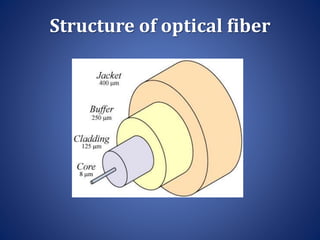
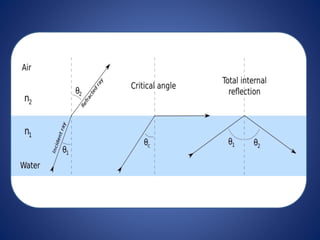
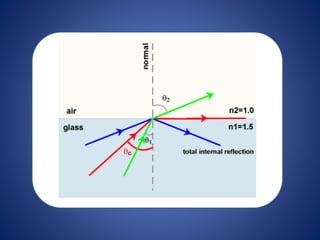
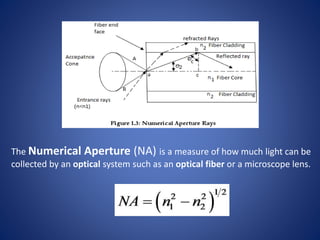
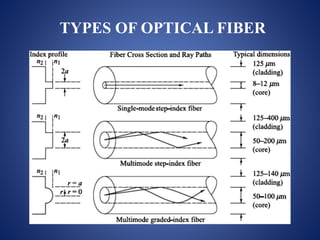
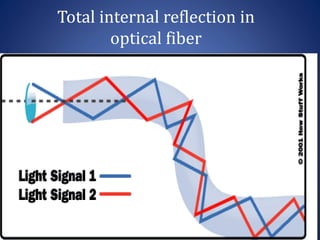
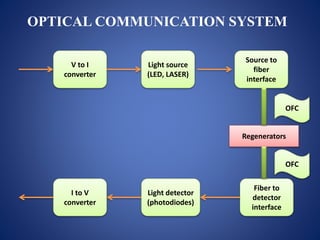
This document discusses optical fibers, including their structure, working principles, types, and applications. An optical fiber consists of a core made of glass or plastic surrounded by a cladding and jacket. Total internal reflection guides light through the fiber due to the difference in refractive index between the core and cladding. Optical fibers have advantages over copper wires like lower attenuation, immunity to EMI, and security. Their main applications are in telecommunications, broadband, and other fields requiring high-speed data transmission over long distances.