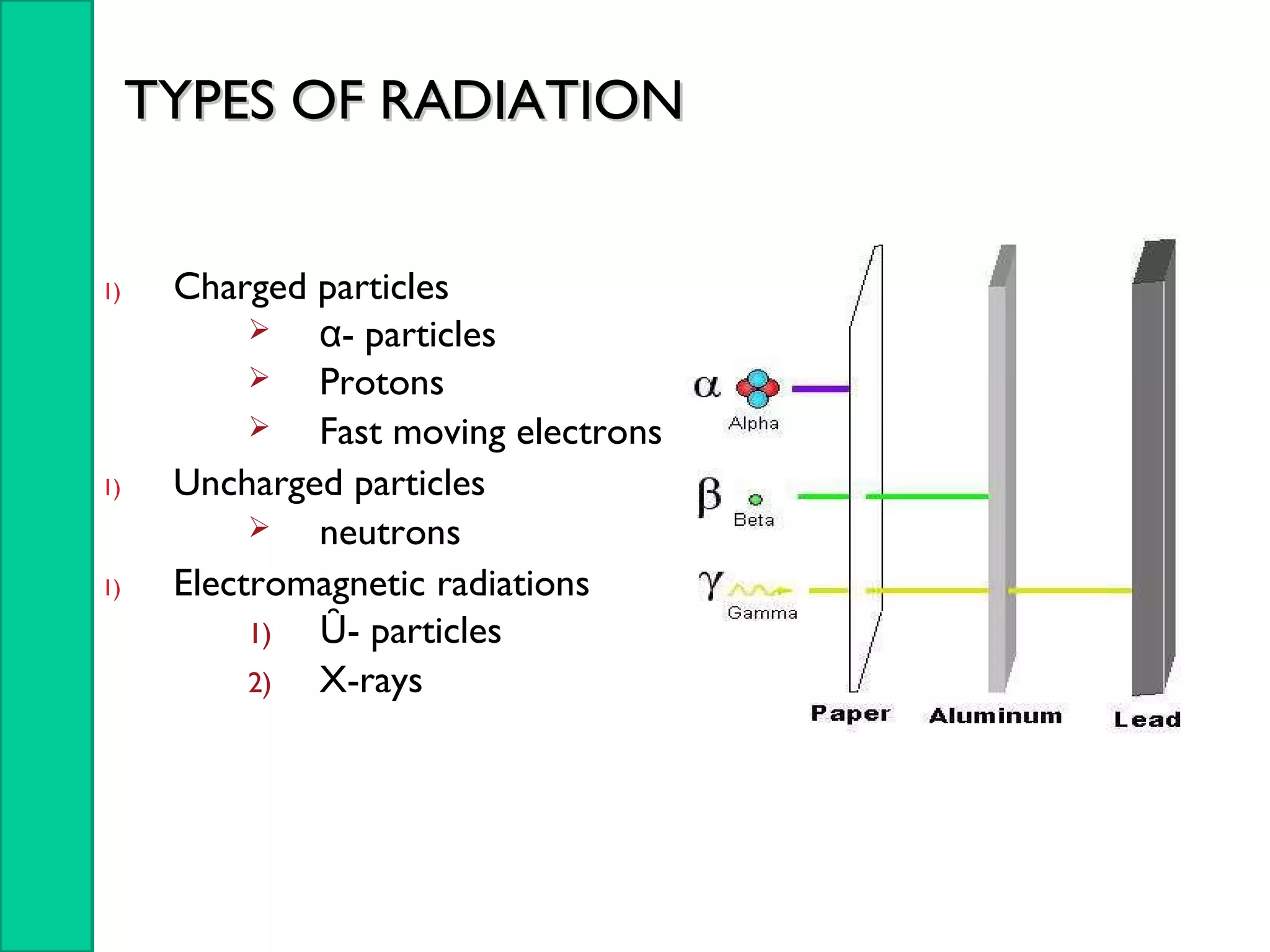
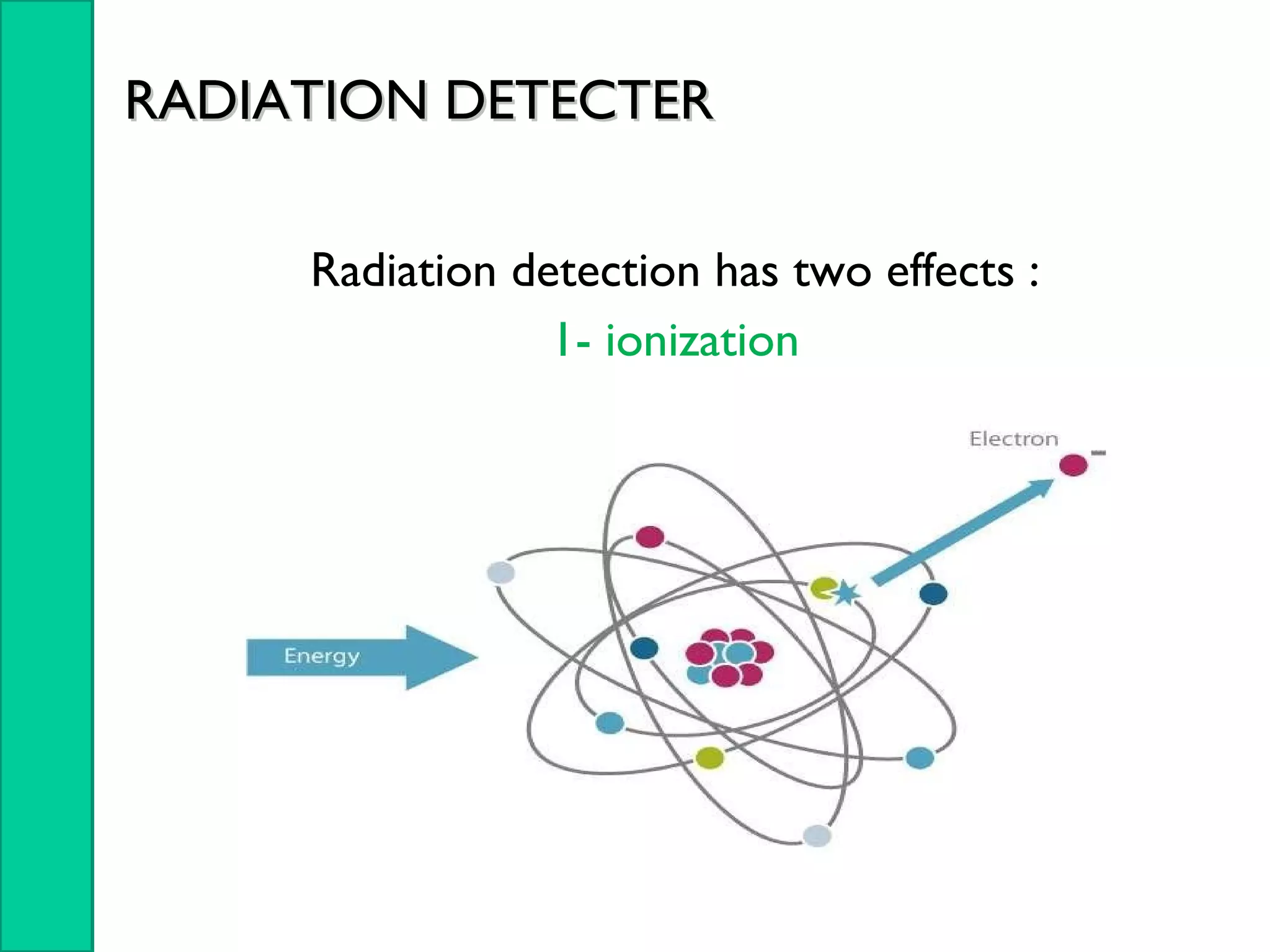
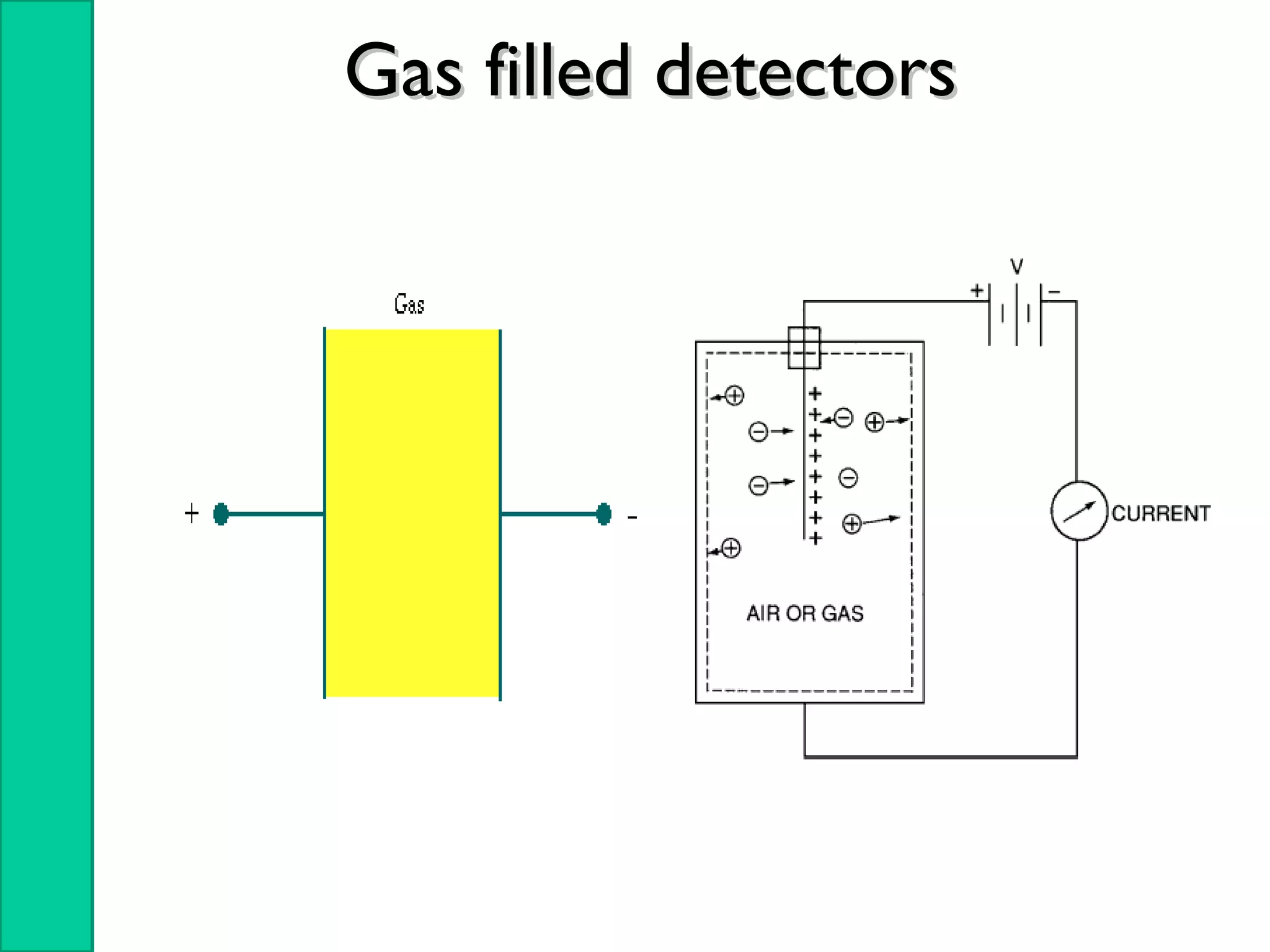
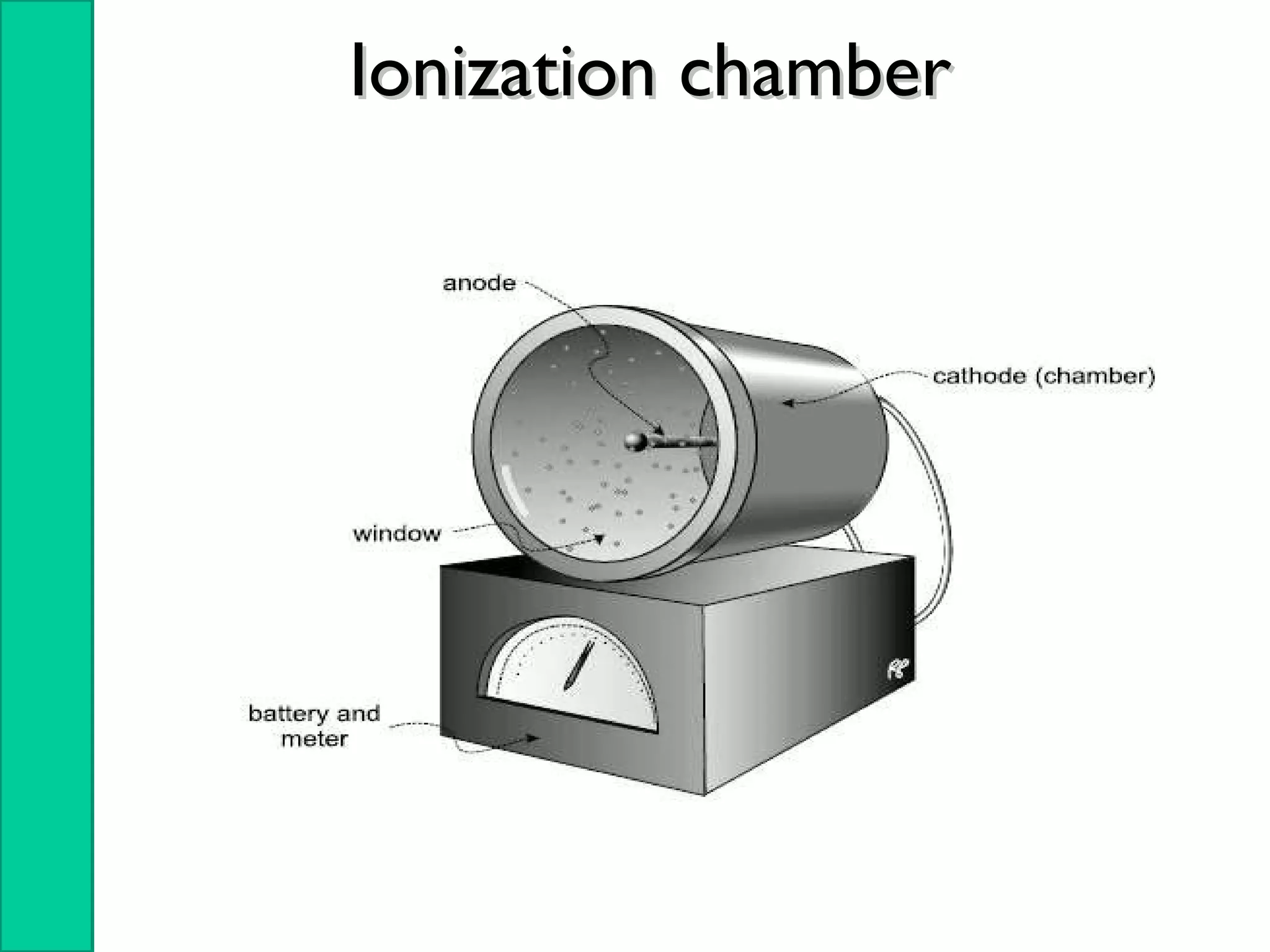
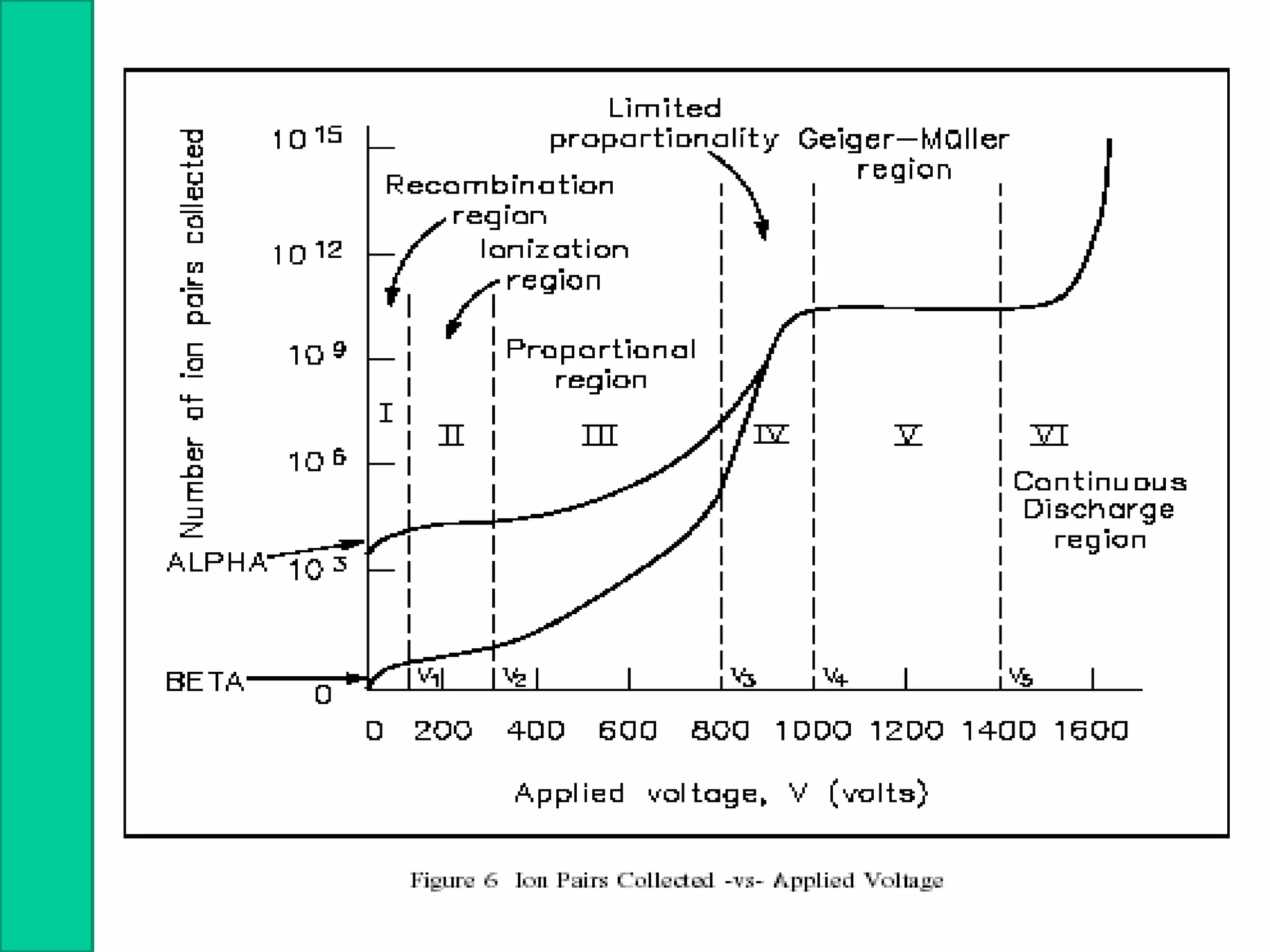
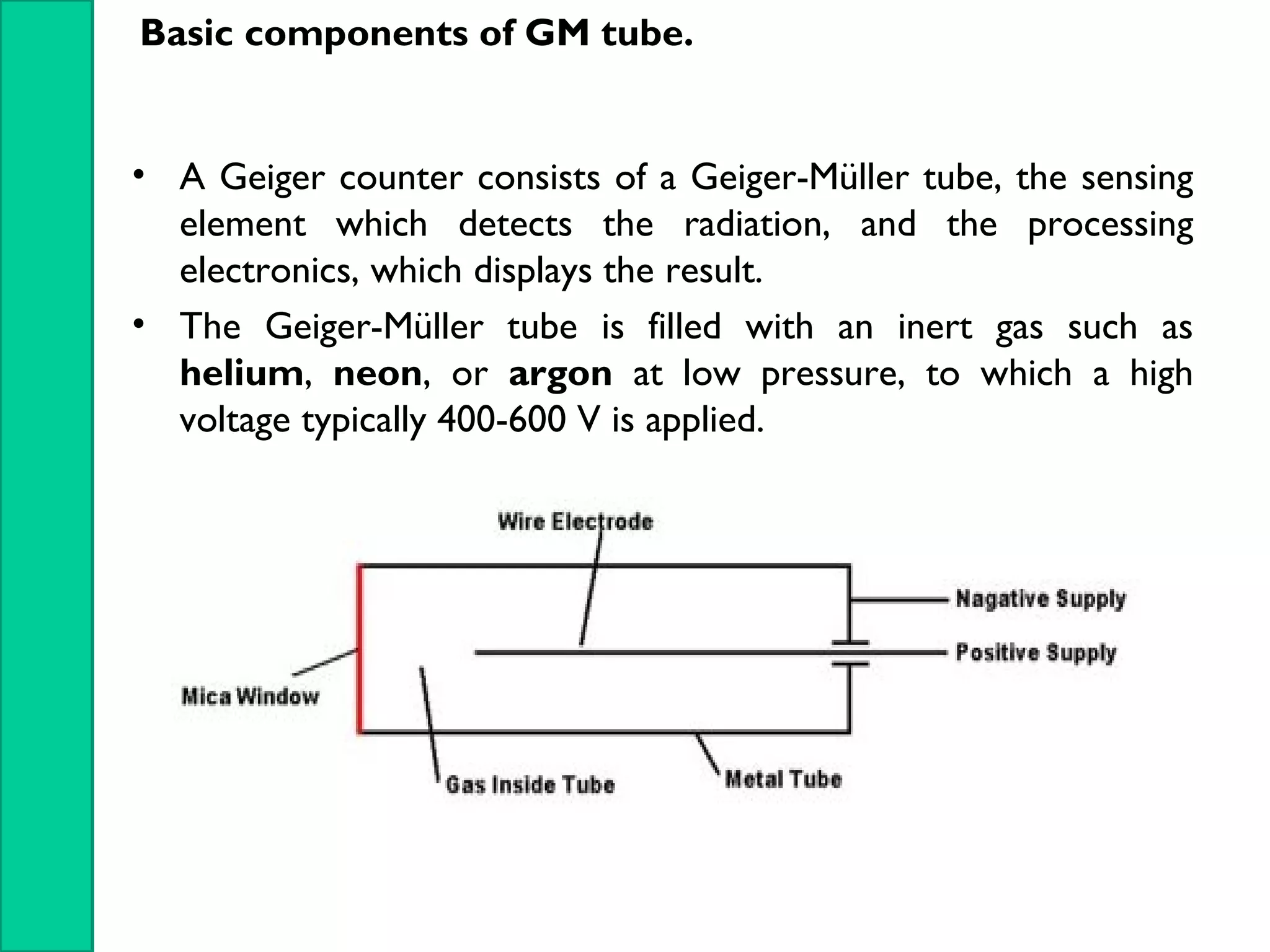
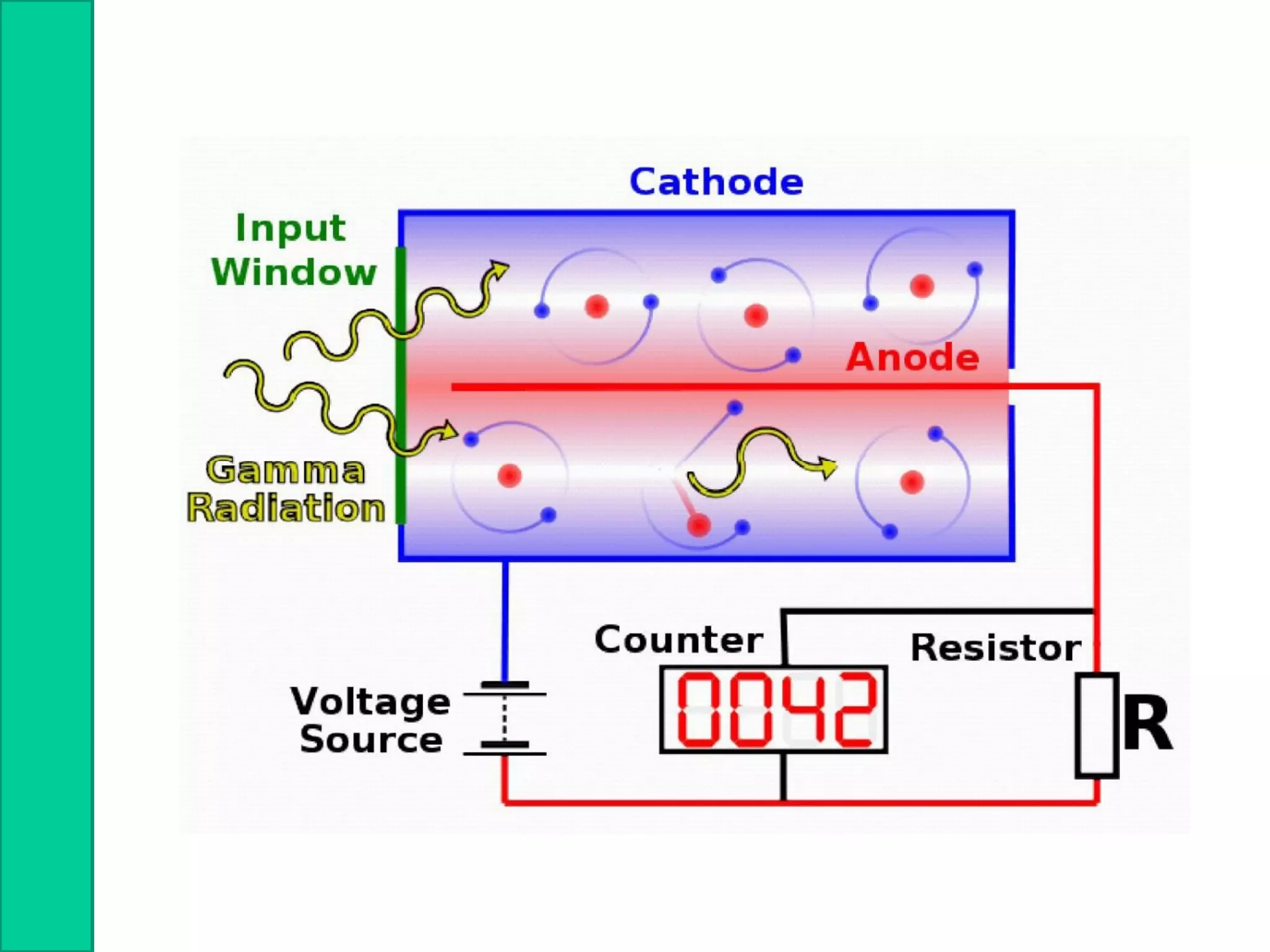
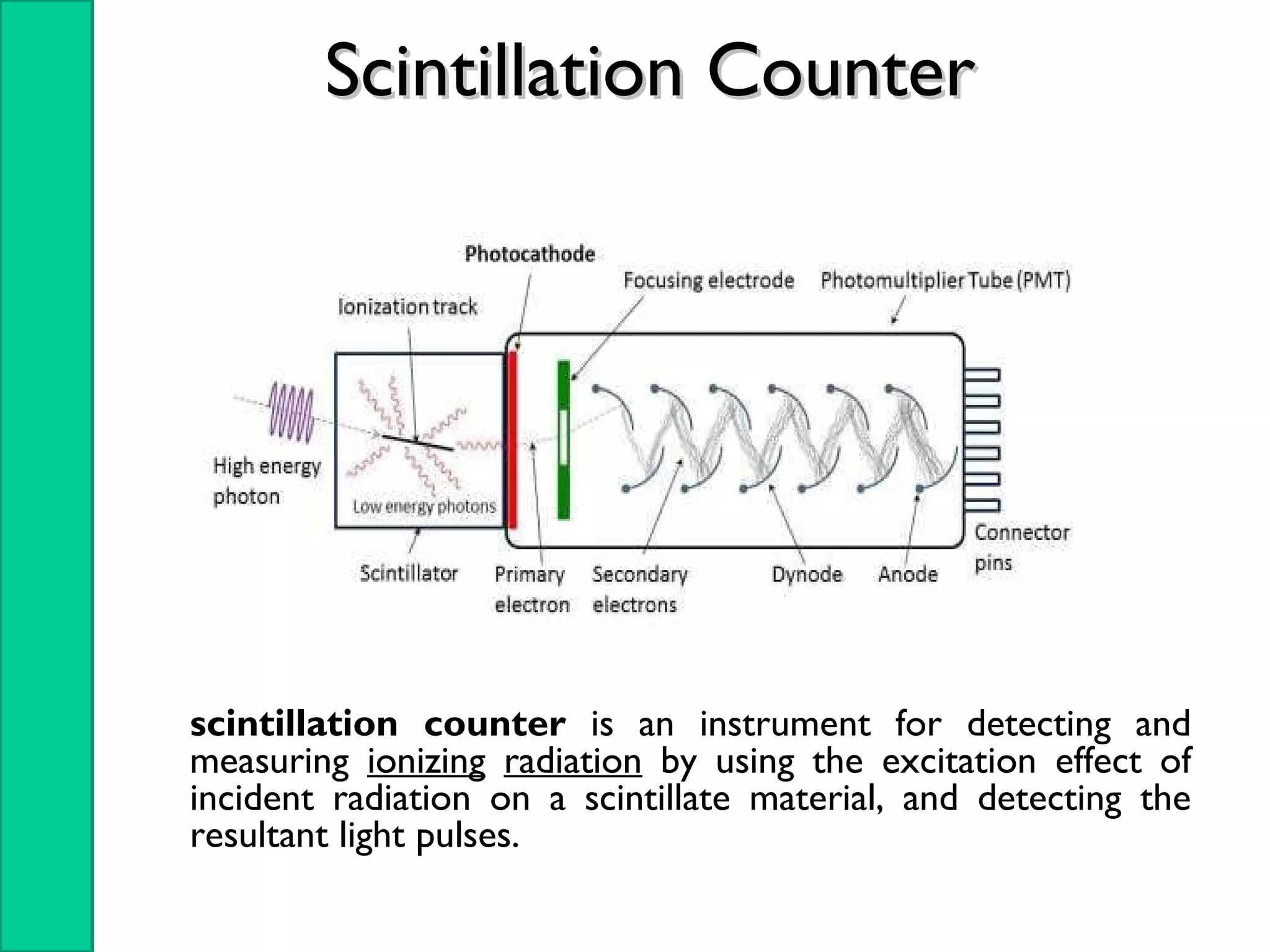
Nuclear radiation detectors function by detecting nuclear particles or radiation using two main principles: ionization and excitation of atoms. There are two main types of radiation detectors: gas-filled detectors like ionization chambers which measure ionization produced in a gas, and scintillation counters which use a scintillator material to produce light pulses from incident radiation that are then converted to electrical signals. Common radiation detectors include Geiger-Muller tubes, which use a gas-filled tube and high voltage to produce a cascade of ion pairs to detect radiation, and scintillation counters, which use a scintillator and photomultiplier tube to convert radiation interactions into light and then an electrical signal.