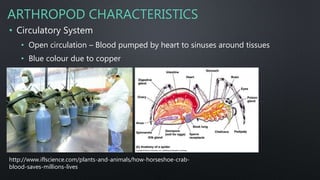
Phylum Arthropoda includes insects, crustaceans, arachnids and makes up over 82% of all living things. They are characterized by having a segmented body, jointed appendages, and an exoskeleton made of chitin. Arthropods have a head with sensory organs and mouthparts, a thorax for appendage attachment, and some have an abdomen. Their exoskeleton provides protection but limits growth, requiring molting. They are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, and have open circulatory, digestive and nervous systems adapted for their habitat.