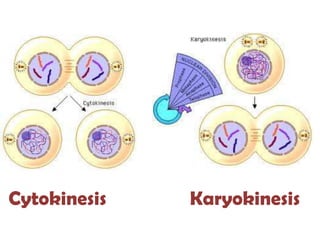
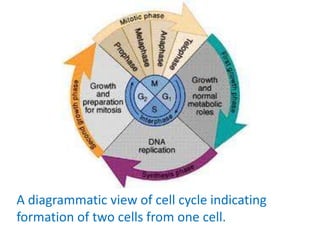
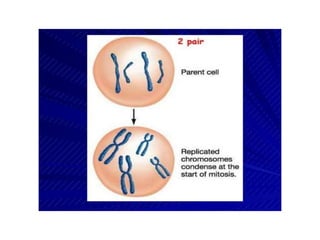
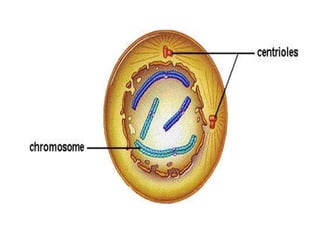
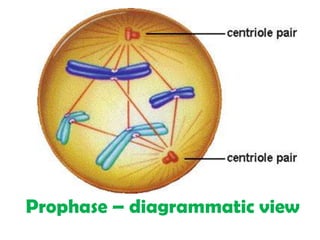
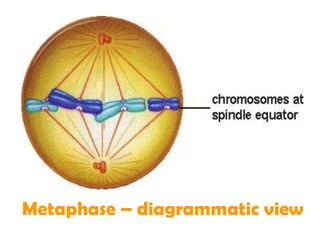
The document outlines the cell cycle, detailing the processes of DNA replication, cell growth, and division into daughter cells, which occur in a coordinated manner under genetic control. It describes the two main phases of the cell cycle: the M phase (mitosis) and interphase, which is further divided into G1, S (DNA synthesis), and G2 phases, along with key processes such as karyokinesis and cytokinesis. Additionally, it mentions variations in cell division rates among different organisms and specific stages of mitosis.