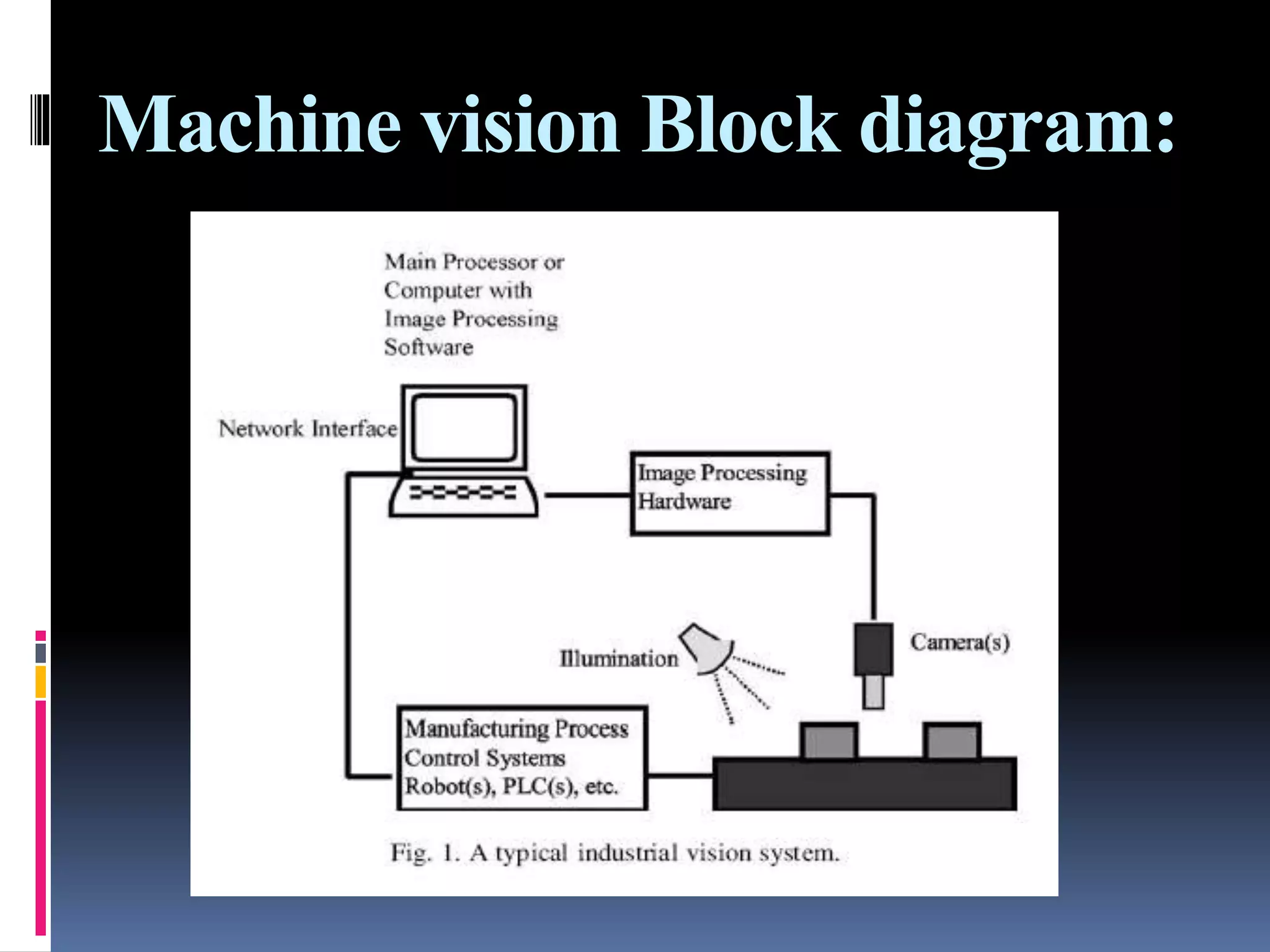
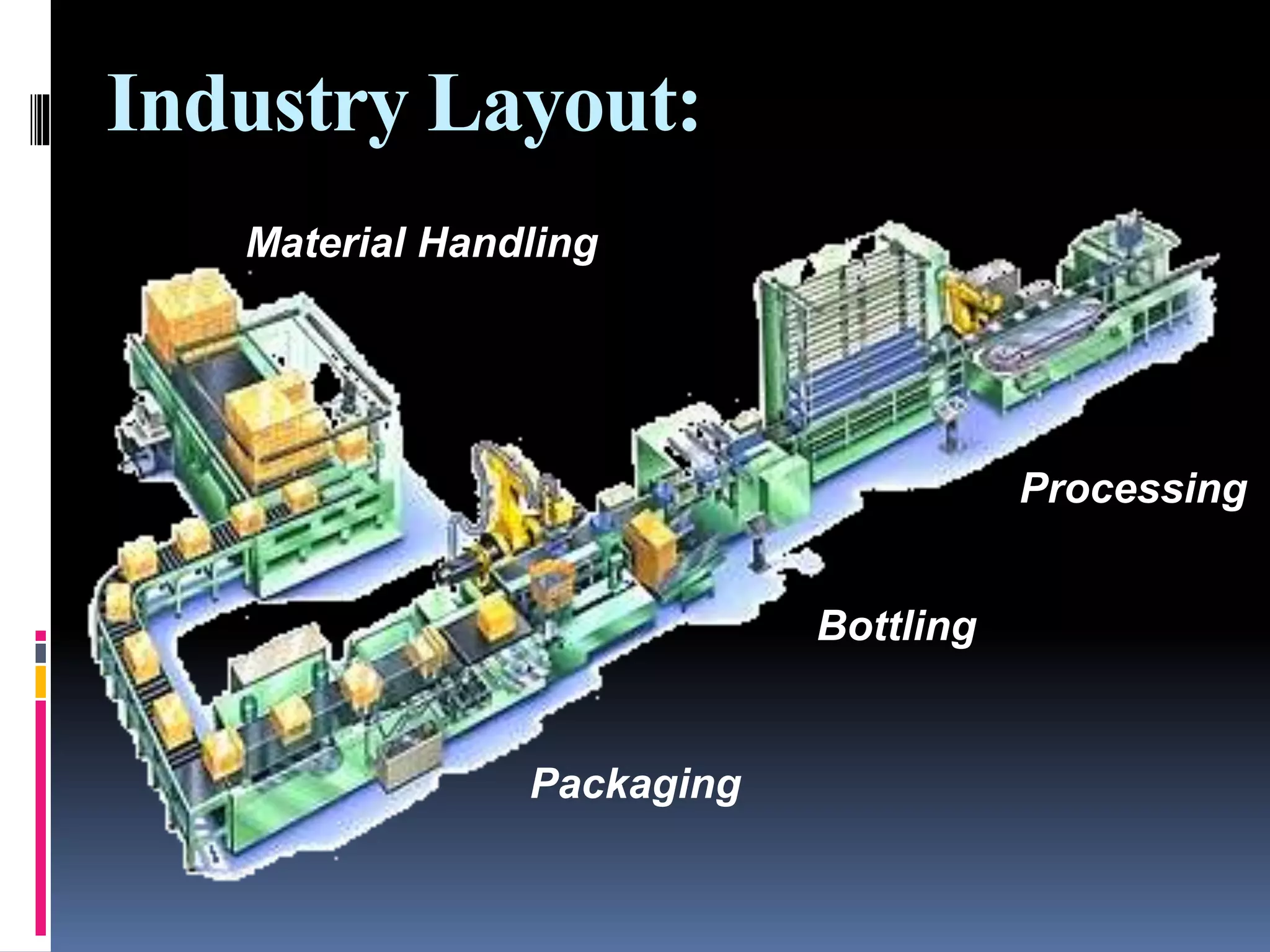
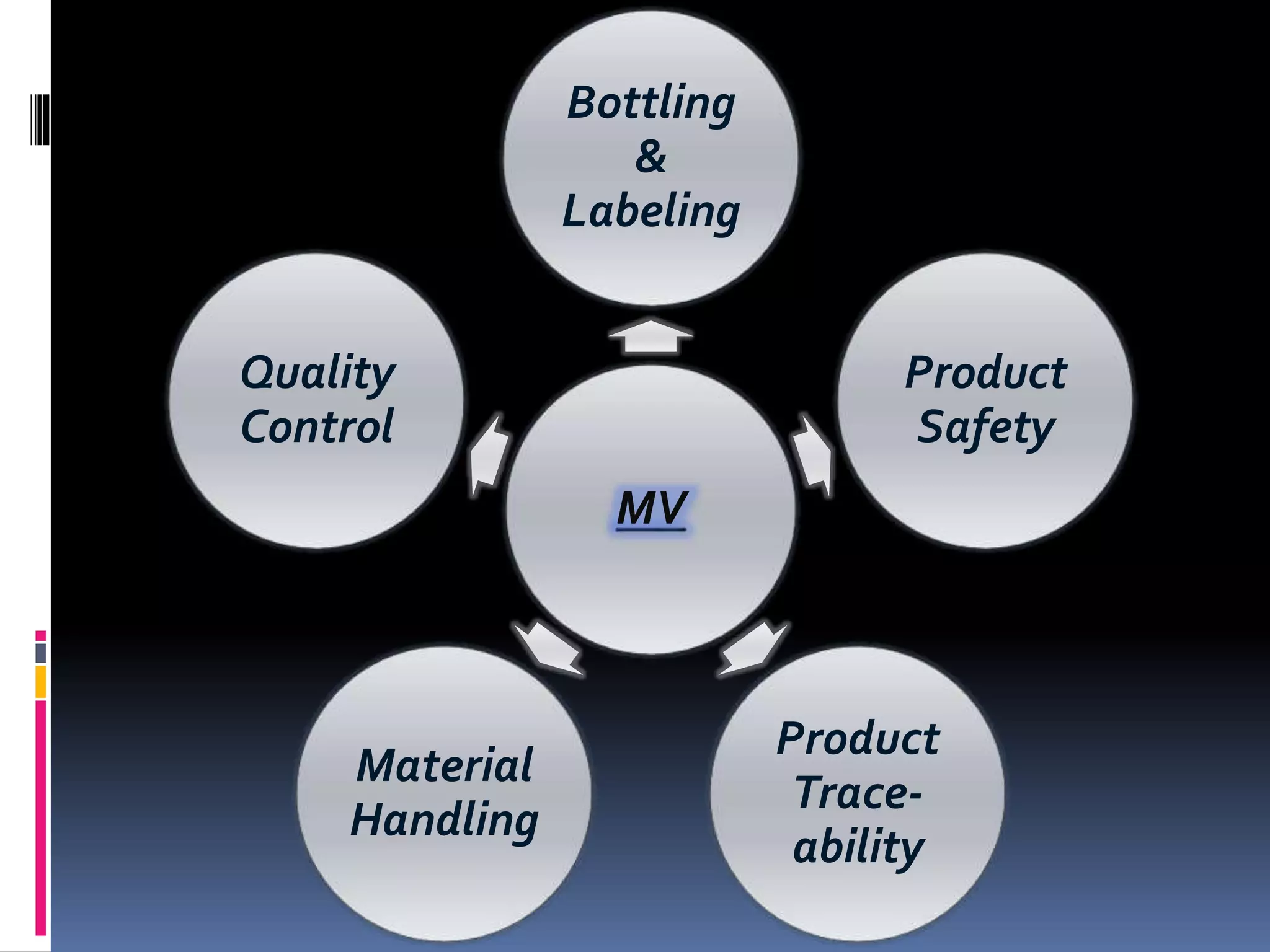
The document provides an overview of machine vision systems, detailing their components, such as image acquisition cameras and lighting techniques, as well as the steps involved in part inspection. It discusses various applications of machine vision in food and beverage industries, including quality control, bottling, labeling, and product safety. Additionally, it highlights the advantages of implementing machine vision systems, such as reduced costs, increased productivity, and improved customer satisfaction.