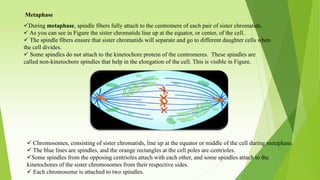
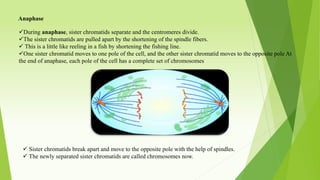
The document provides information about mitosis cell division. It begins by defining the cell and cell cycle. It then describes the stages of mitosis in order - interphase consisting of G1, S, and G2 phases, followed by the M phase including prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. It explains the key events that occur during each phase, such as chromosome condensation and separation. It also discusses cytokinesis and the importance of mitosis in growth, repair, asexual reproduction and maintaining genetic stability.