Embed presentation
Downloaded 97 times

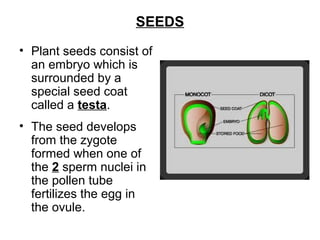

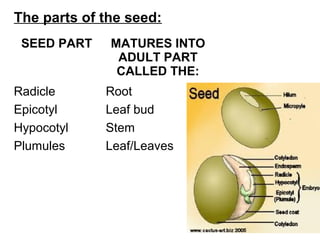

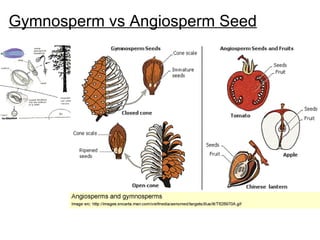
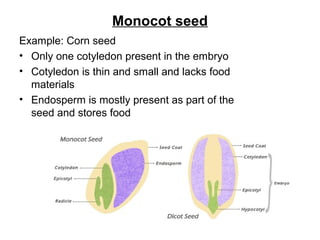
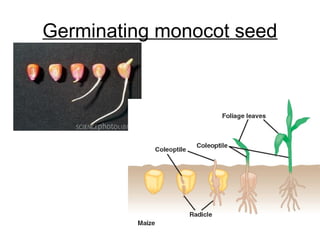
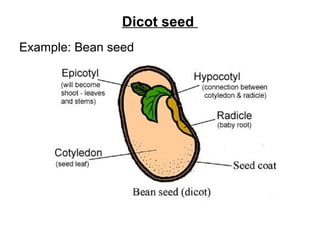
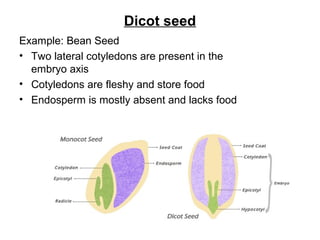
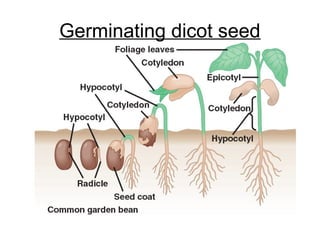
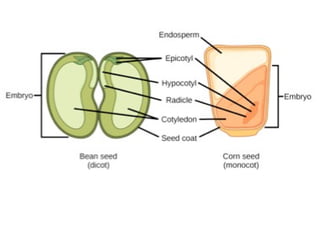
Seeds consist of an embryo surrounded by a protective seed coat. The seed develops from fertilization, with one sperm cell fusing with the egg to form a zygote. When conditions are right, the seed will germinate by breaking through the seed coat. Germination begins with the root emerging, followed by the shoot and stem. Seeds contain parts that will mature into the adult plant, such as the radicle developing into the root and hypocotyl into the stem. Angiosperm seeds are enclosed in fruits while gymnosperm seeds are bare. Monocot seeds have one thin cotyledon while dicot seeds have two fleshy cotyledons that store food.











