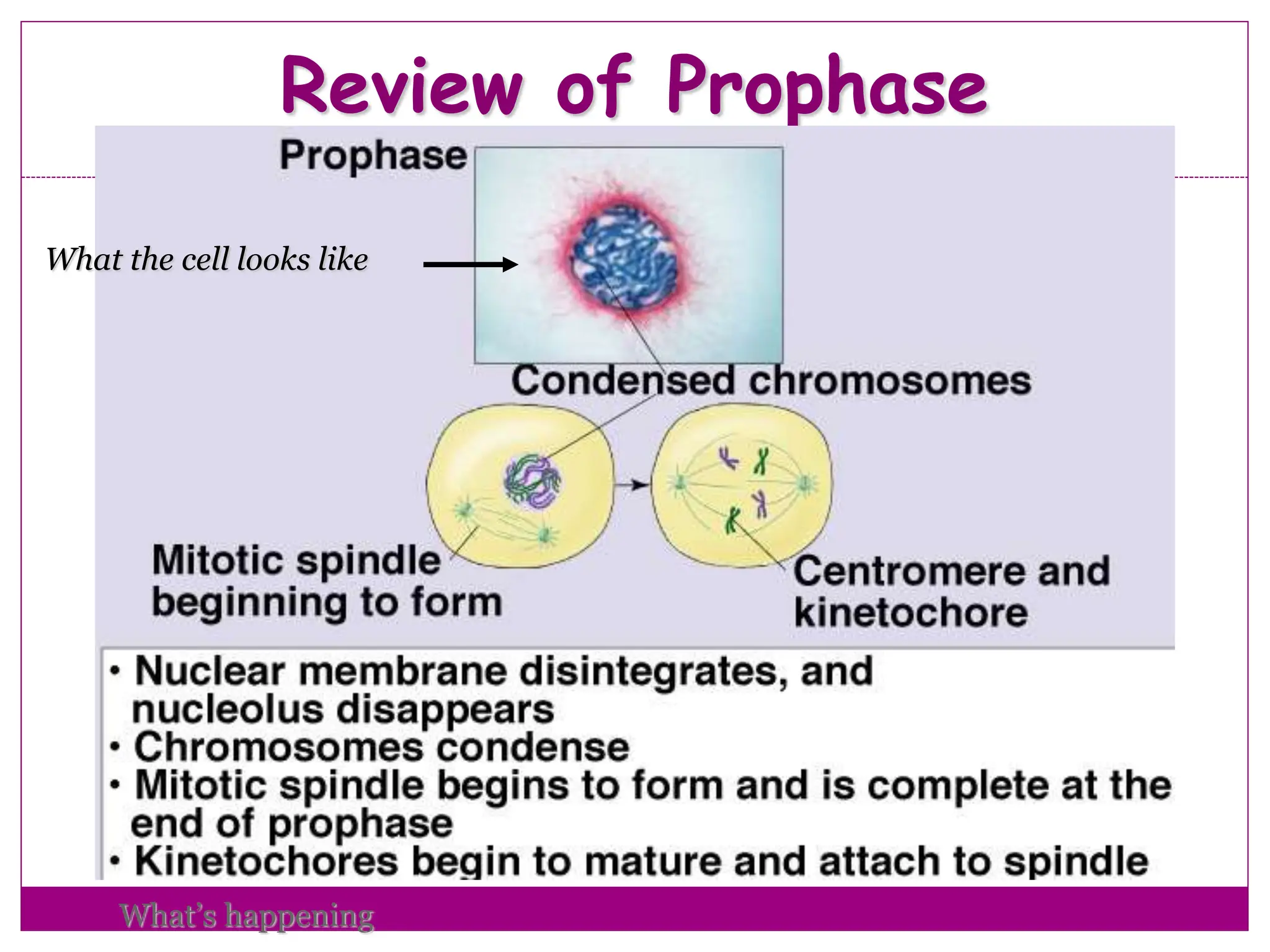
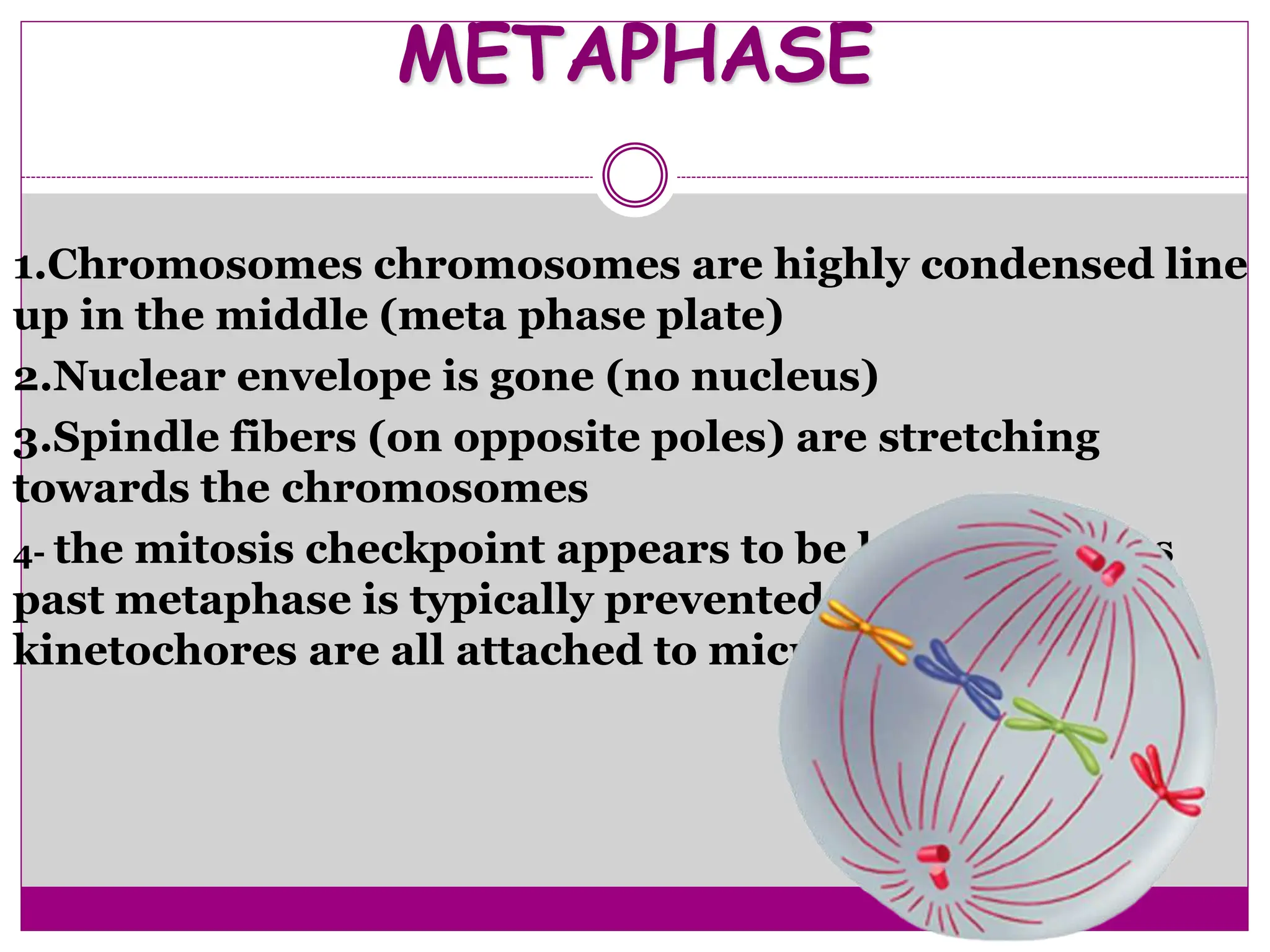
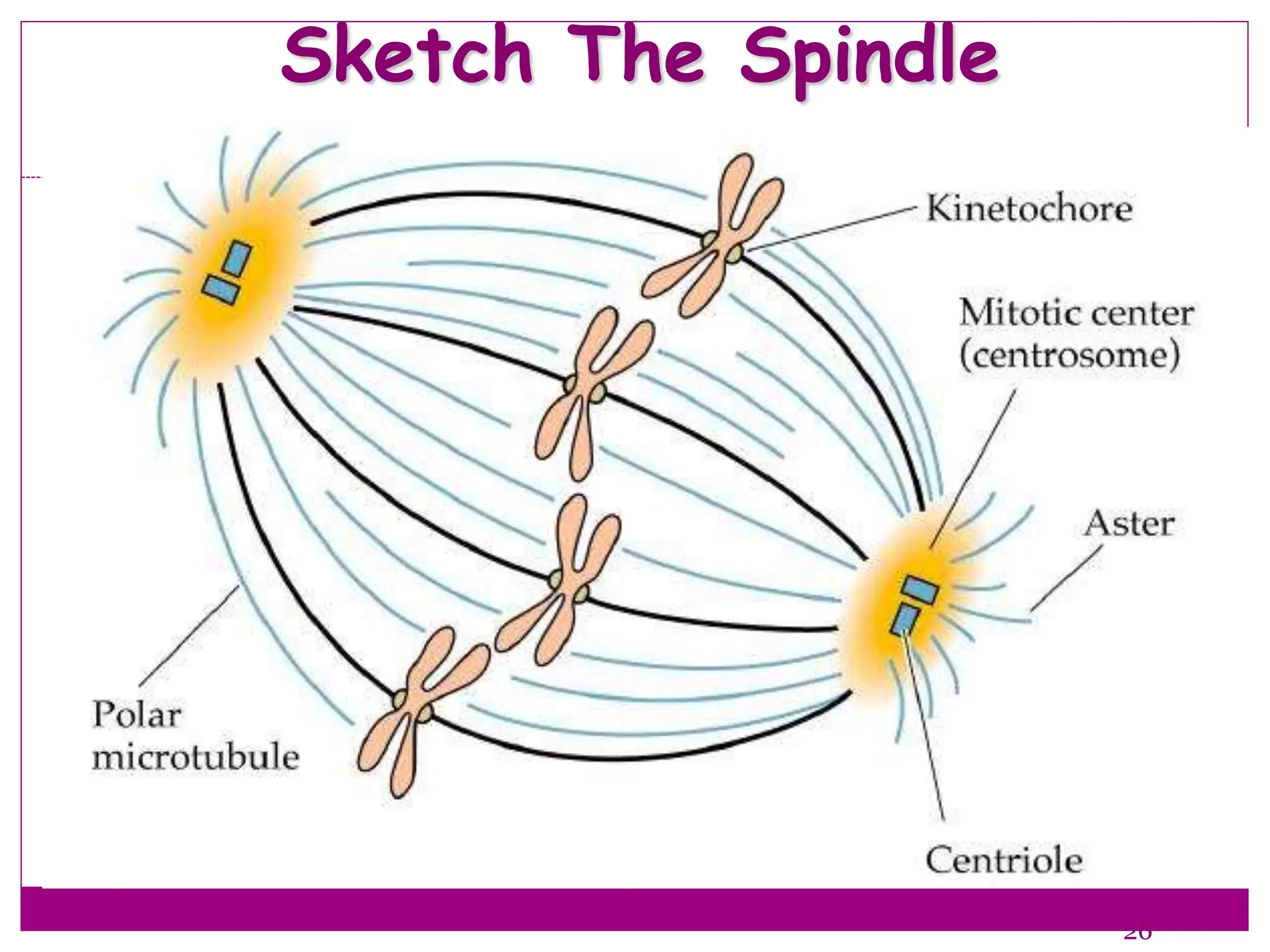
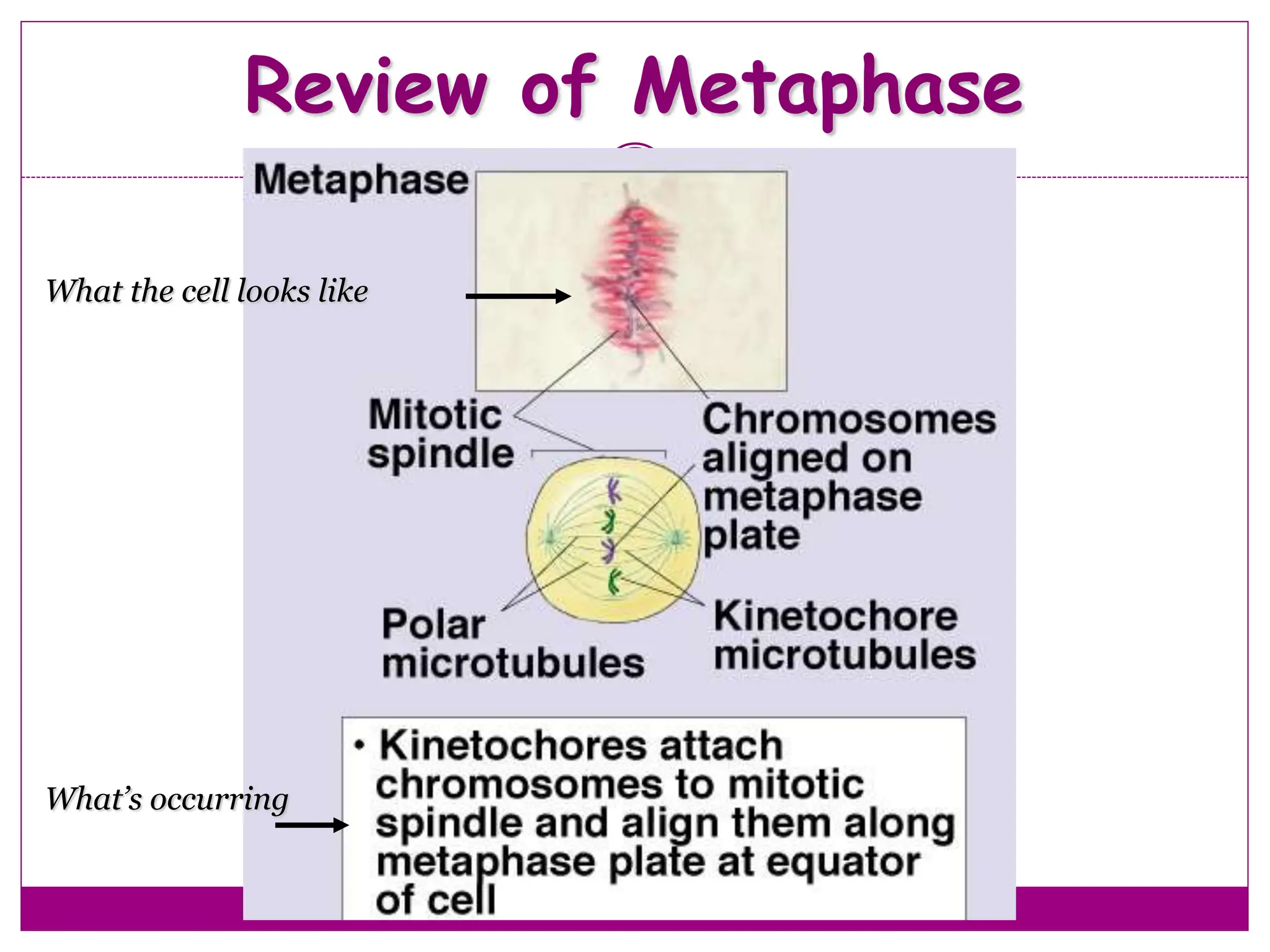
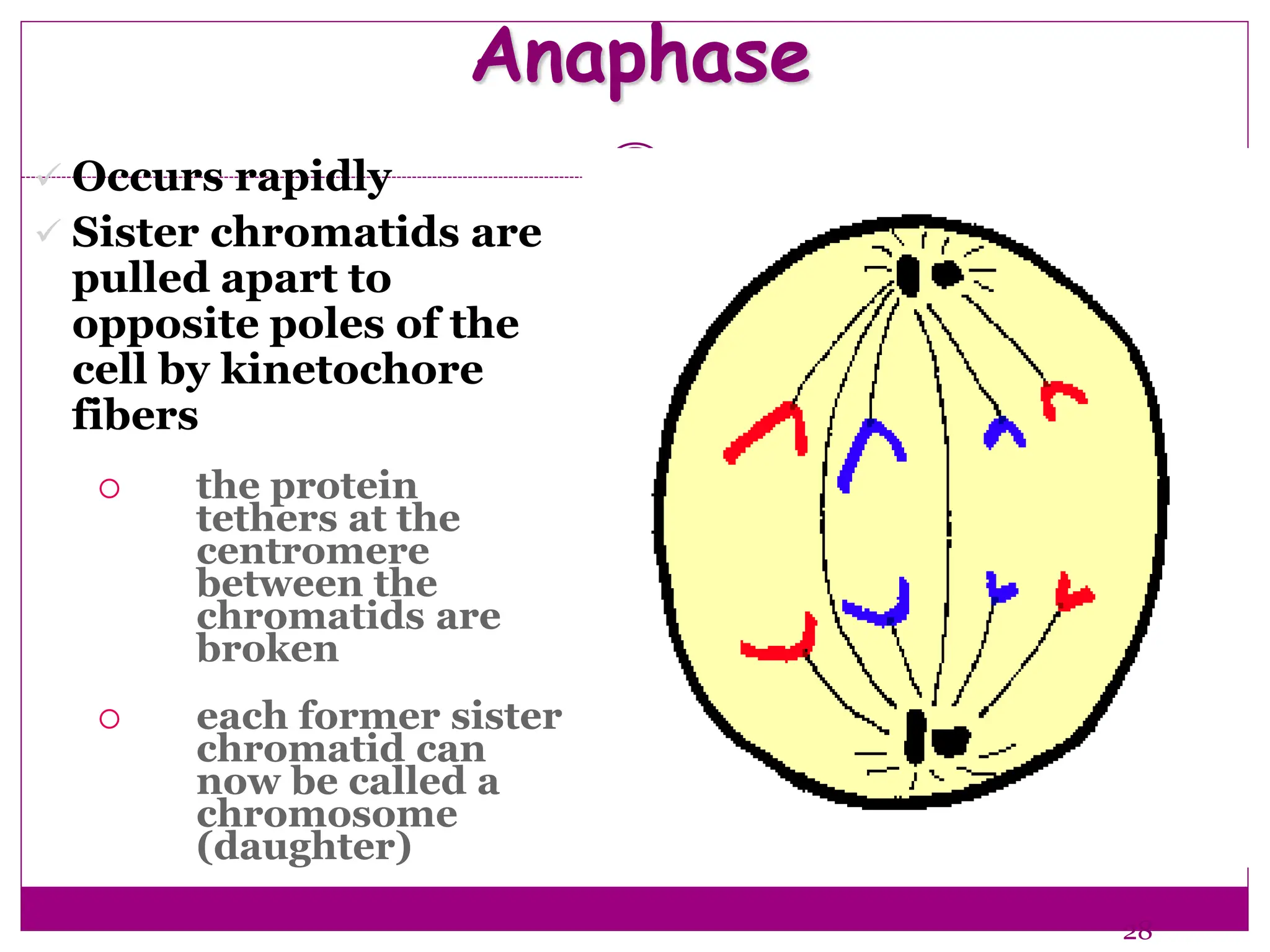
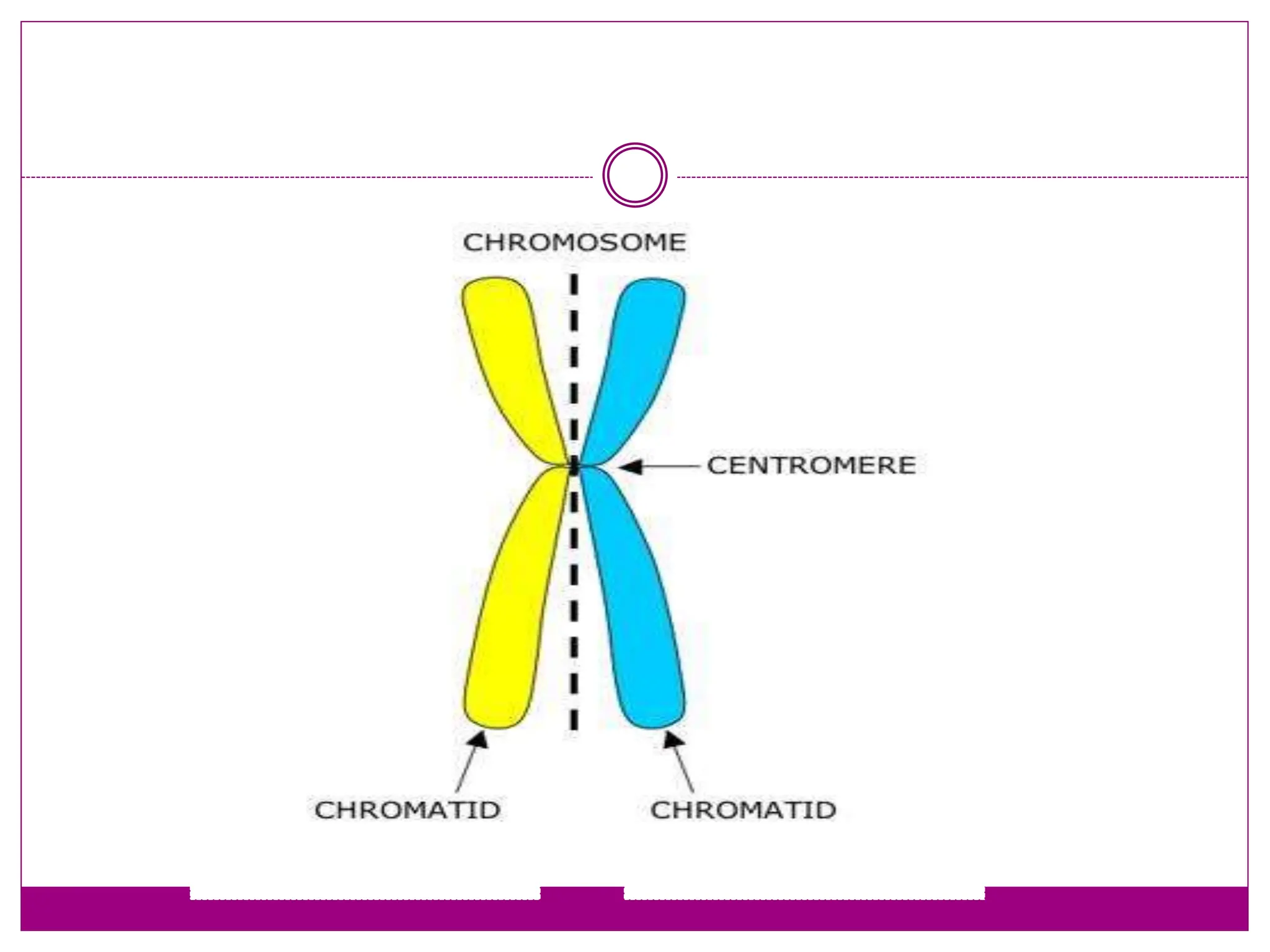
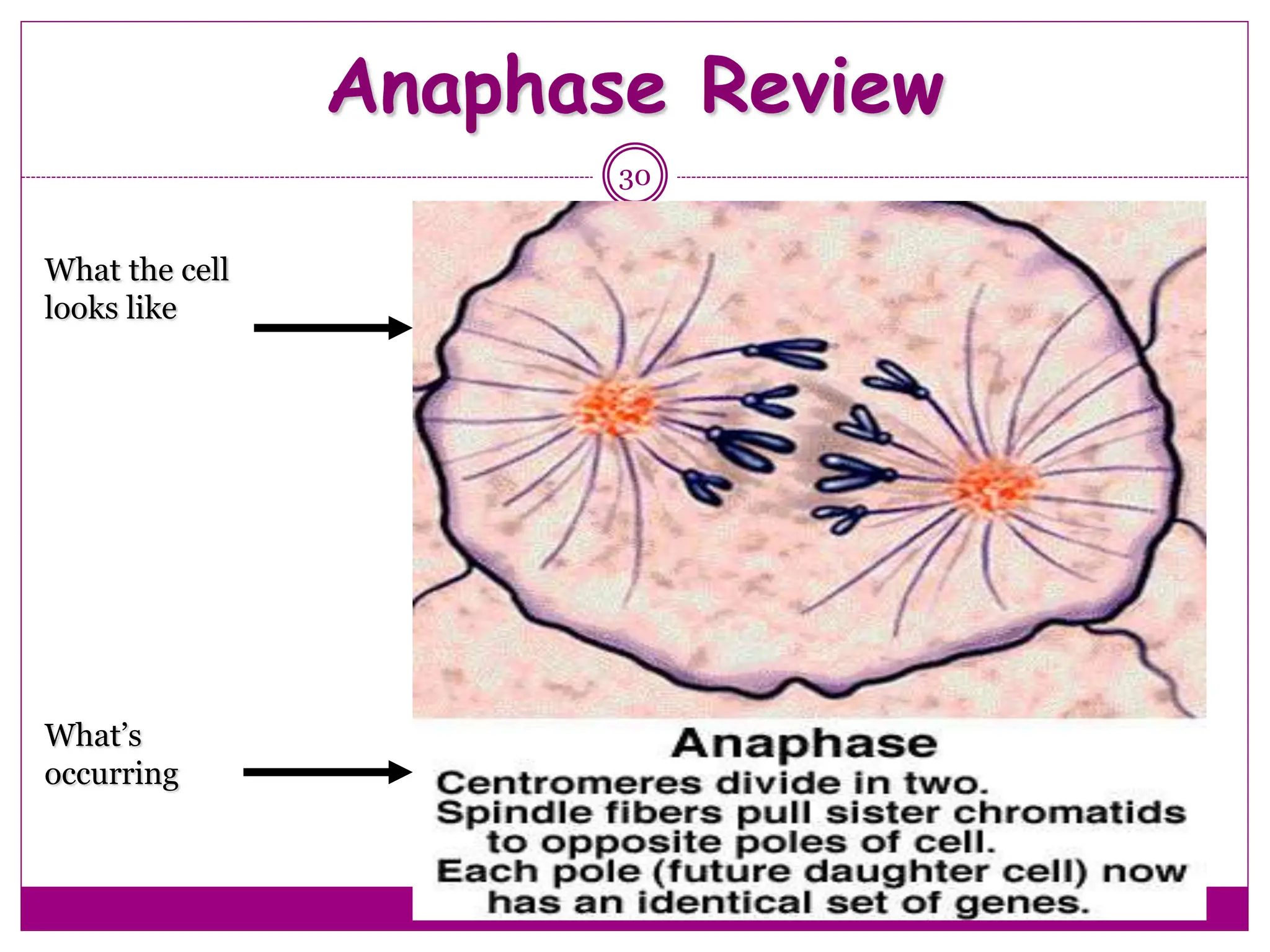
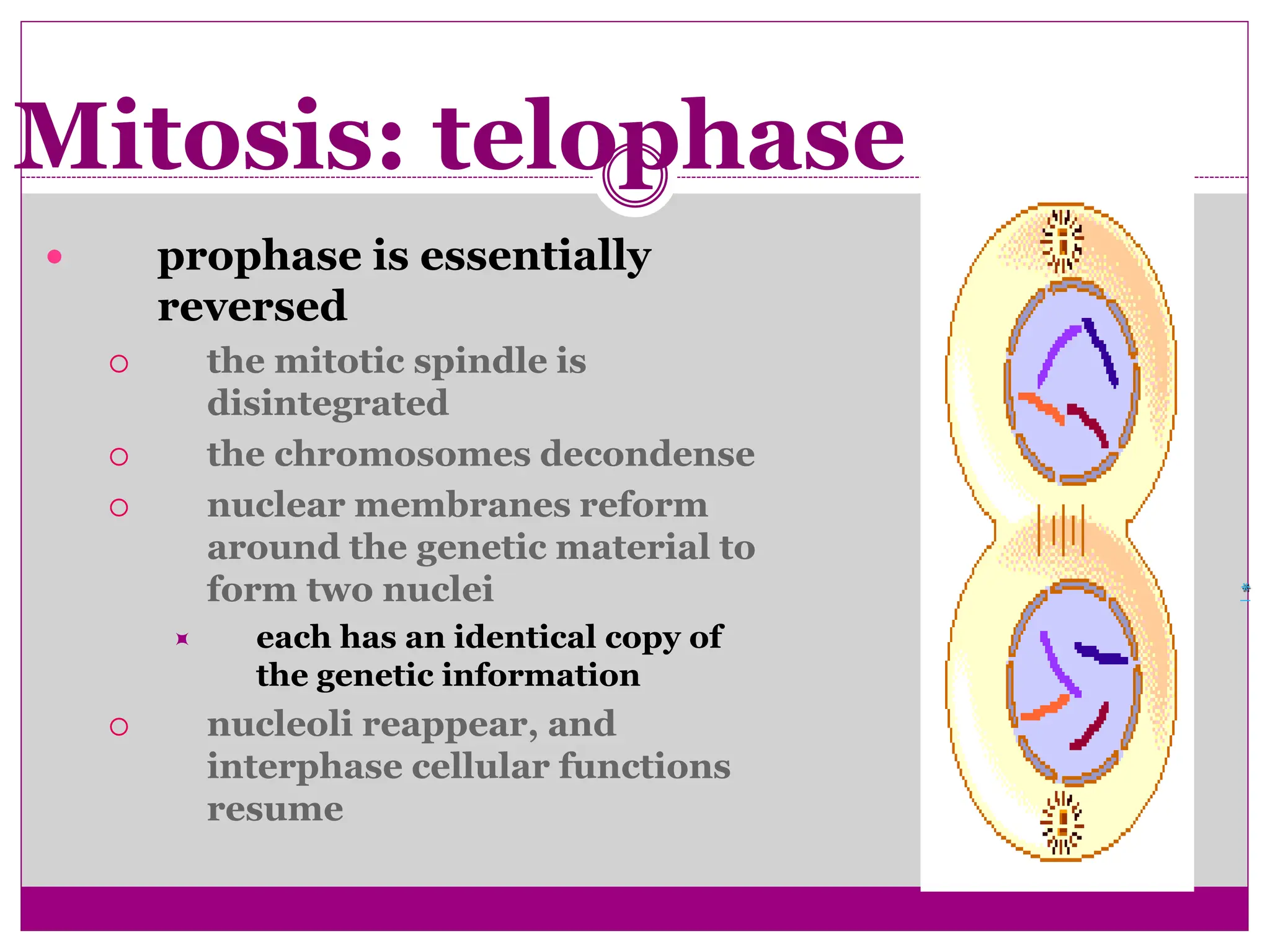
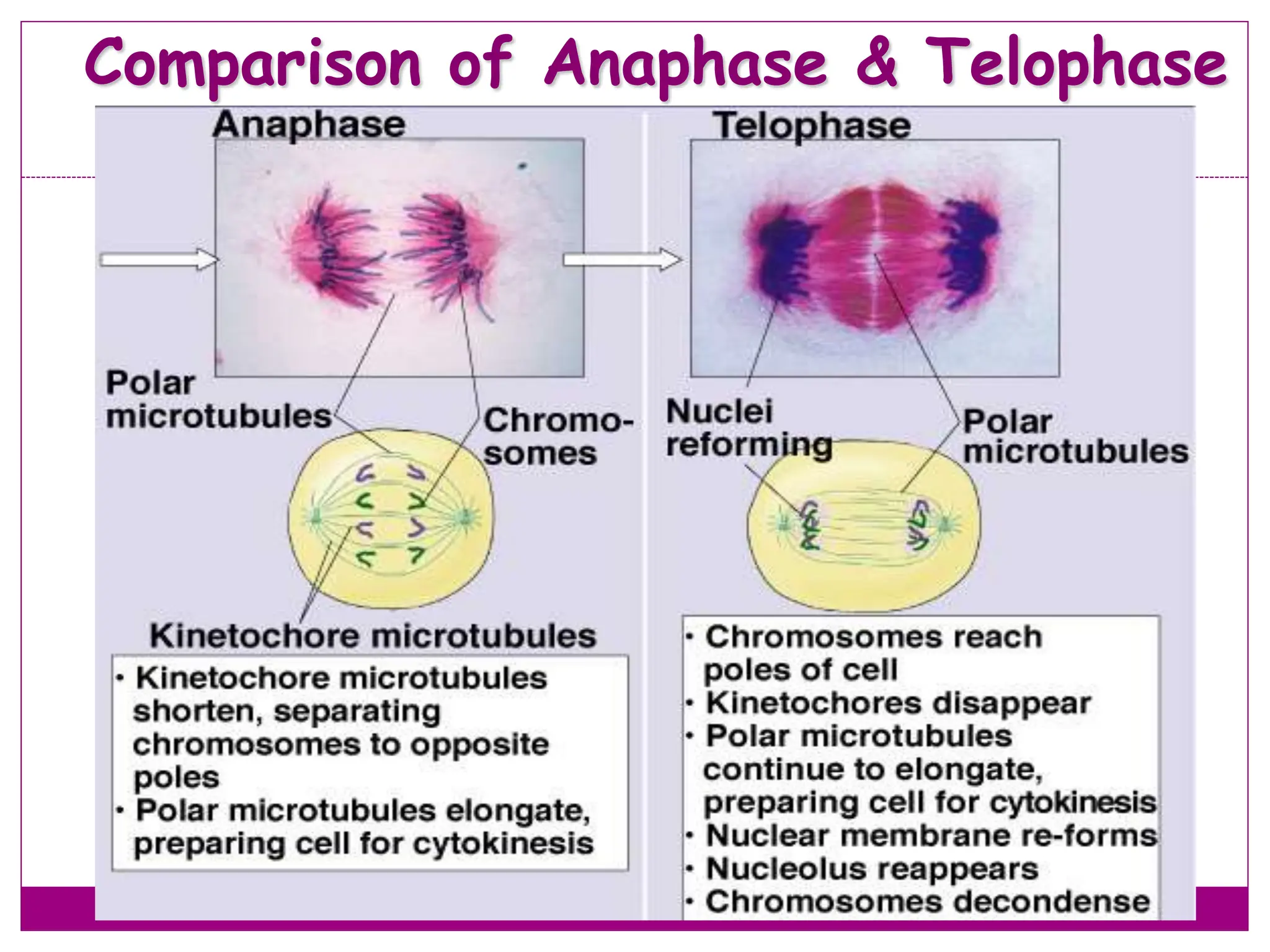
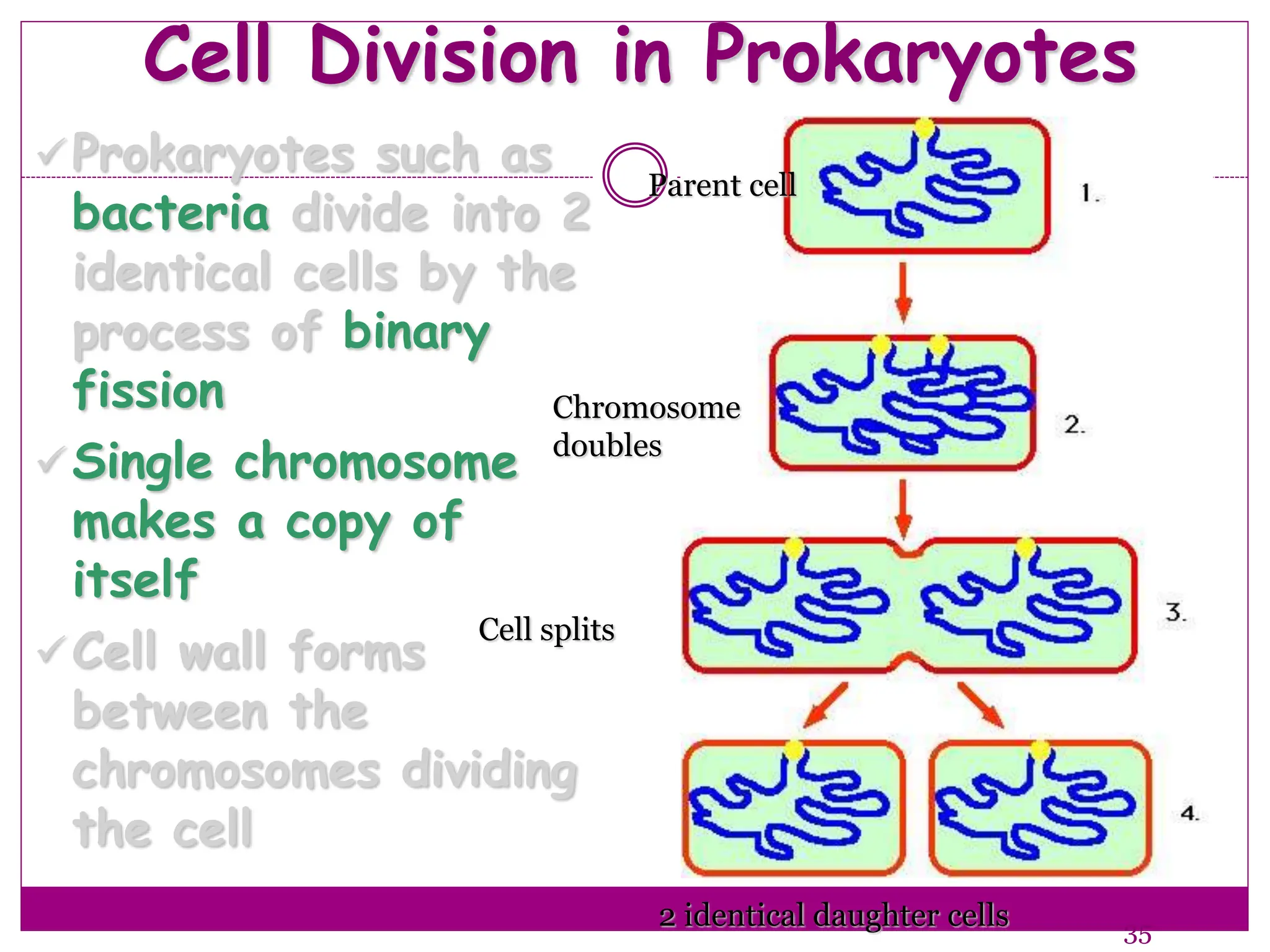
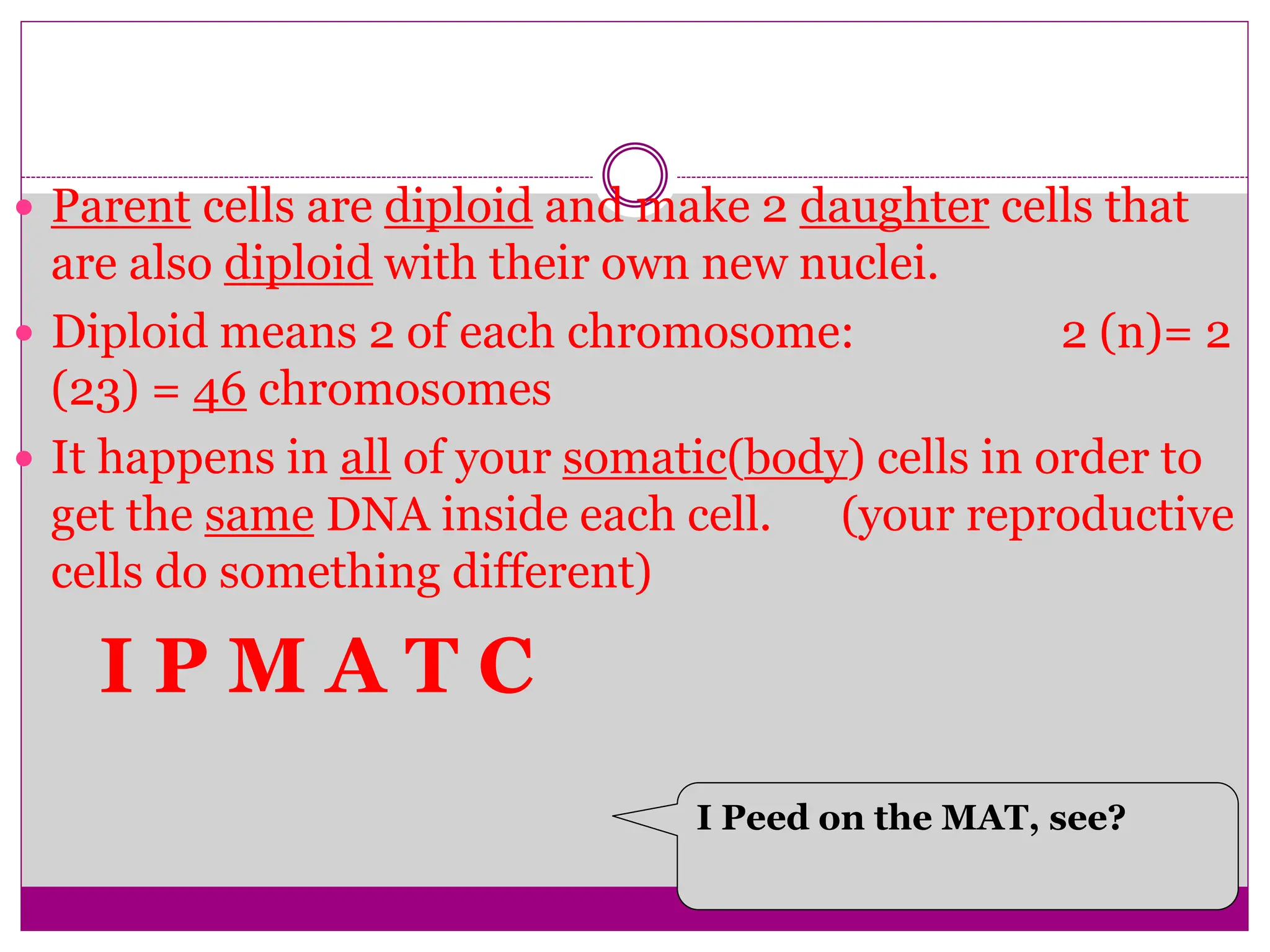
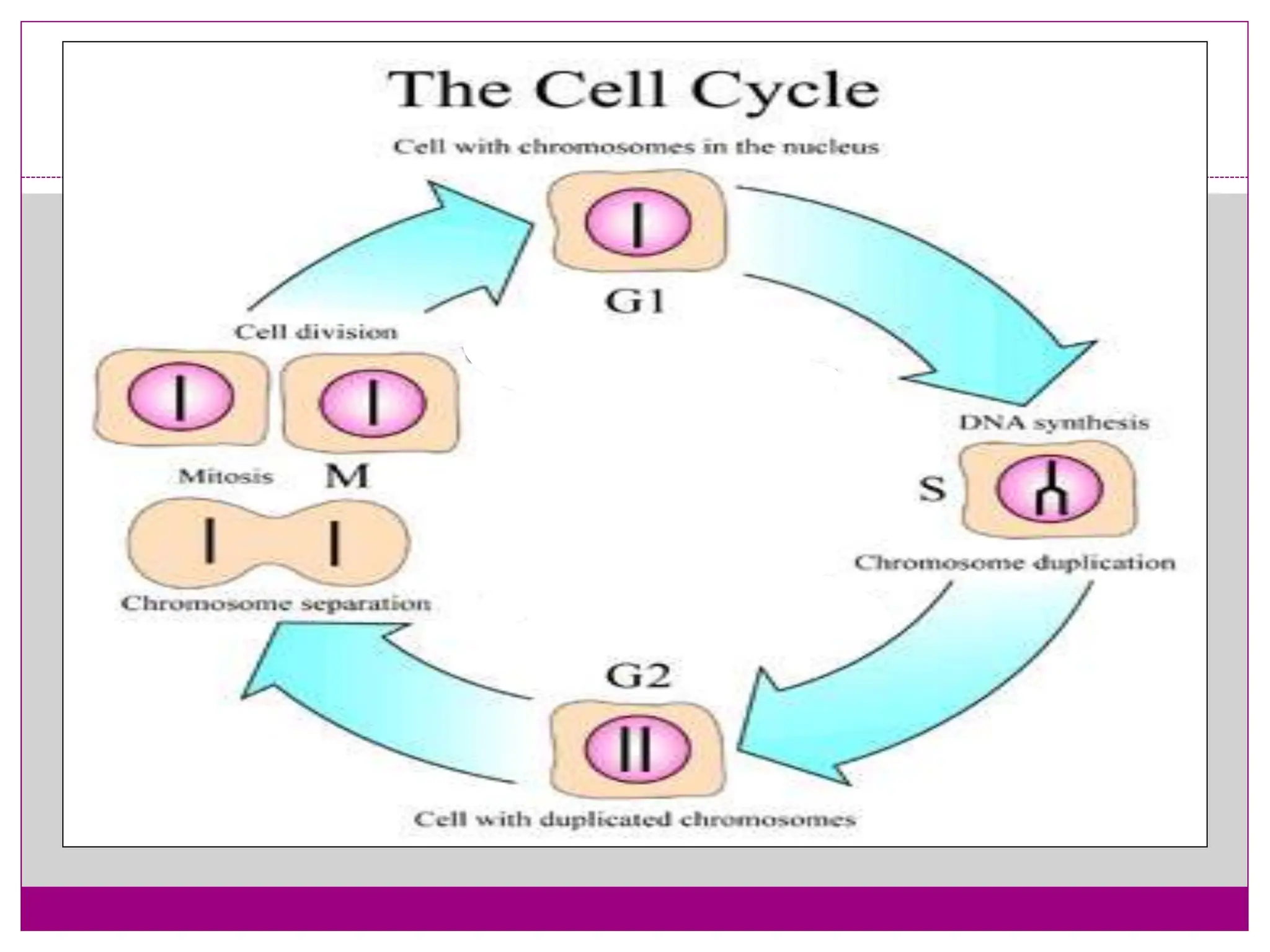
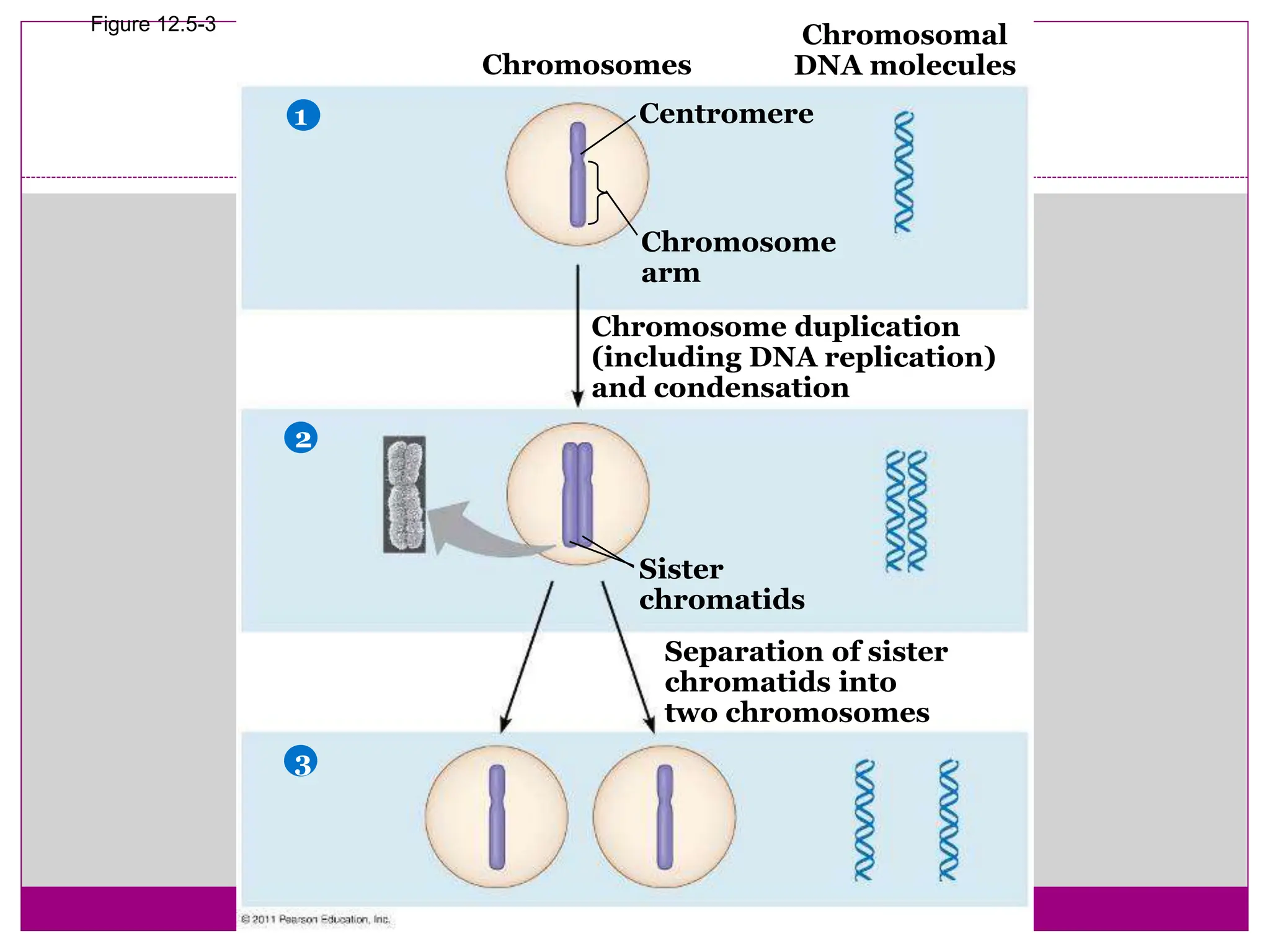
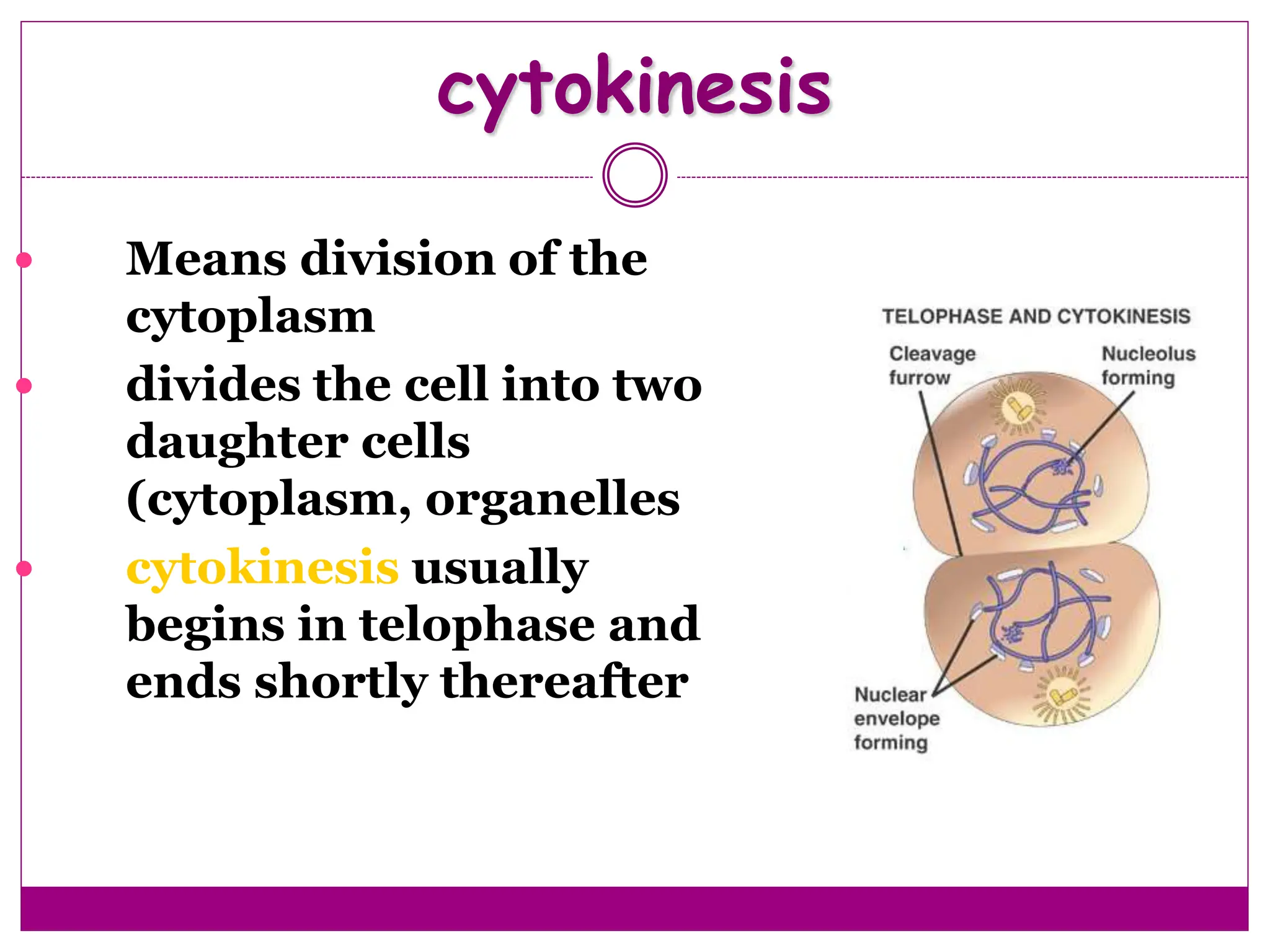
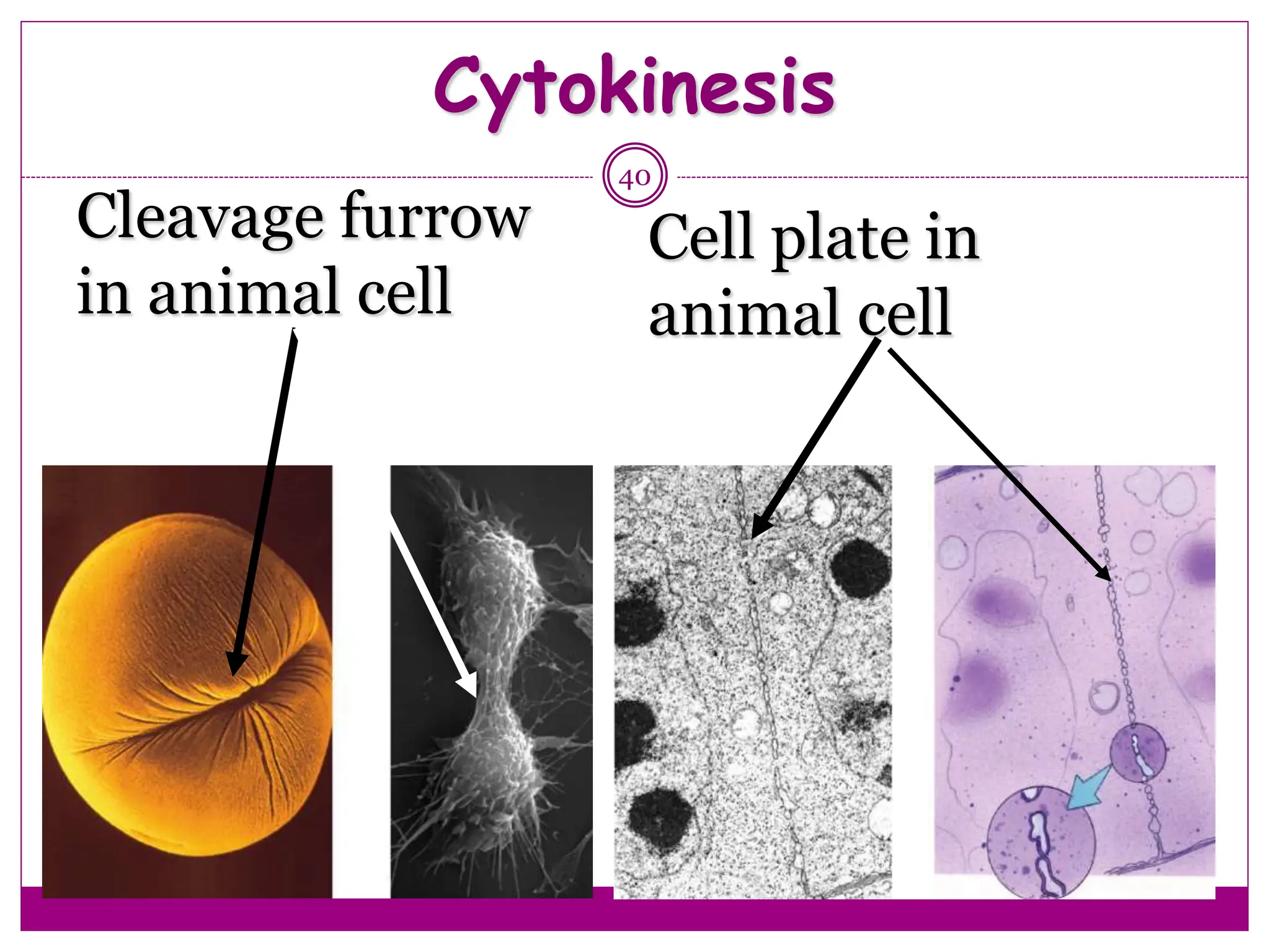
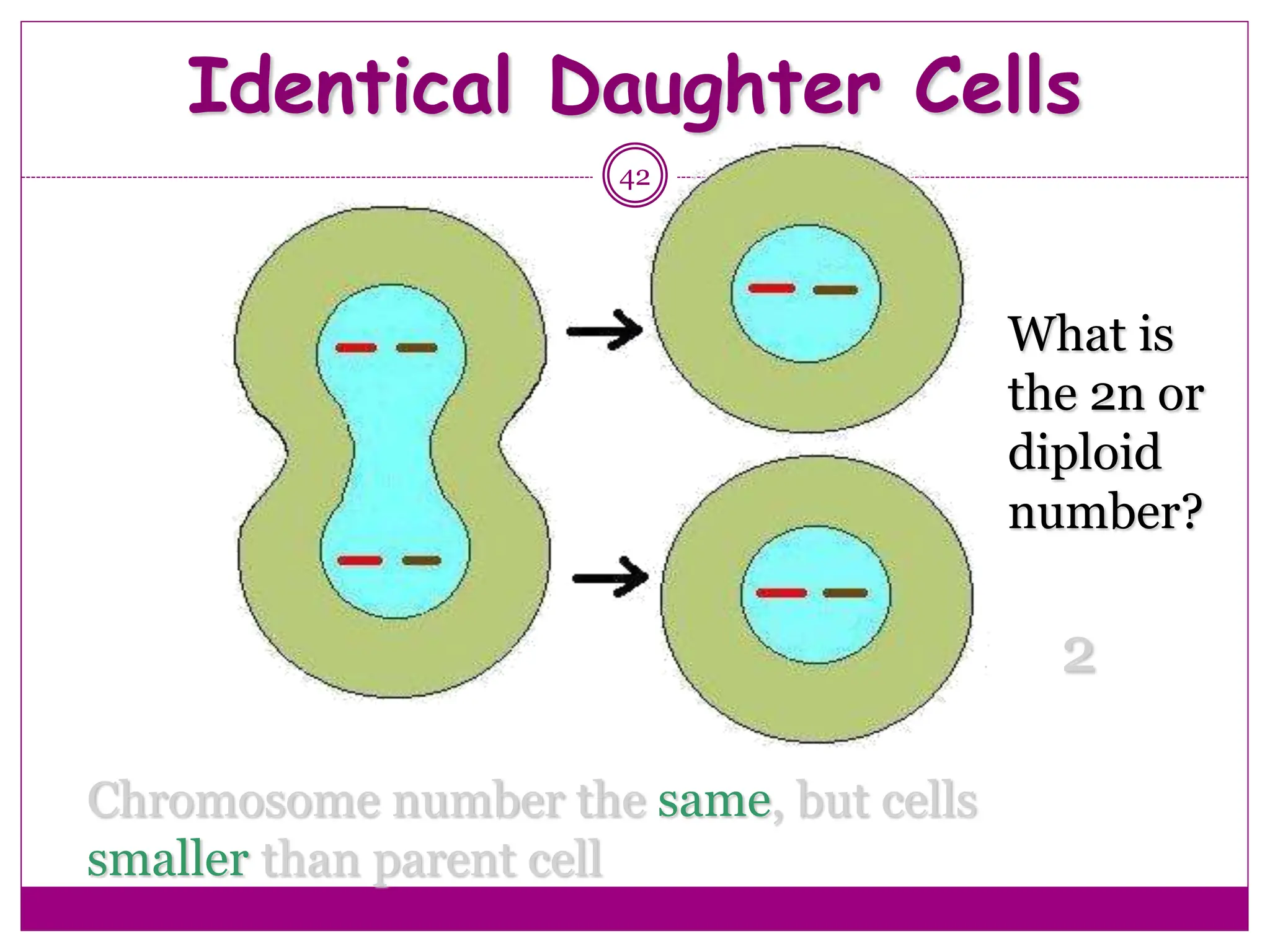
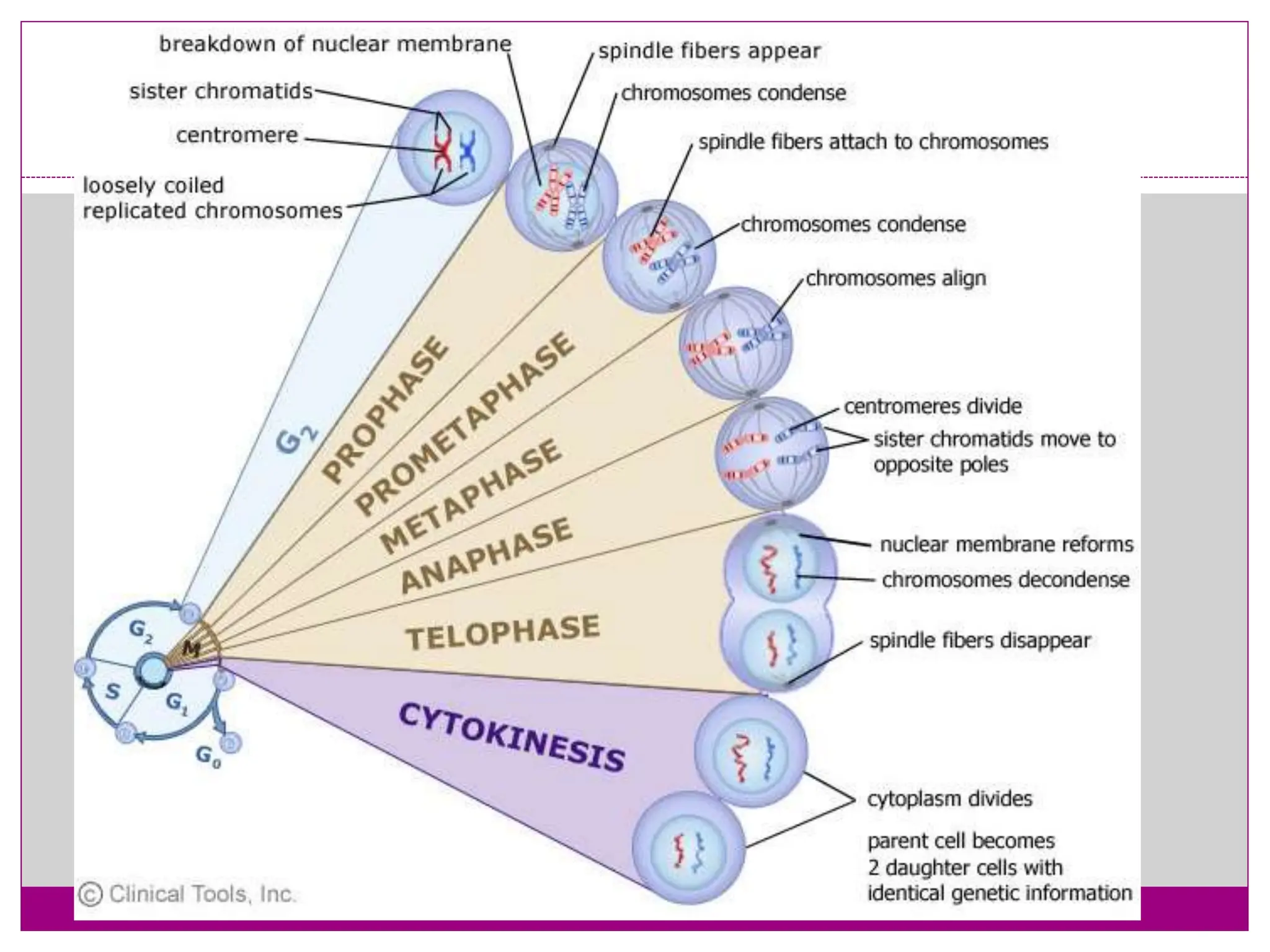
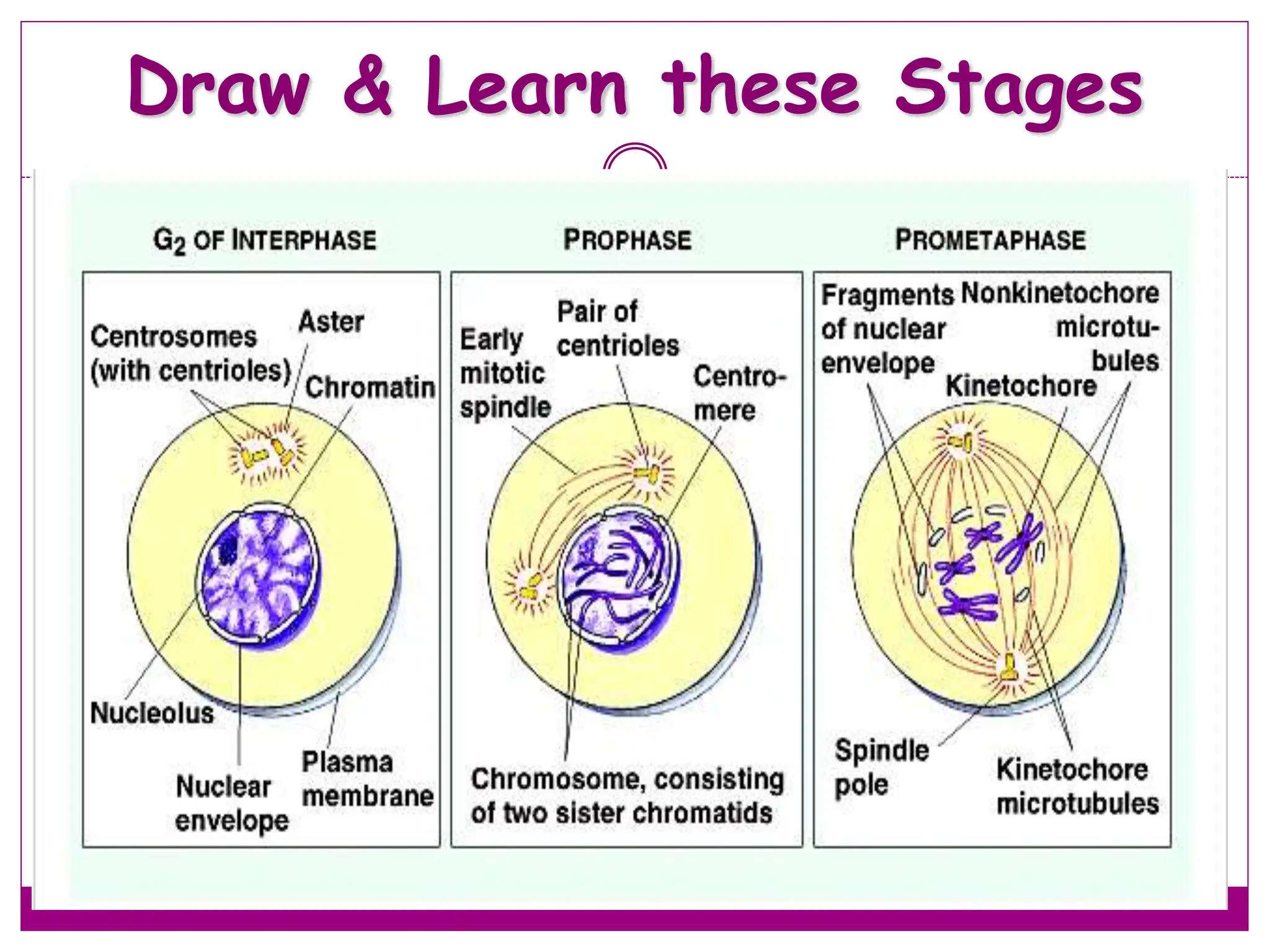
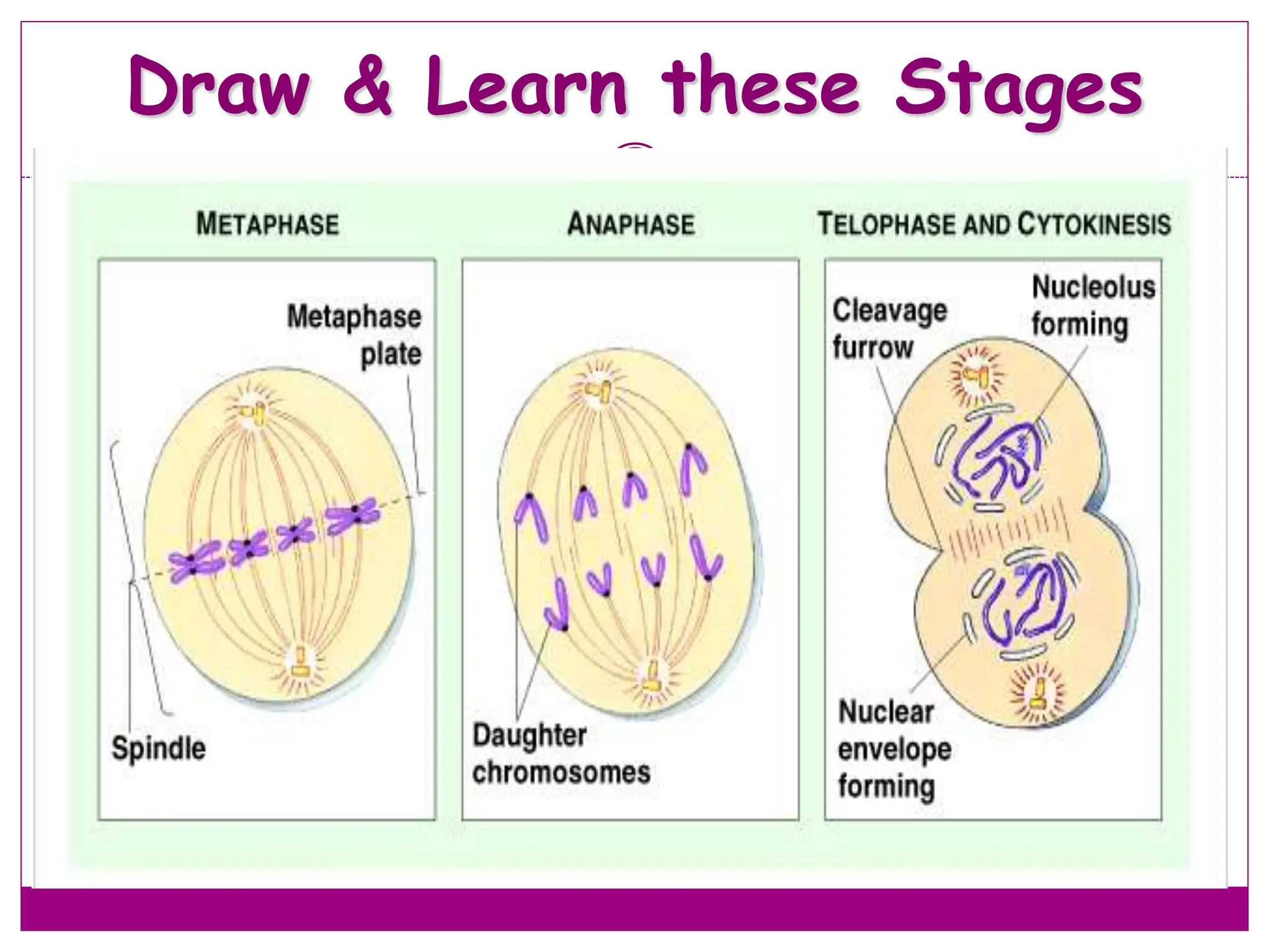
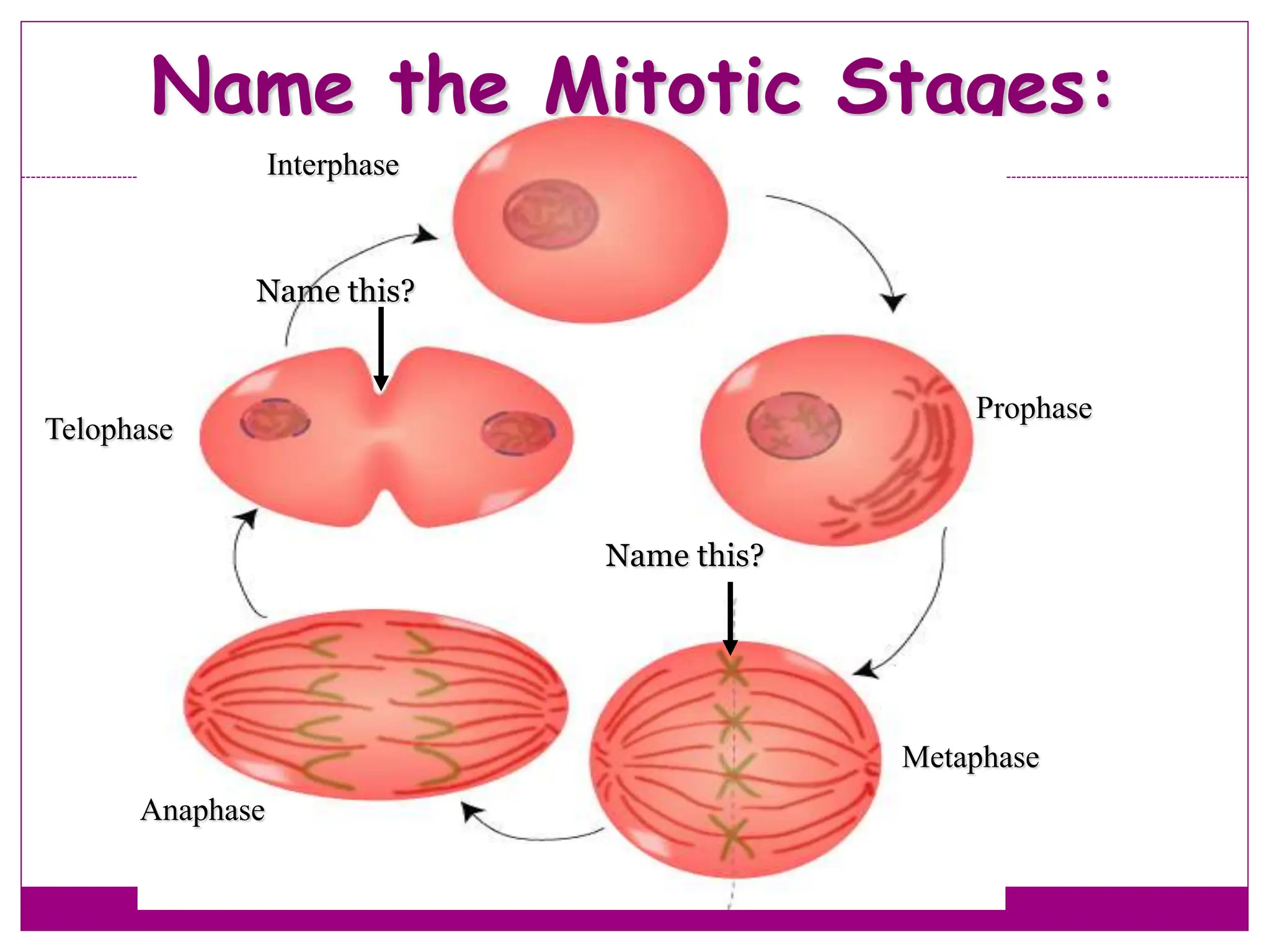
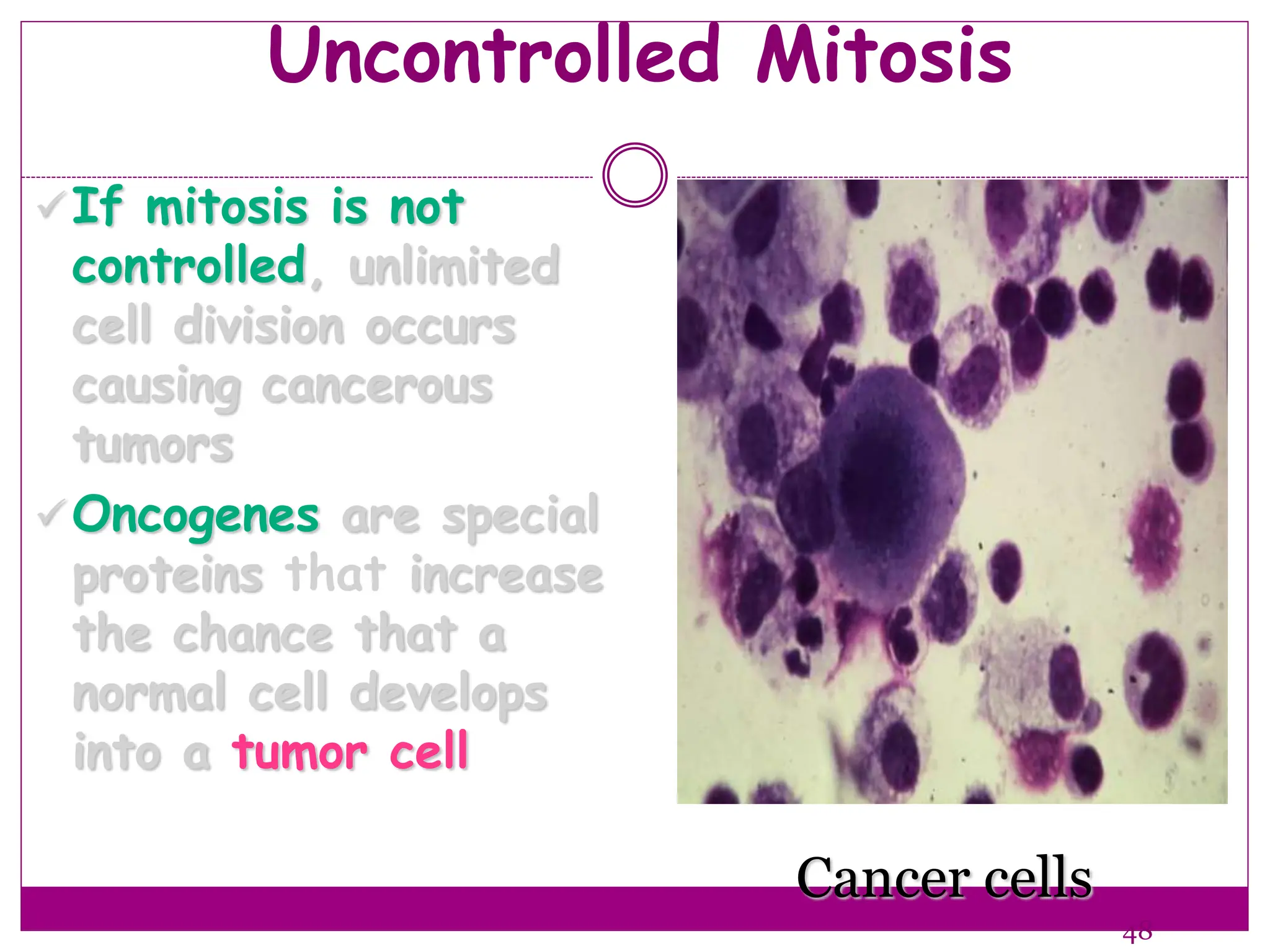
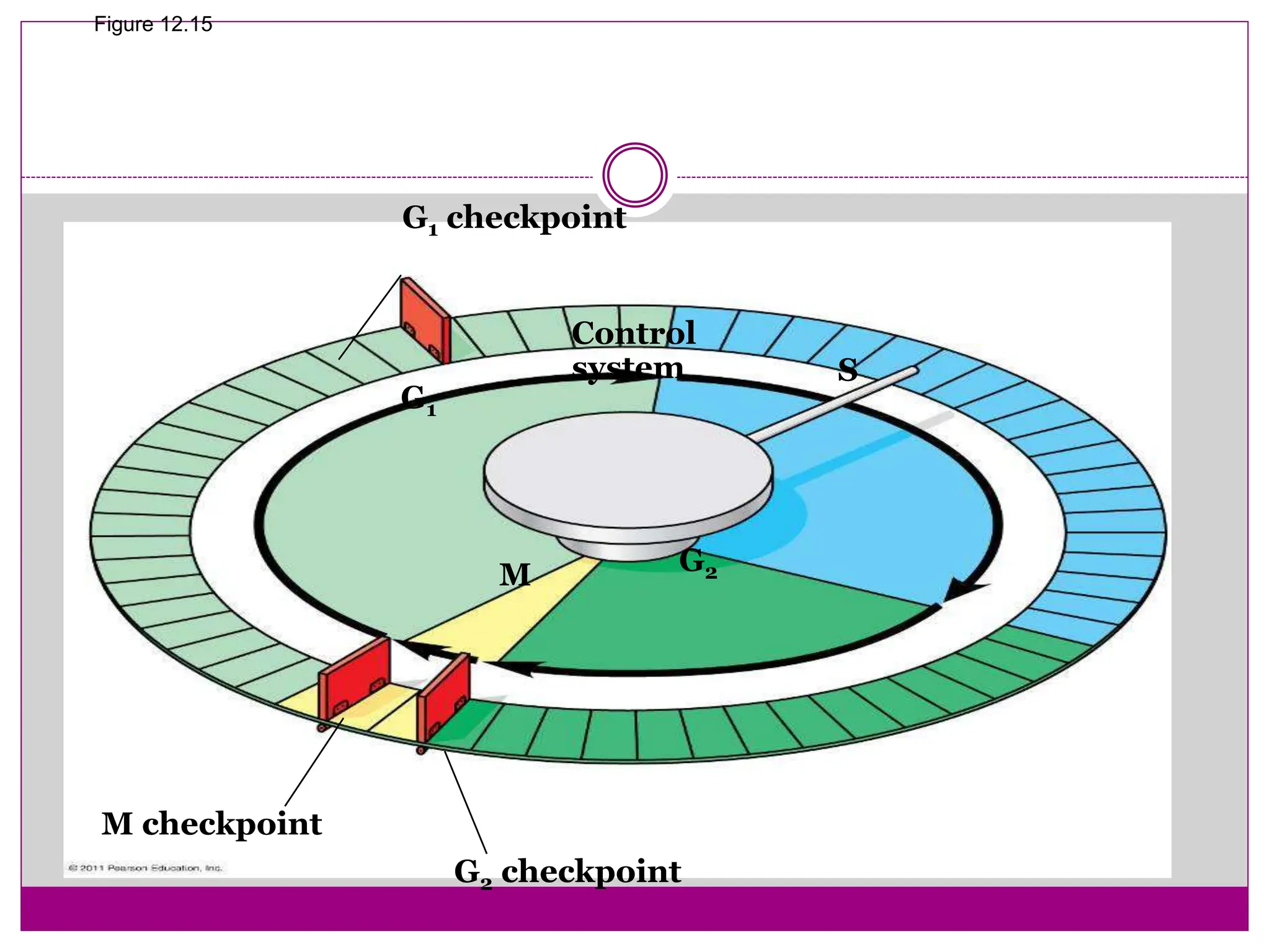
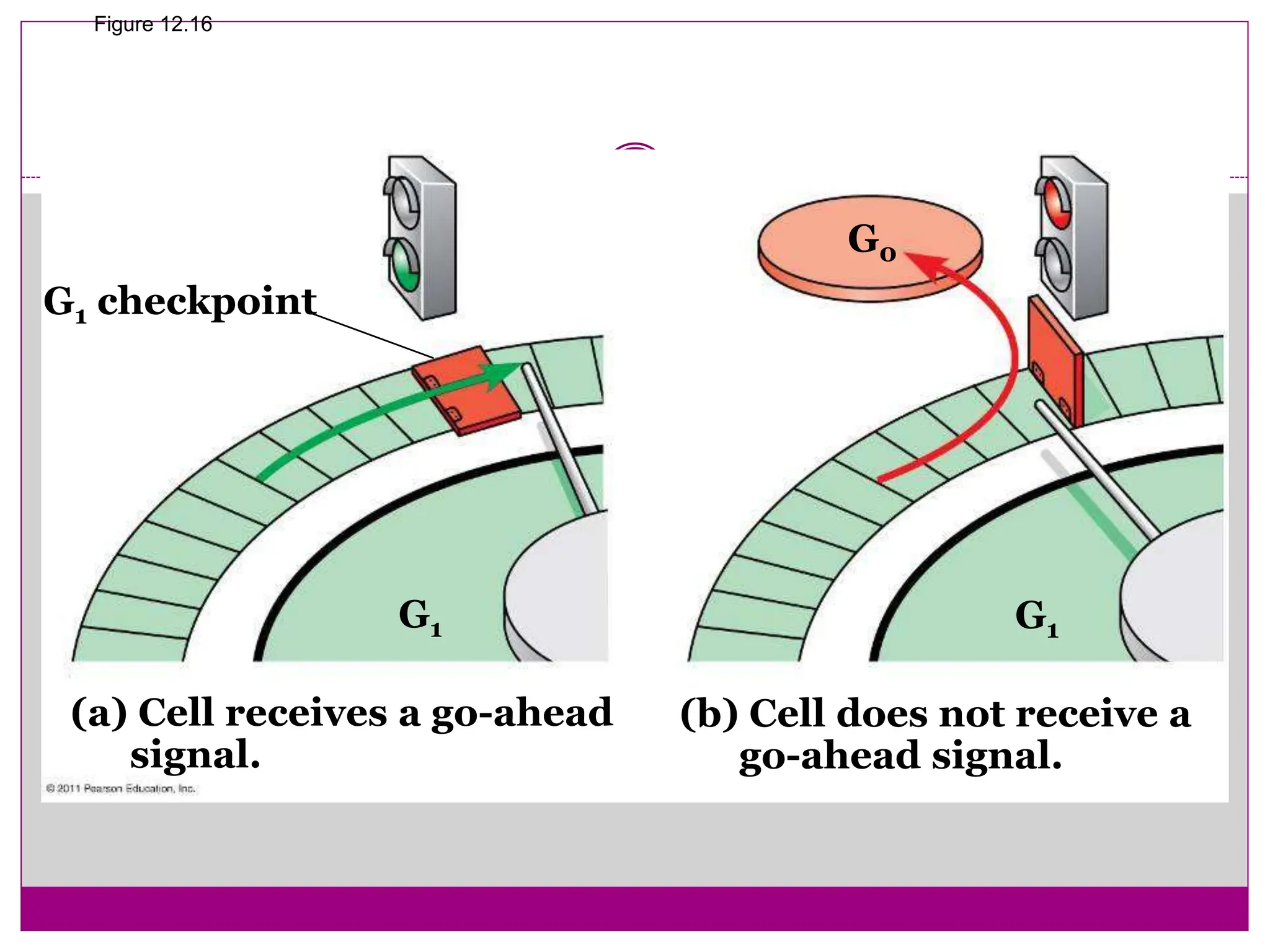
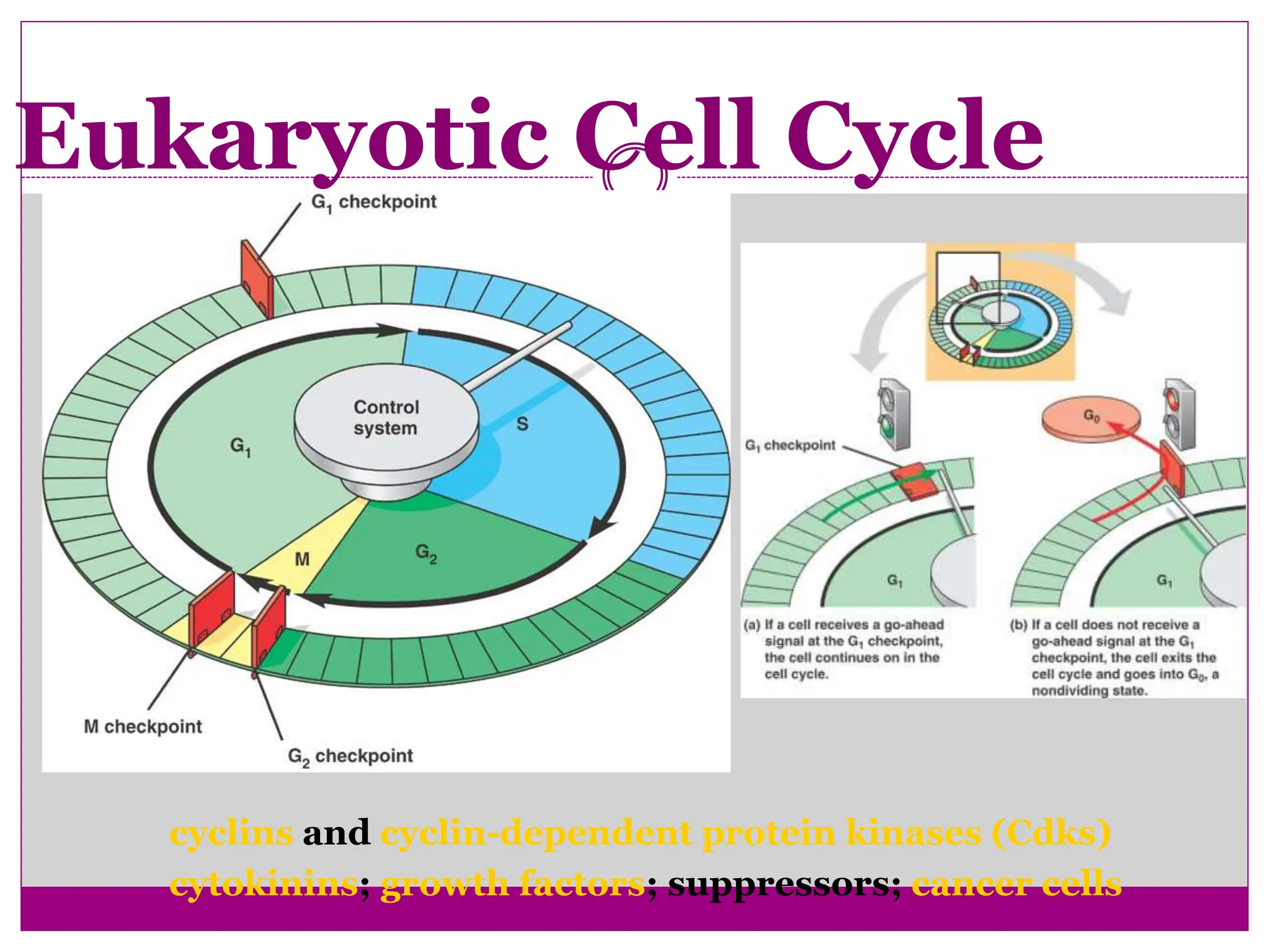
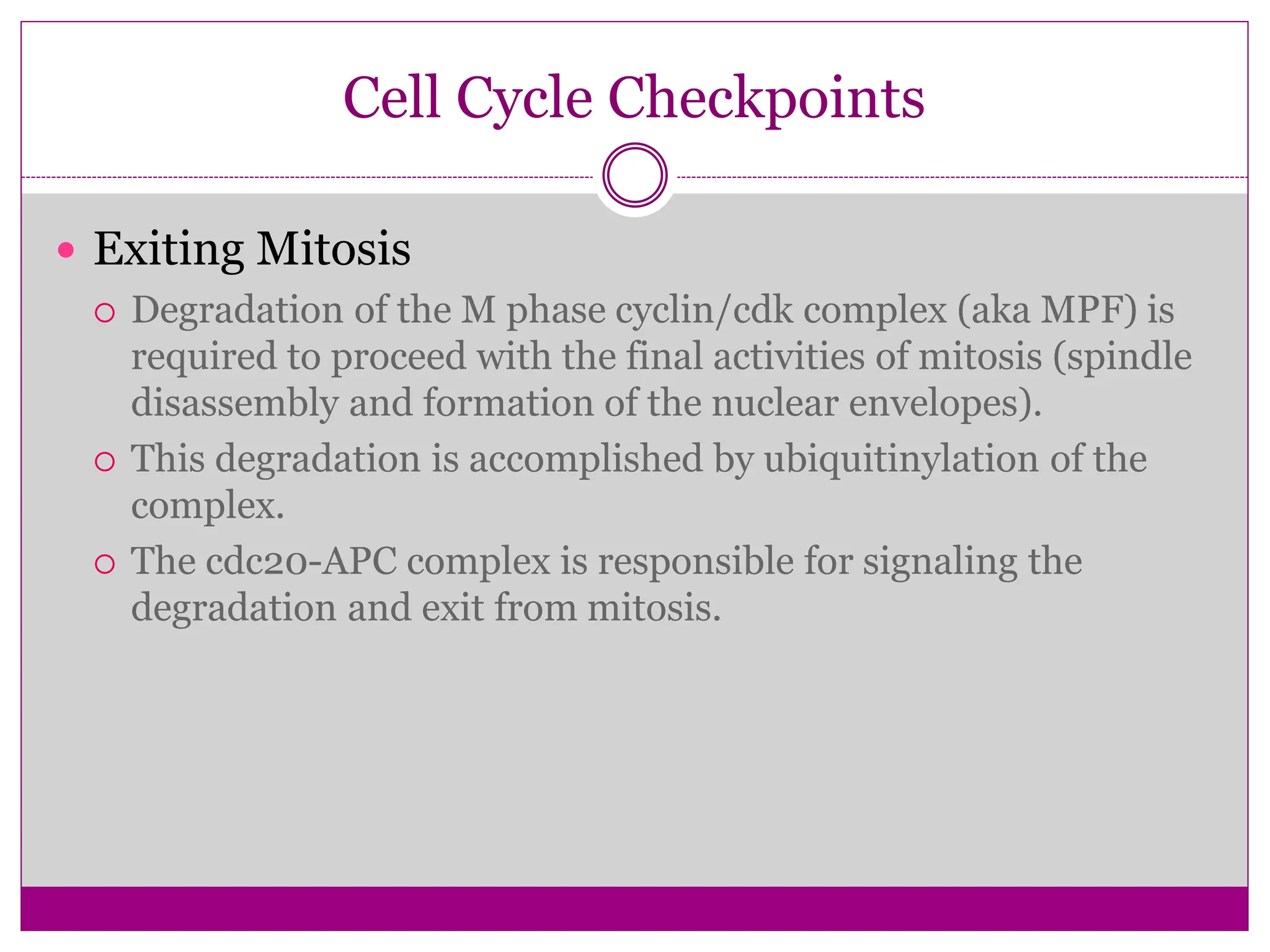
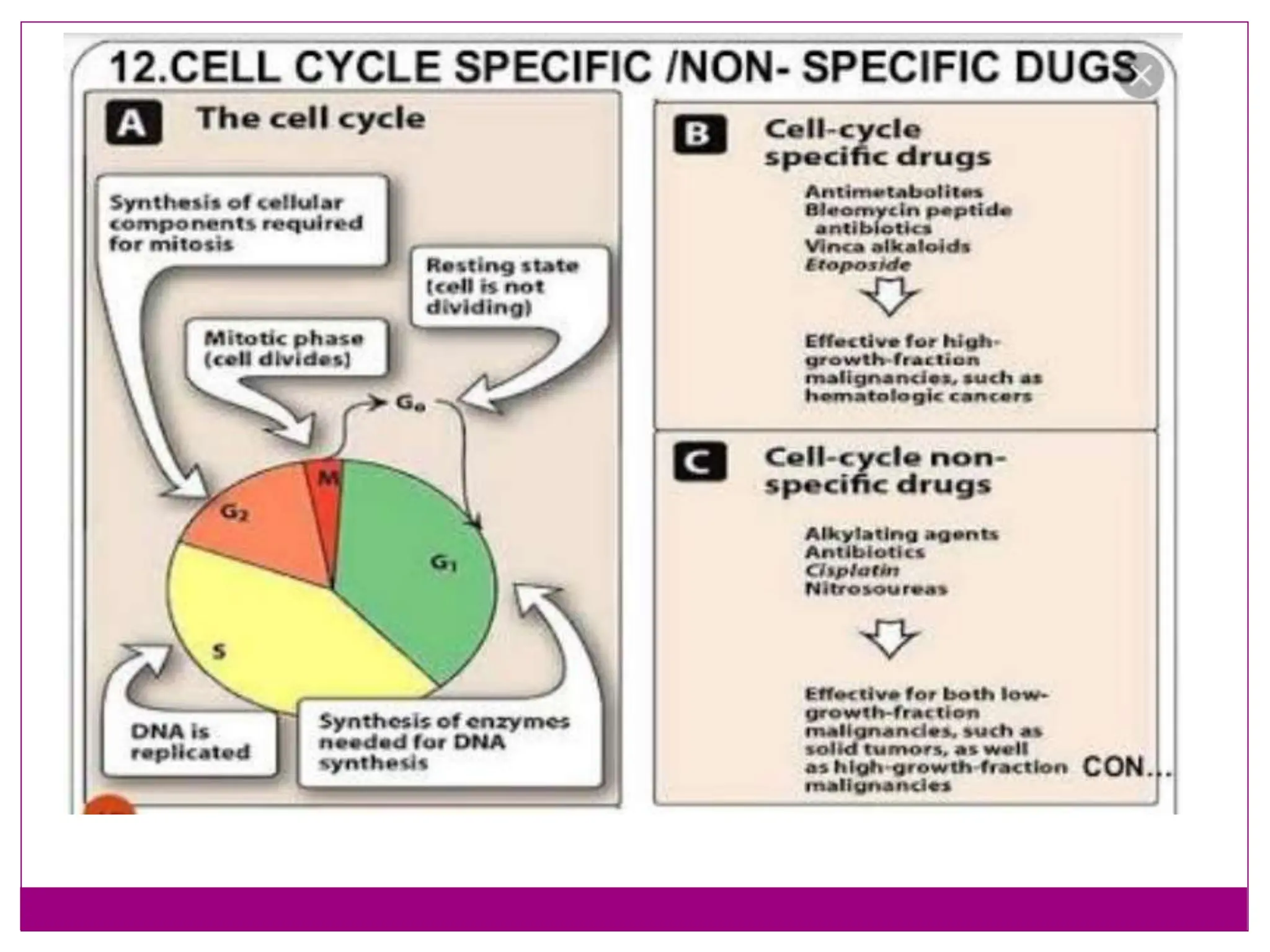
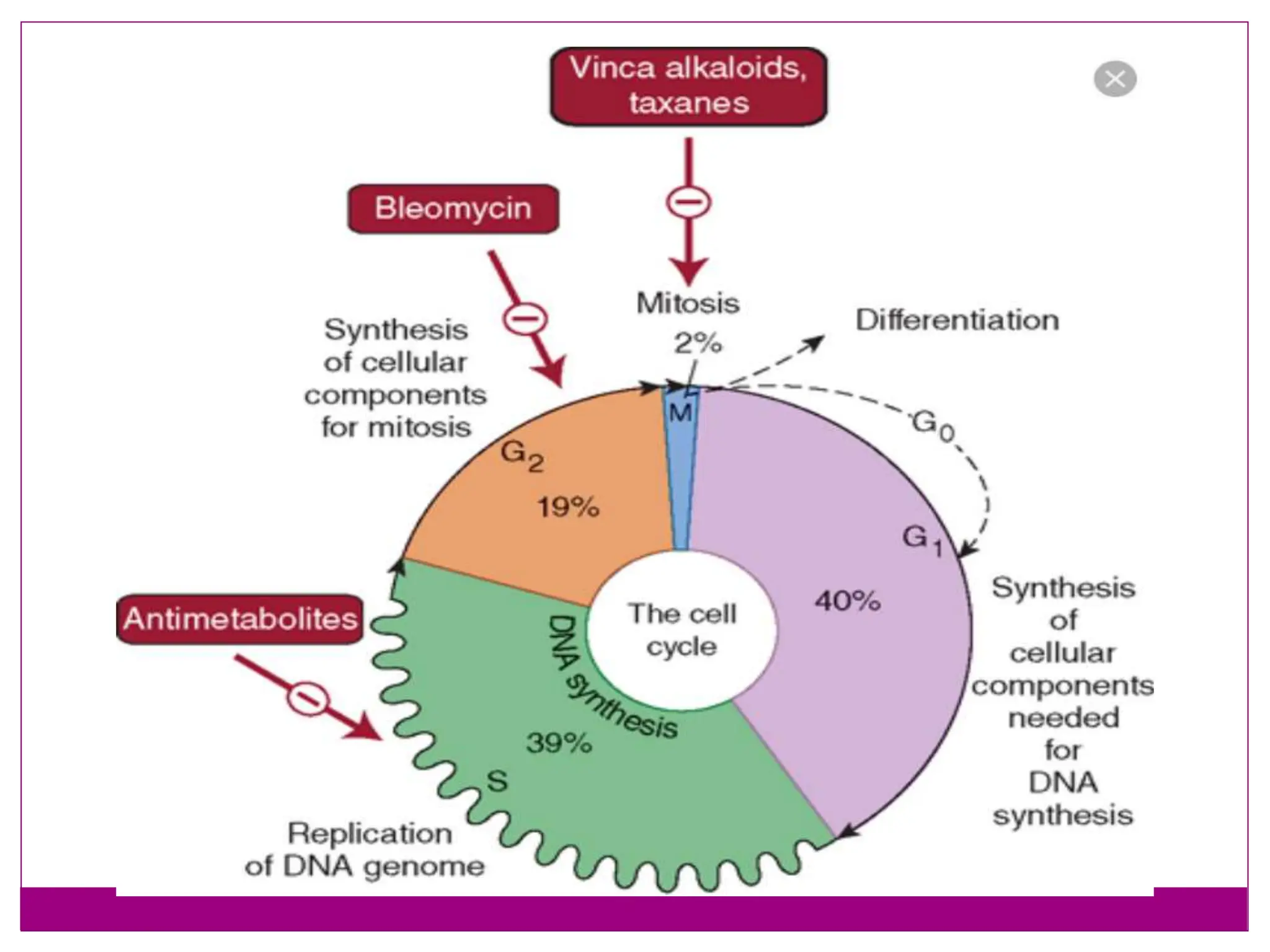
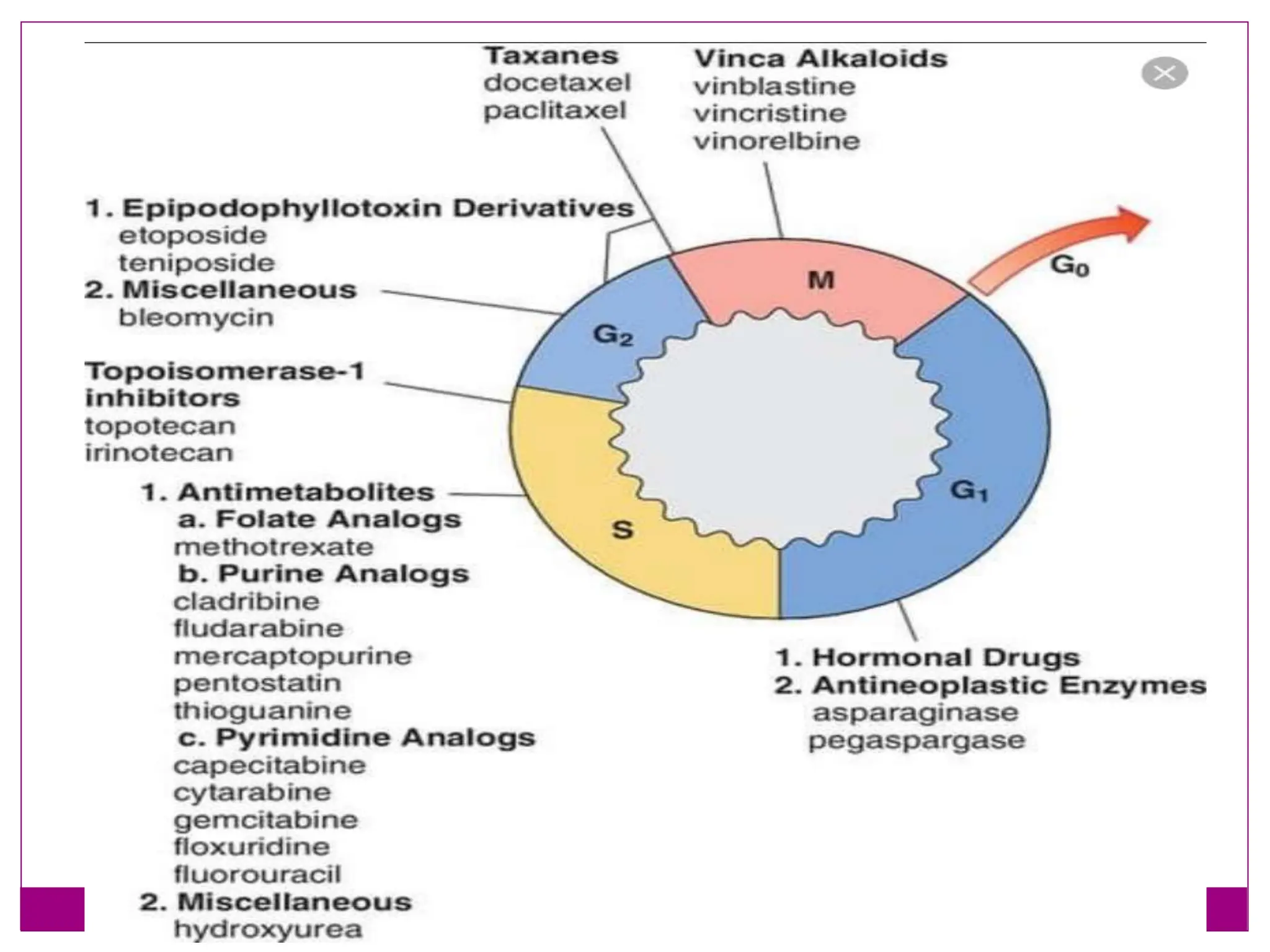
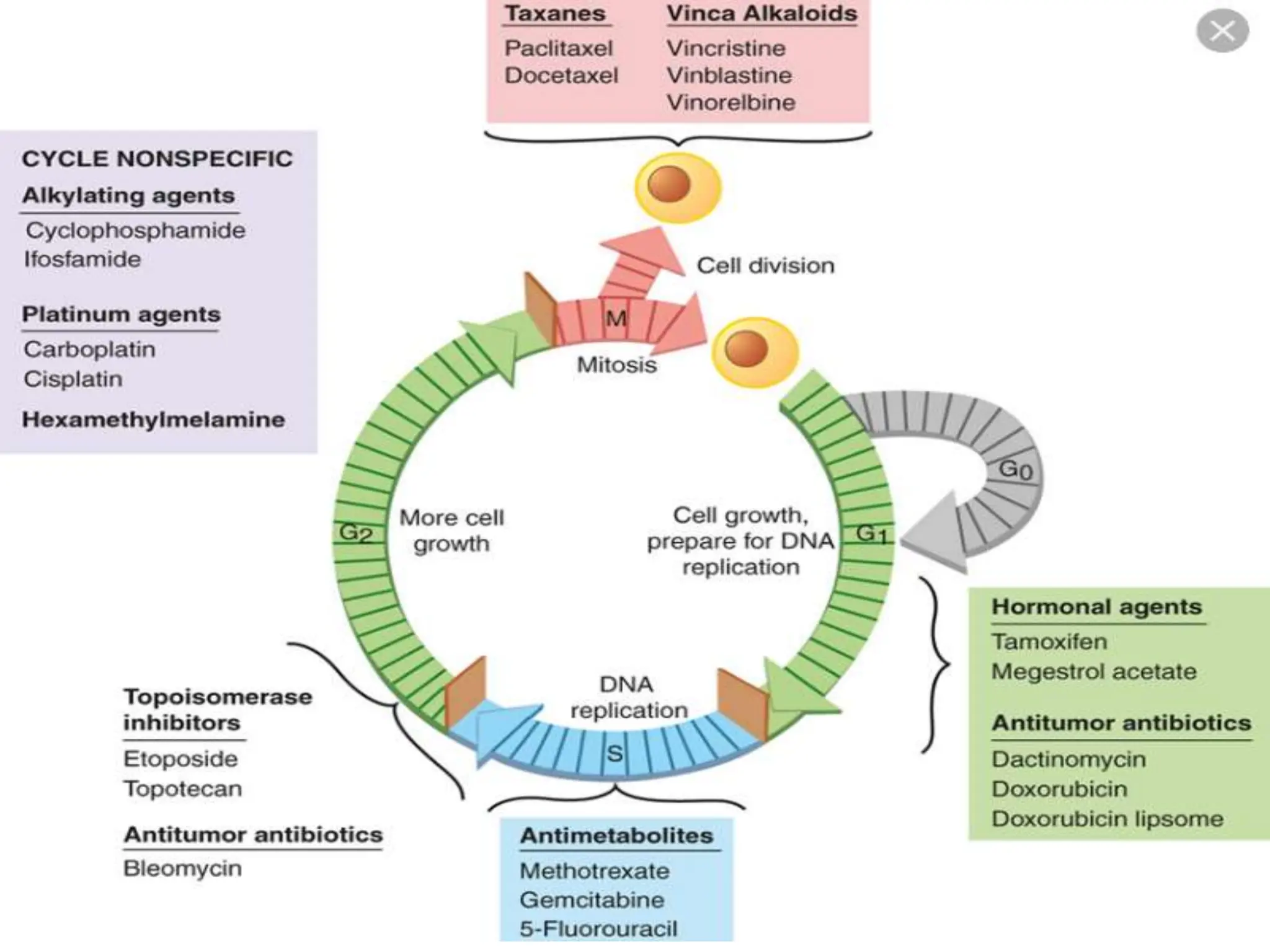
The cell cycle involves an ordered series of events that leads to cell division. It has two main functions: copying cellular components and DNA, and dividing the cell so components are distributed evenly in the daughter cells. The cell cycle consists of interphase, where the cell grows and duplicates its DNA, and M phase, where the cell divides. Interphase includes G1, S, and G2 phases, while M phase involves mitosis and cytokinesis. Checkpoints ensure the cell is ready to progress through the cycle. Deregulation of these checkpoints can lead to uncontrolled cell division and cancer.