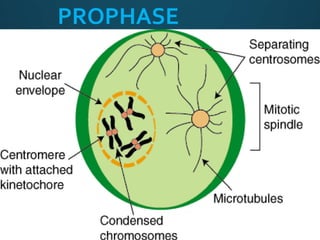
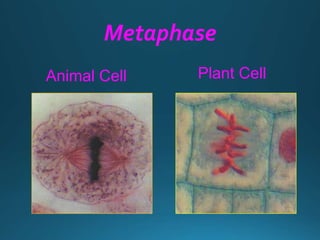
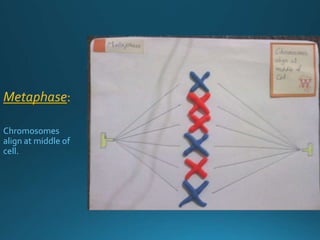
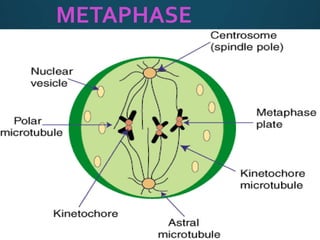
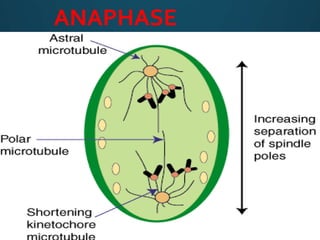
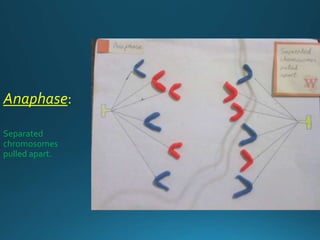
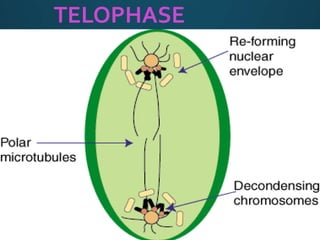
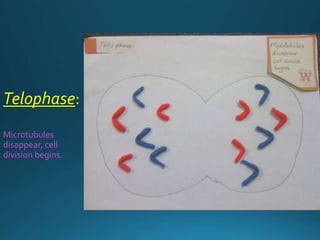
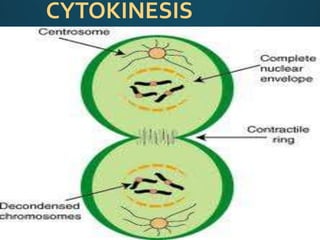
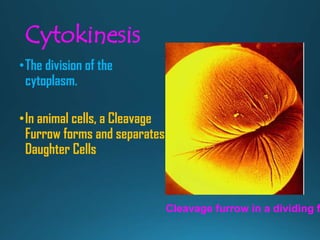
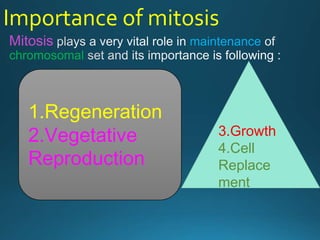
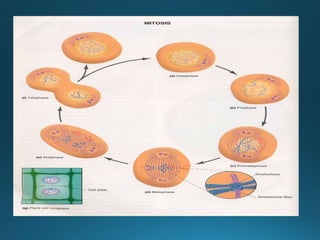
Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in two daughter cells with identical genetic material as the parent cell. It occurs in eukaryotic cells and has five stages: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During interphase the cell grows and duplicates its DNA. In prophase the chromosomes condense and become visible. Metaphase involves the chromosomes aligning at the center of the cell. Anaphase separates the sister chromatids so that each daughter cell receives one set. Telophase involves the division of the cytoplasm and formation of new cell membranes. Mitosis plays an important role in growth, regeneration, and cell replacement. Errors can result in genetic mutations.










![Reference list:
• Babbileo. (2013). [Online], Available at: http://www.slideshare.net/babbileo/mitosis-
21017634?qid=b3beeb2f-8051-4032-9655-
55f08e494357&v=default&b=&from_search=8 (Accessed 06 March 2014)
Charlie. (2013) . [Online], Available at:
http://www.slideshare.net/charlietheteacher/mitosis-ppt-27467916?qid=c96528ae-
3a55-47e7-bb09-fa9c5e784b45&v=qf1&b=&from_search=18
Kalember, J. (2014). [Online], Available at:
http://www.slideshare.net/MRKALEMBER/mitosis-30635784?qid=c96528ae-3a55-47e7-
bb09-fa9c5e784b45&v=qf1&b=&from_search=6 (Accessed 06 March 2014)
• Memon , N. (2012). [Online], Available at :
http://www.slideshare.net/NailaMemon/presentation1-11659810 (Accessed 03 March
2014)
• Dreyngerous . (2008). [Online], Available at:
http://www.slideshare.net/dreyngerous/mitosis-539875](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/profpresentationslidesahre-140310065718-phpapp02/85/MITOSIS-LIFE-SCIENCES-FOR-GRADE-10-S-24-320.jpg)