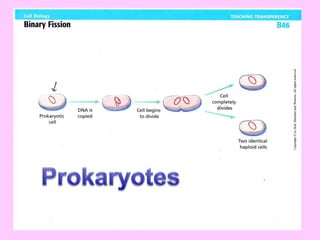
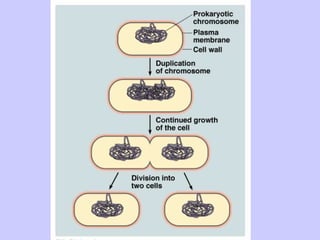
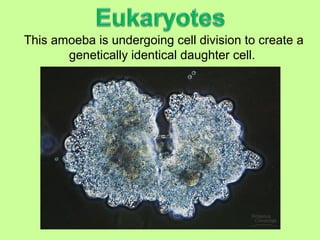
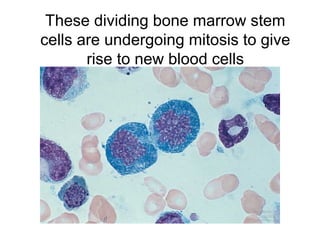
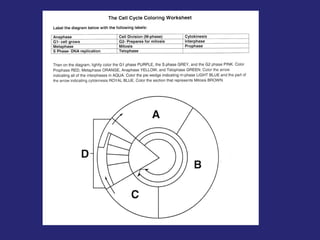
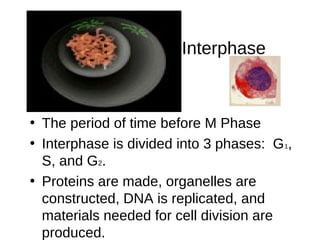
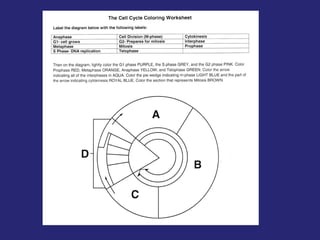
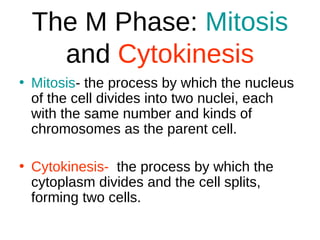
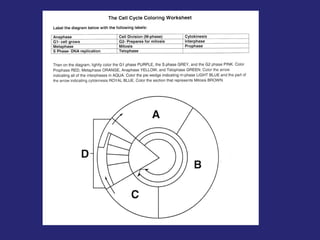
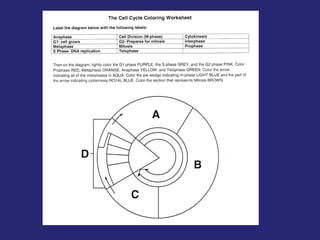
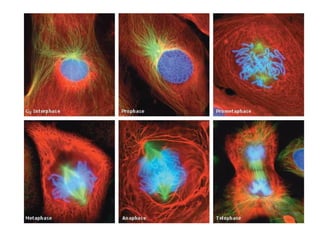
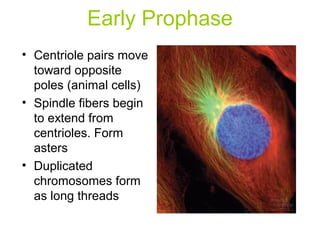
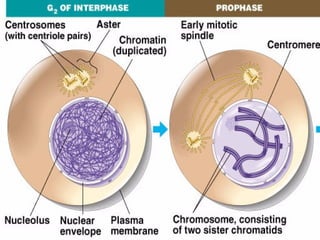
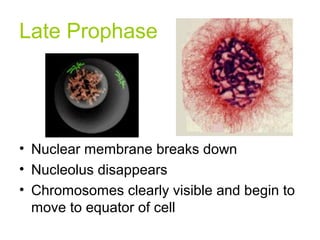
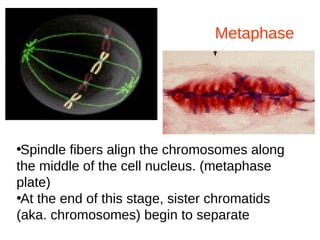
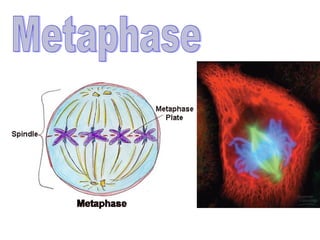
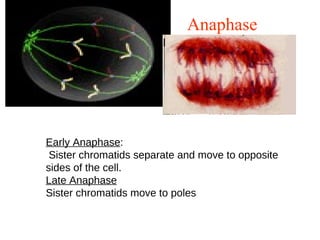
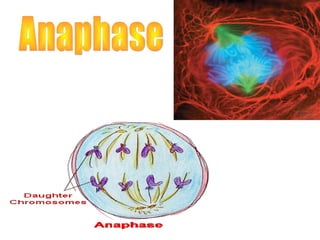
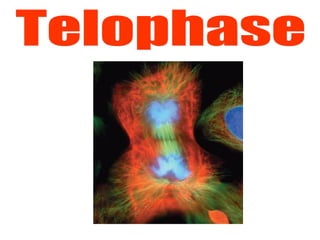
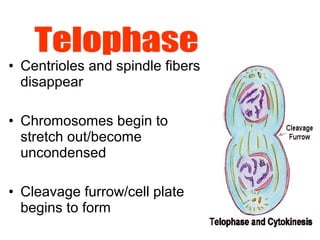
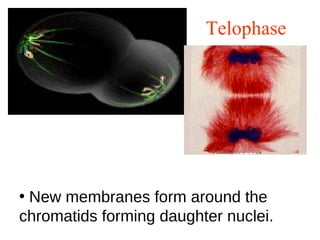
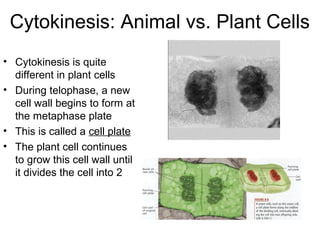
The document discusses the cell cycle and cell reproduction. It describes the main stages as interphase, where the cell grows and prepares for division, and the M phase where the nucleus and cell divide. Interphase includes the G1, S, and G2 phases where the cell makes proteins, organelles and replicates DNA. The M phase consists of mitosis, where the nucleus divides, and cytokinesis, where the cell splits into two. Mitosis is further broken down into the prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase stages where the chromosomes align and separate. Cytokinesis differs in animal and plant cells in how the cell membrane pinches or a cell plate forms to divide the cell. The result of