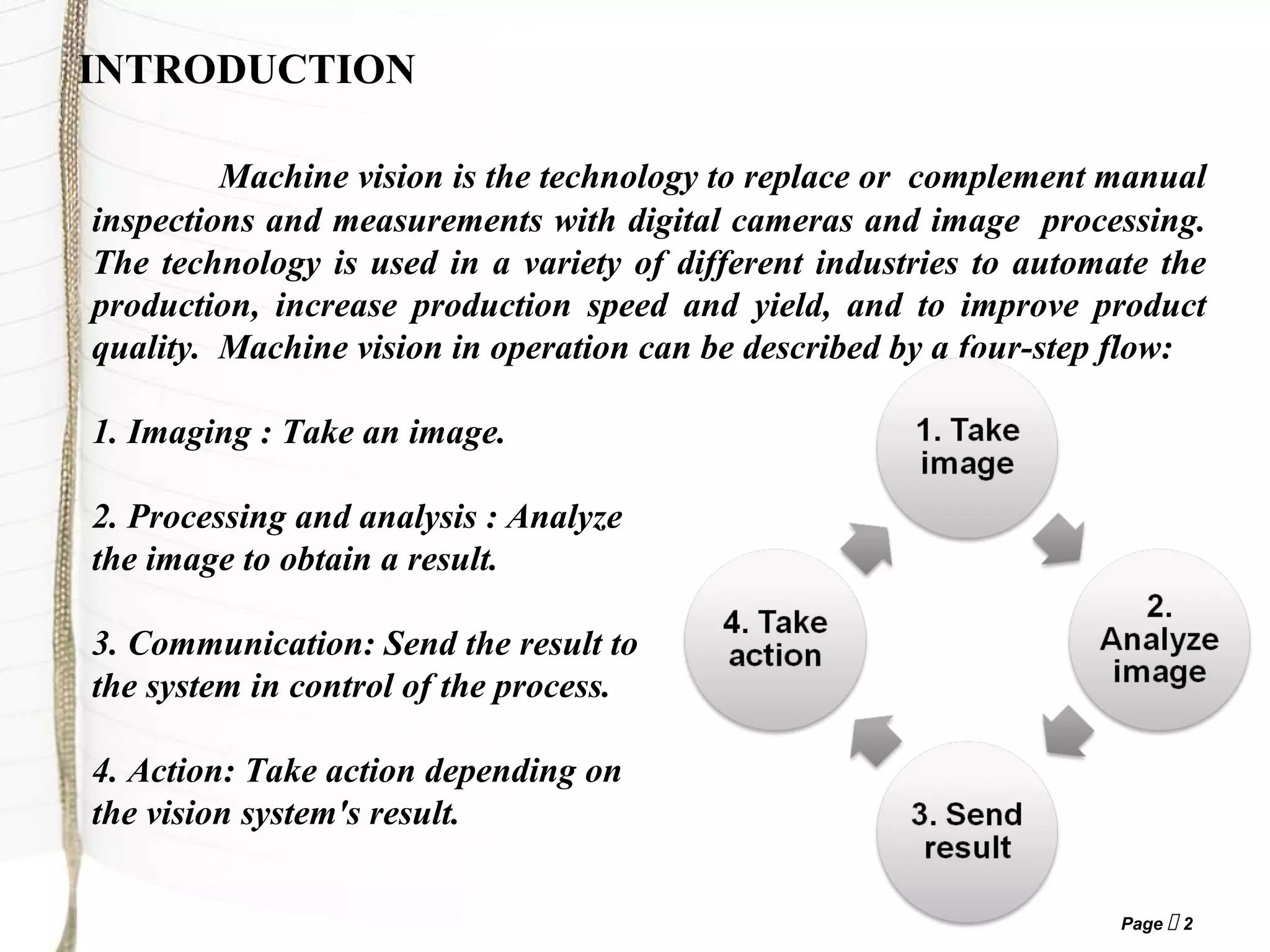
1) Machine vision uses digital cameras and image processing to automate production processes and quality inspections by replacing manual methods.
2) A machine vision system involves four steps: imaging, image processing/analysis, communicating results to the control system, and taking appropriate action.
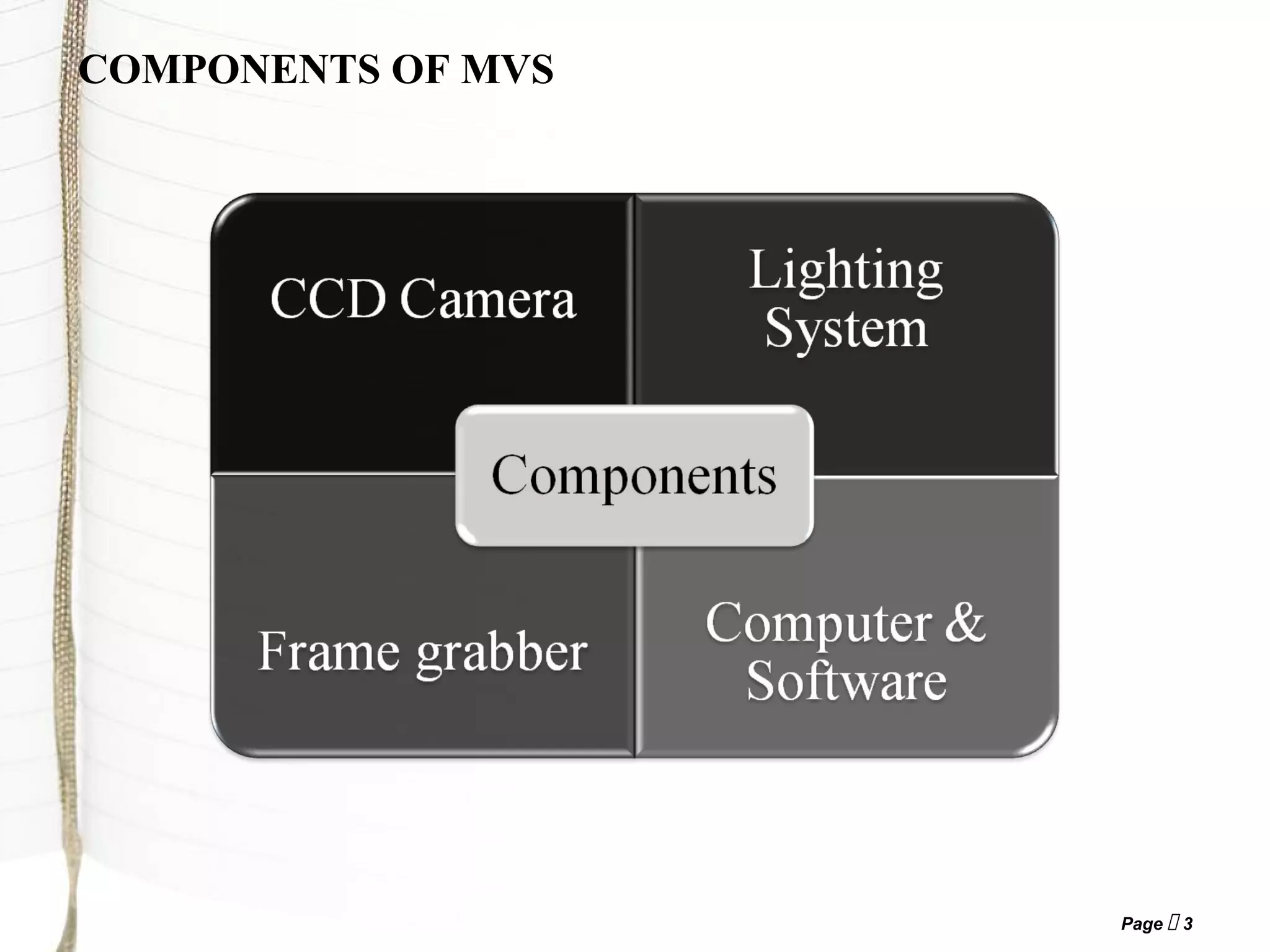
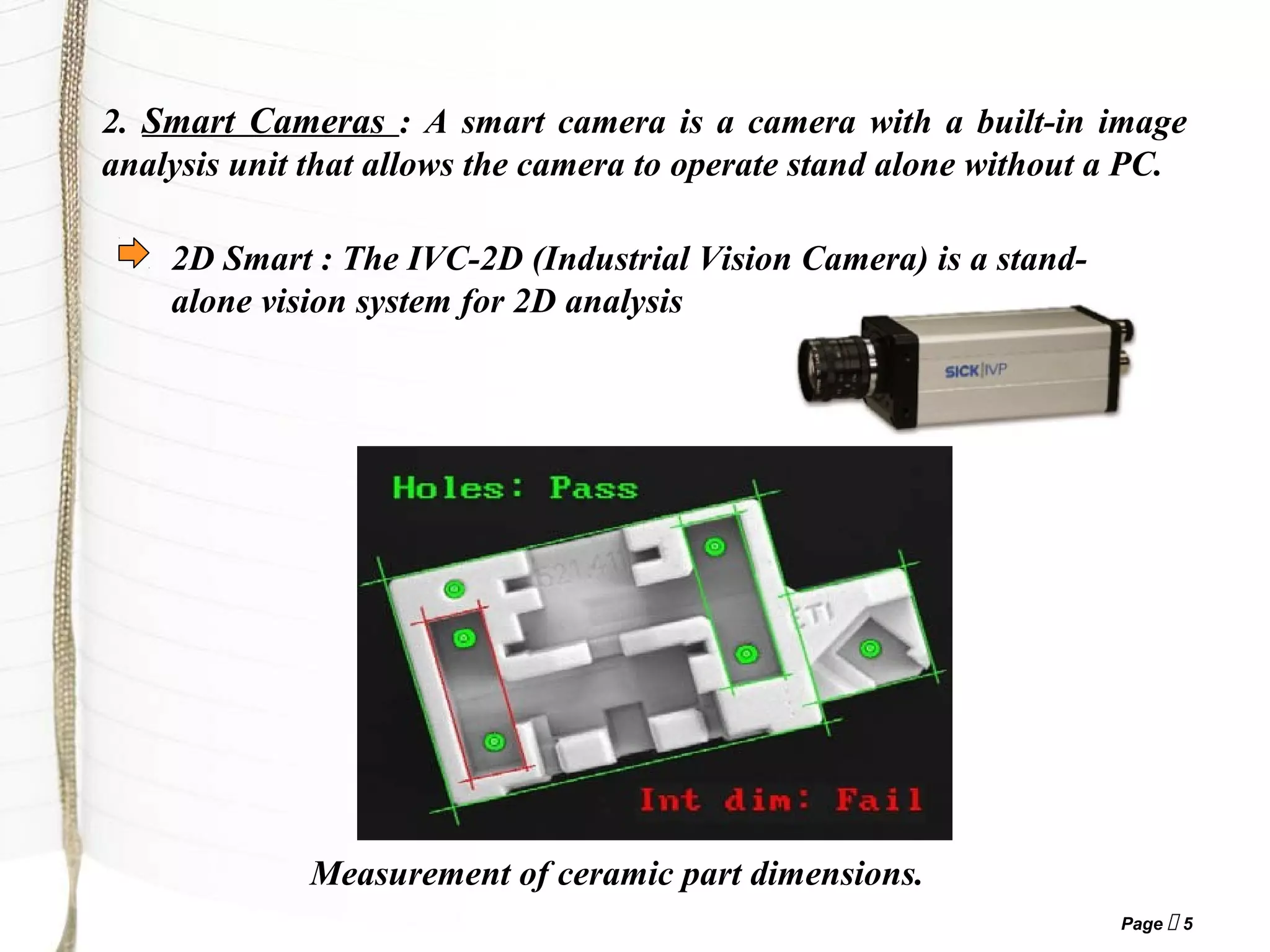
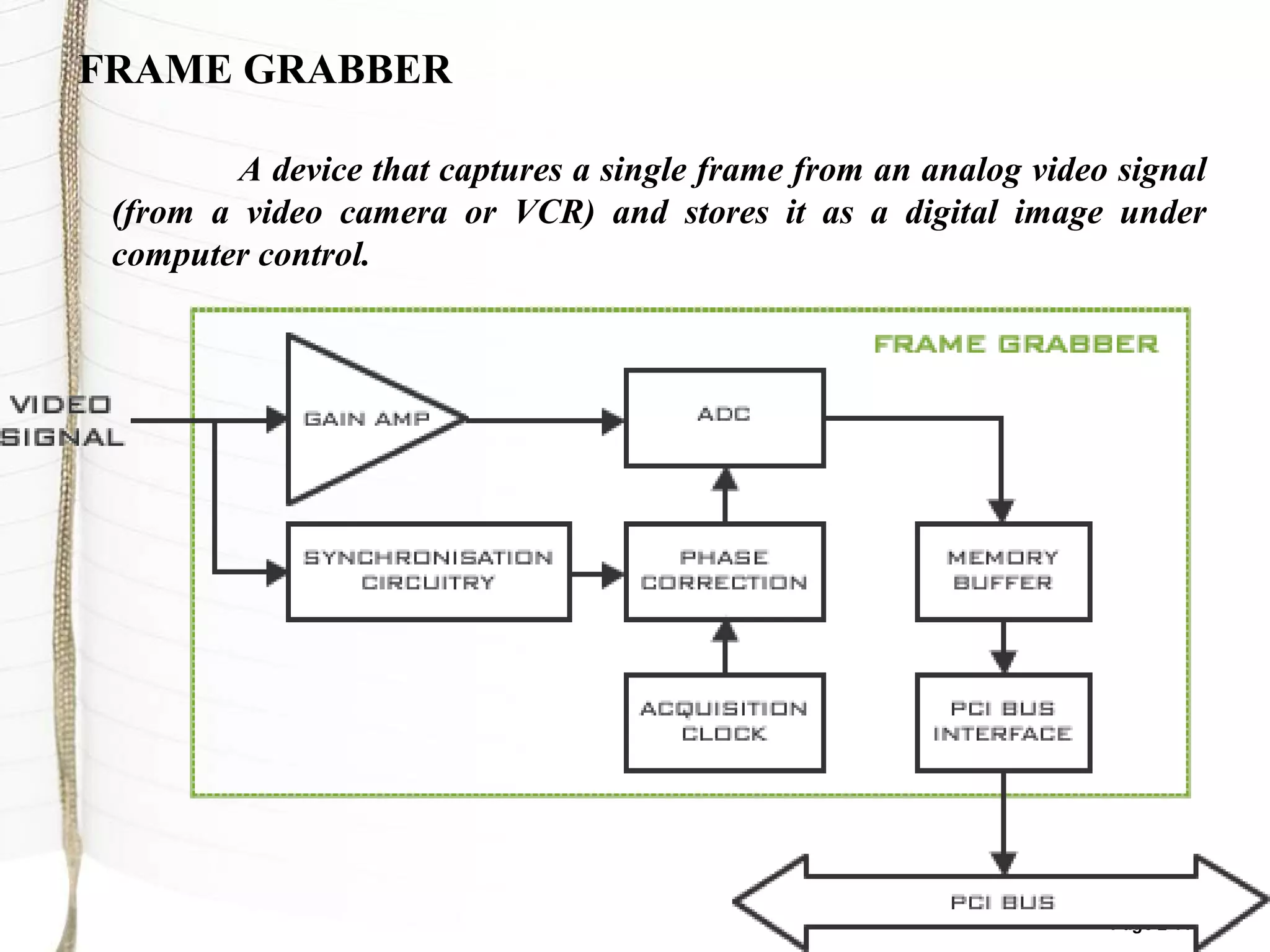
3) The main components of a machine vision system are cameras, lighting systems, frame grabbers, and computer/software to process images and analyze results.