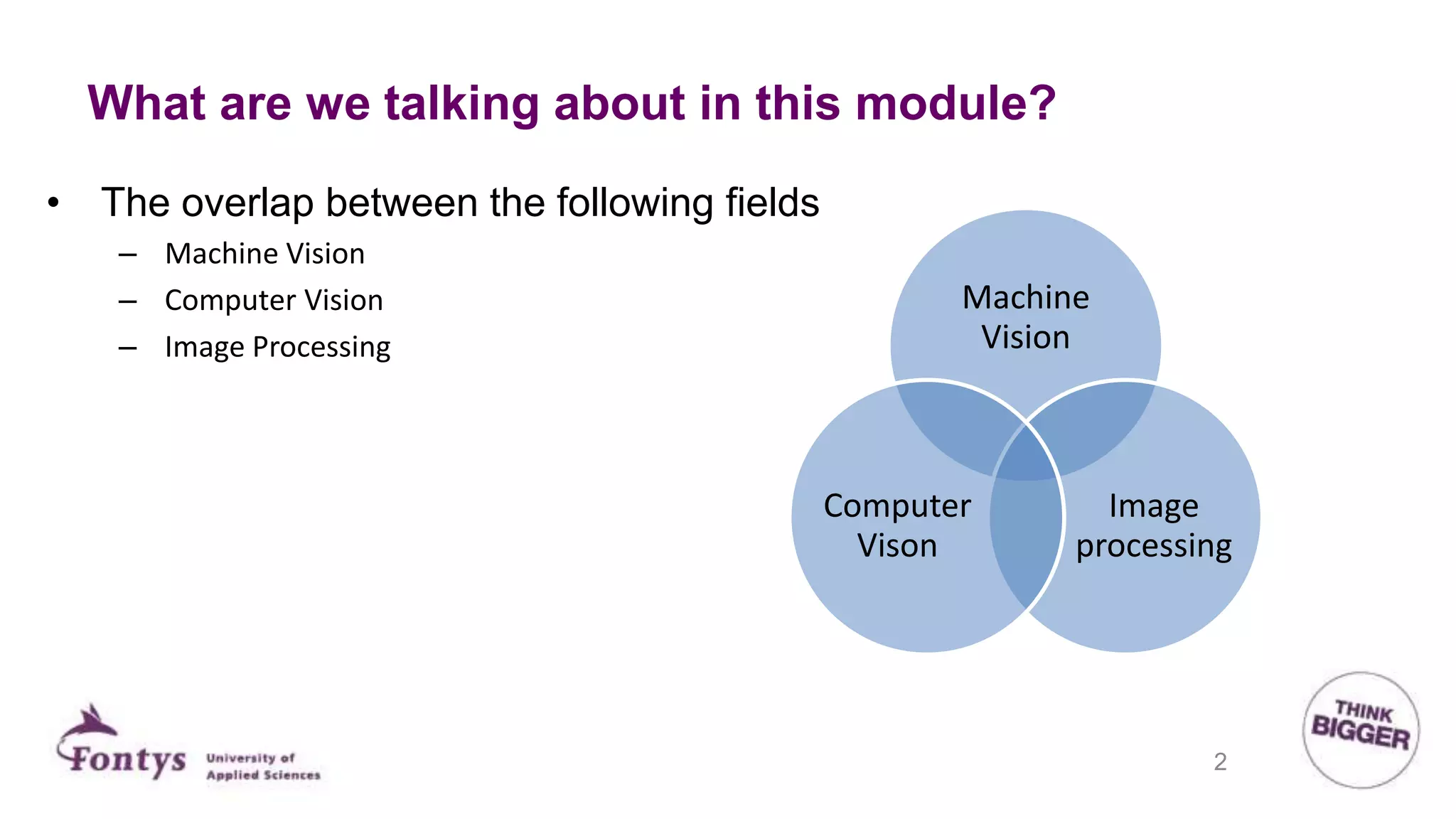
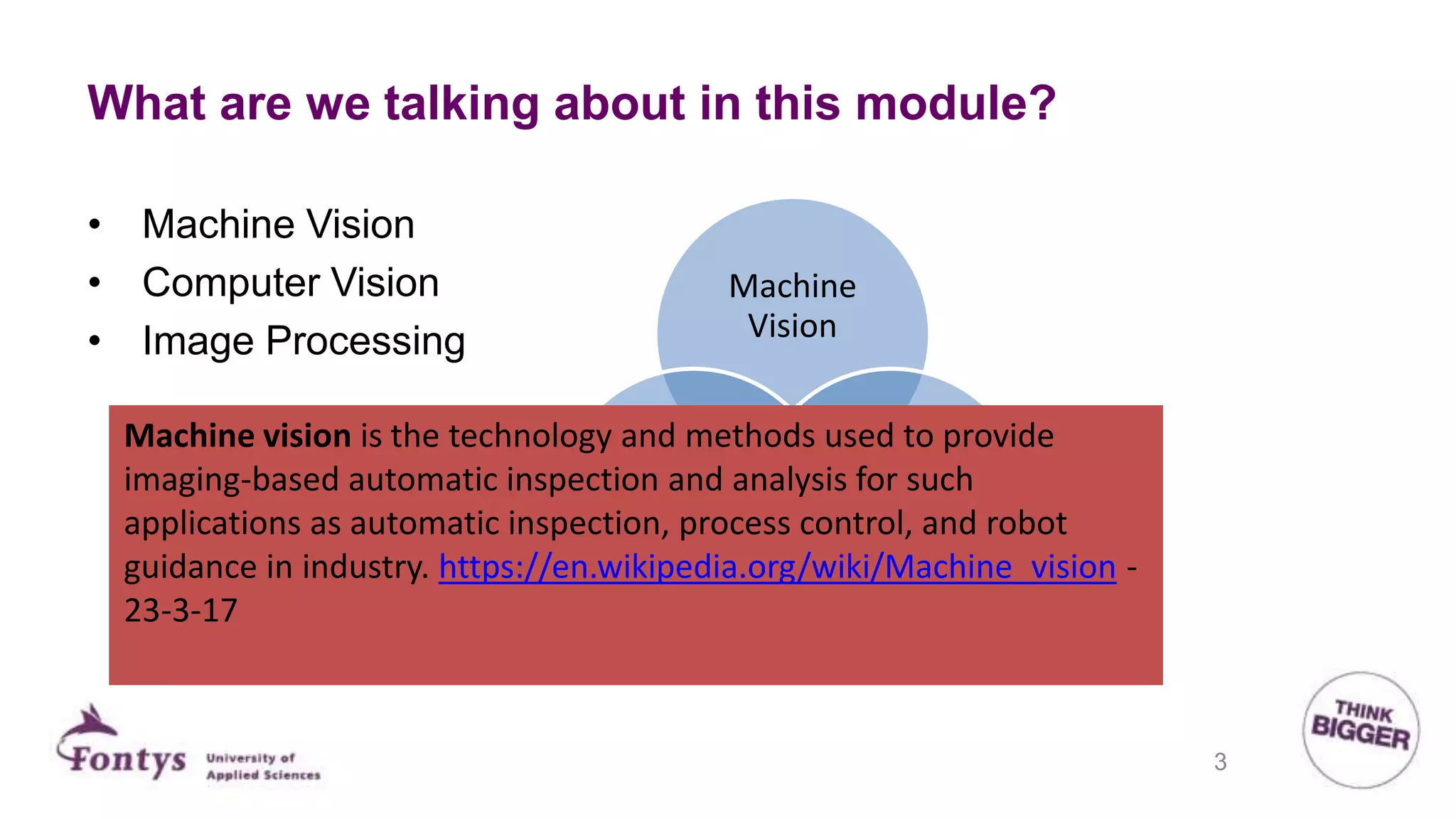
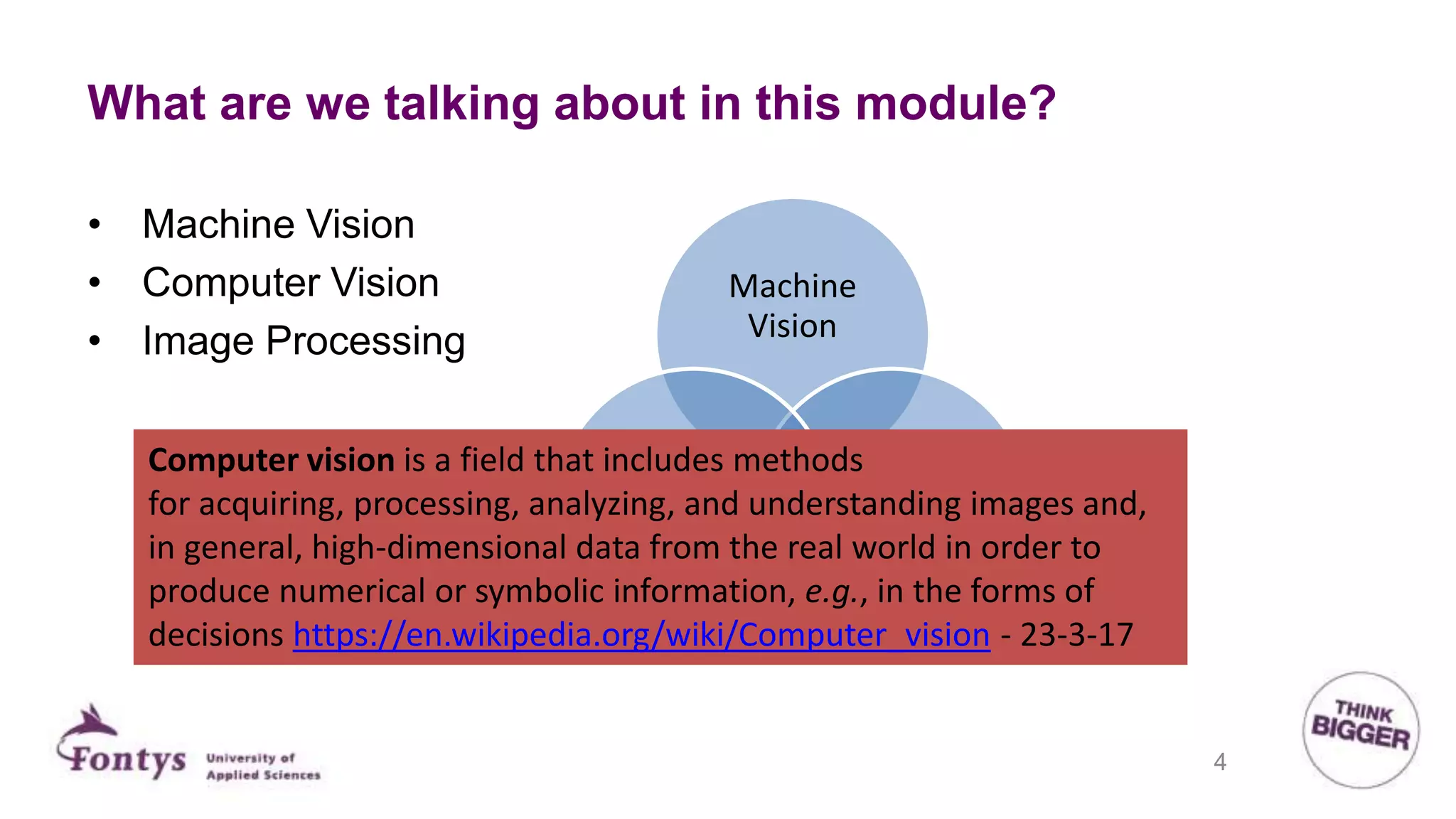
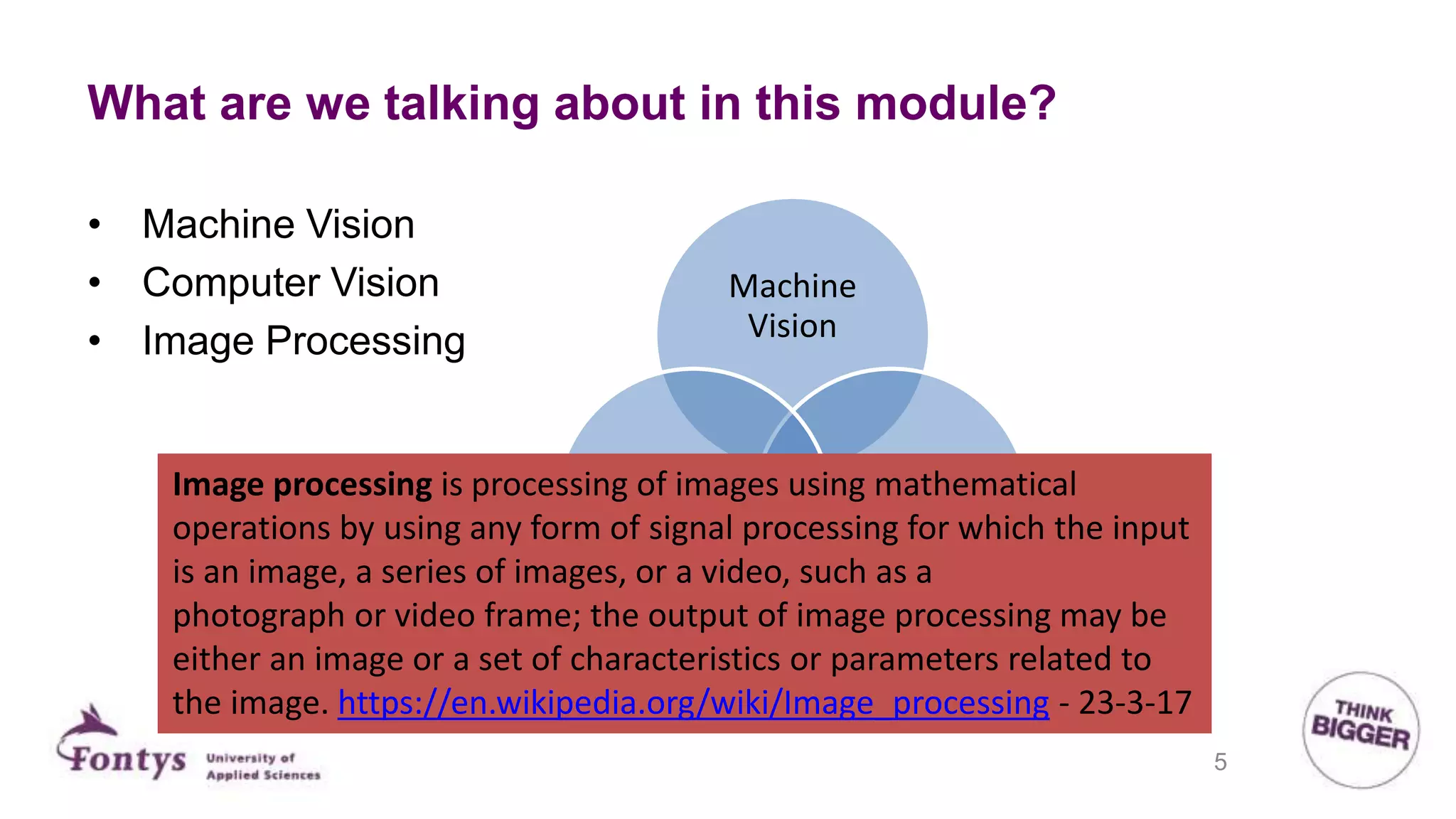
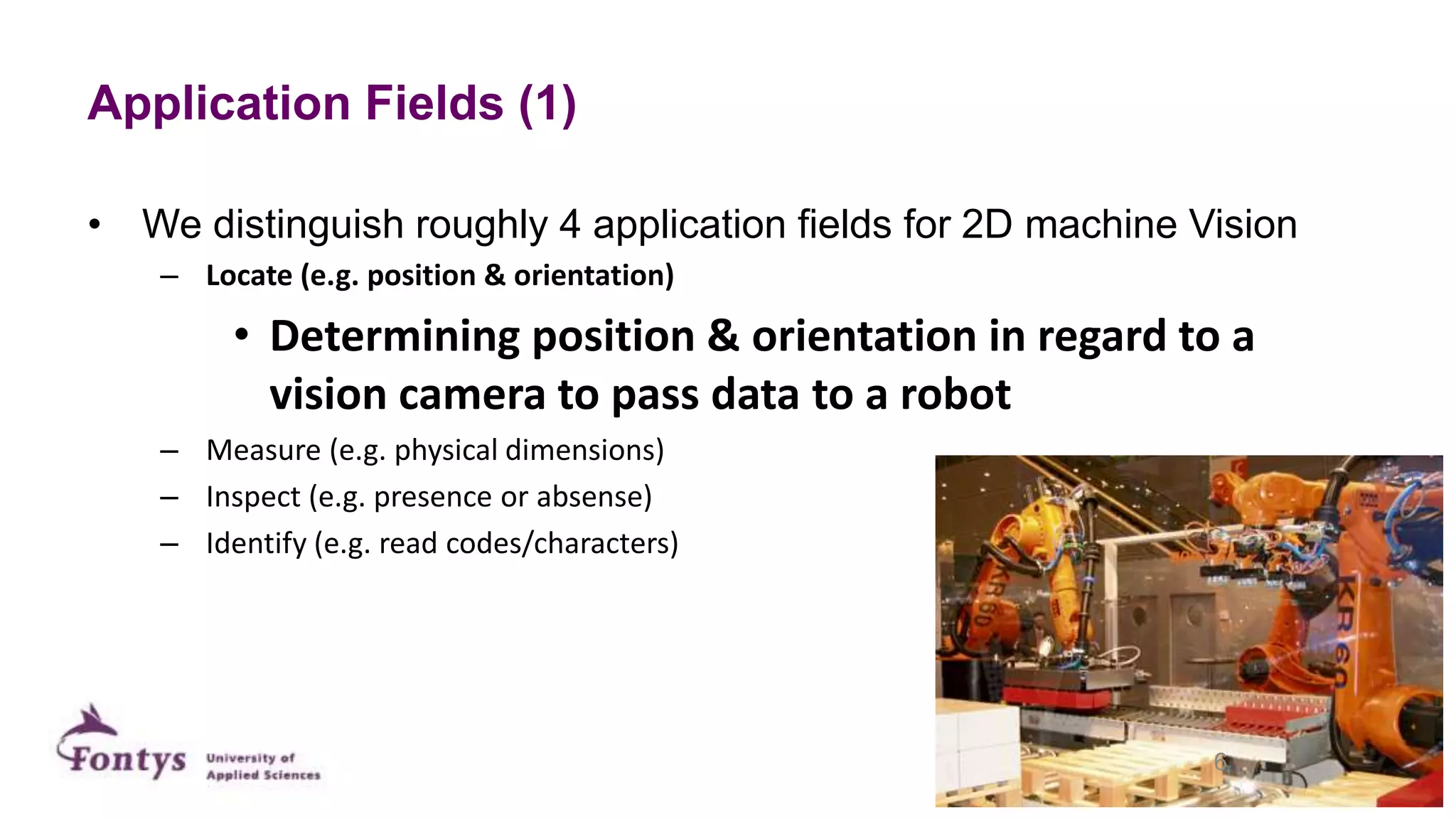
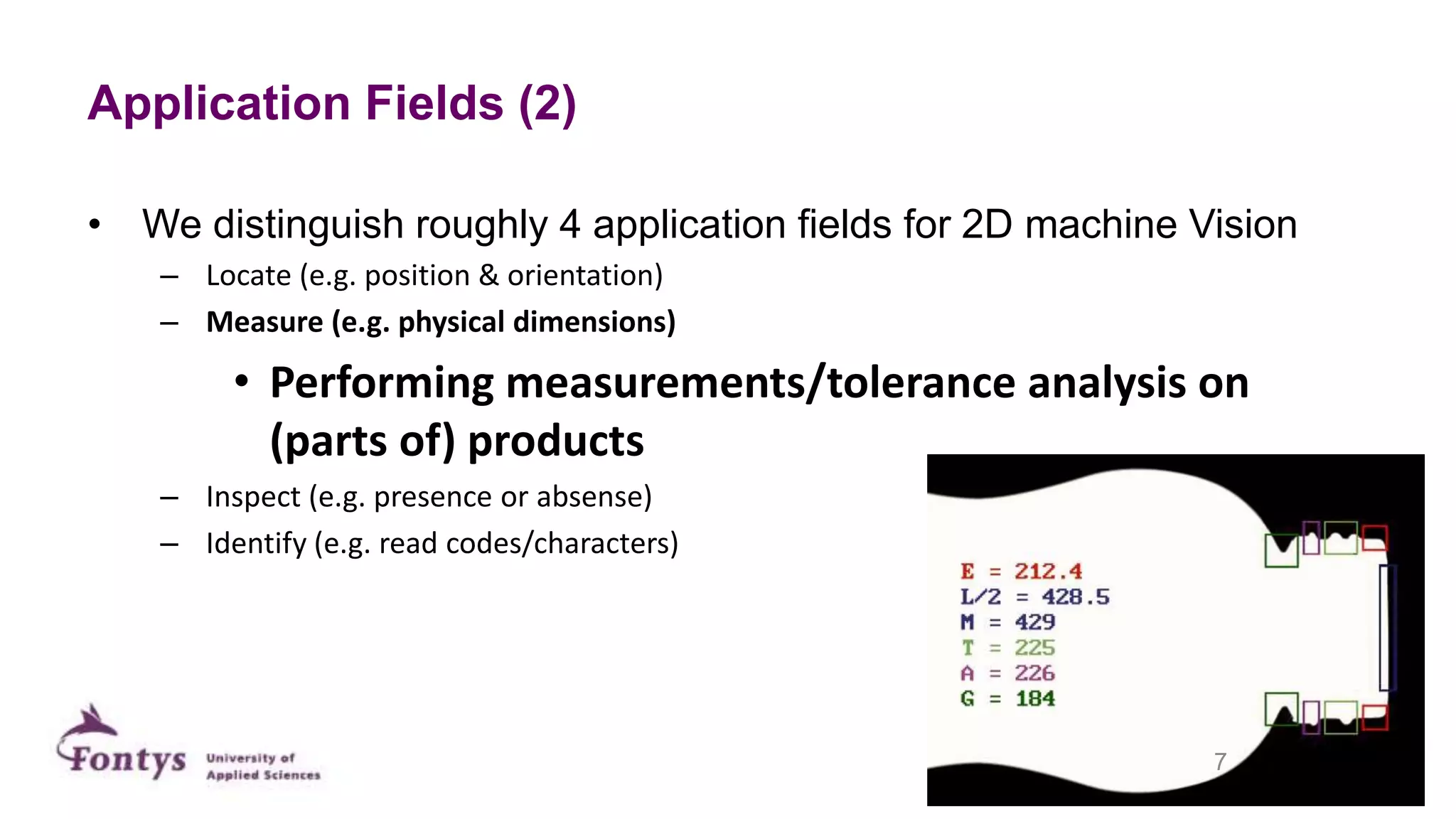
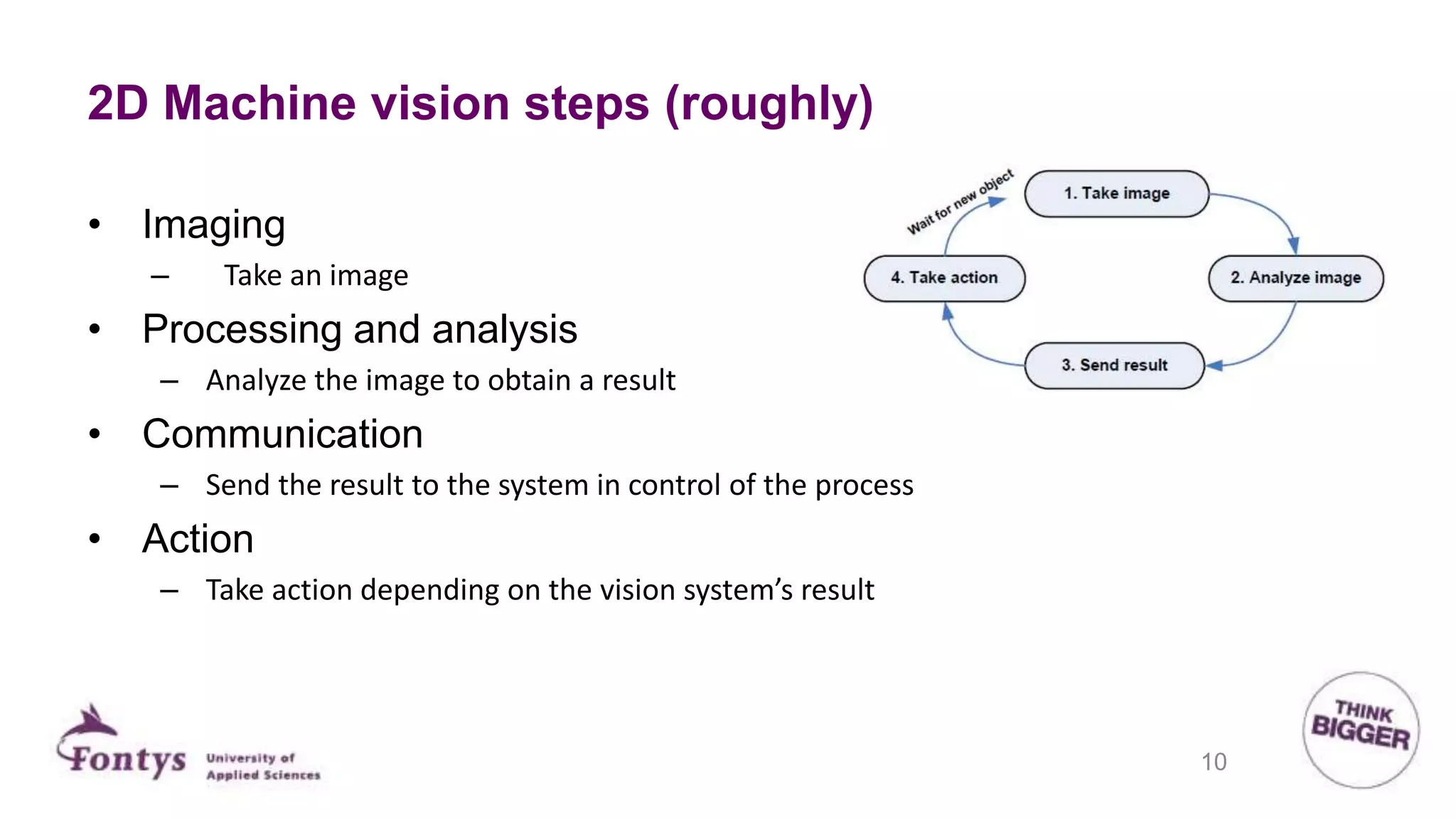
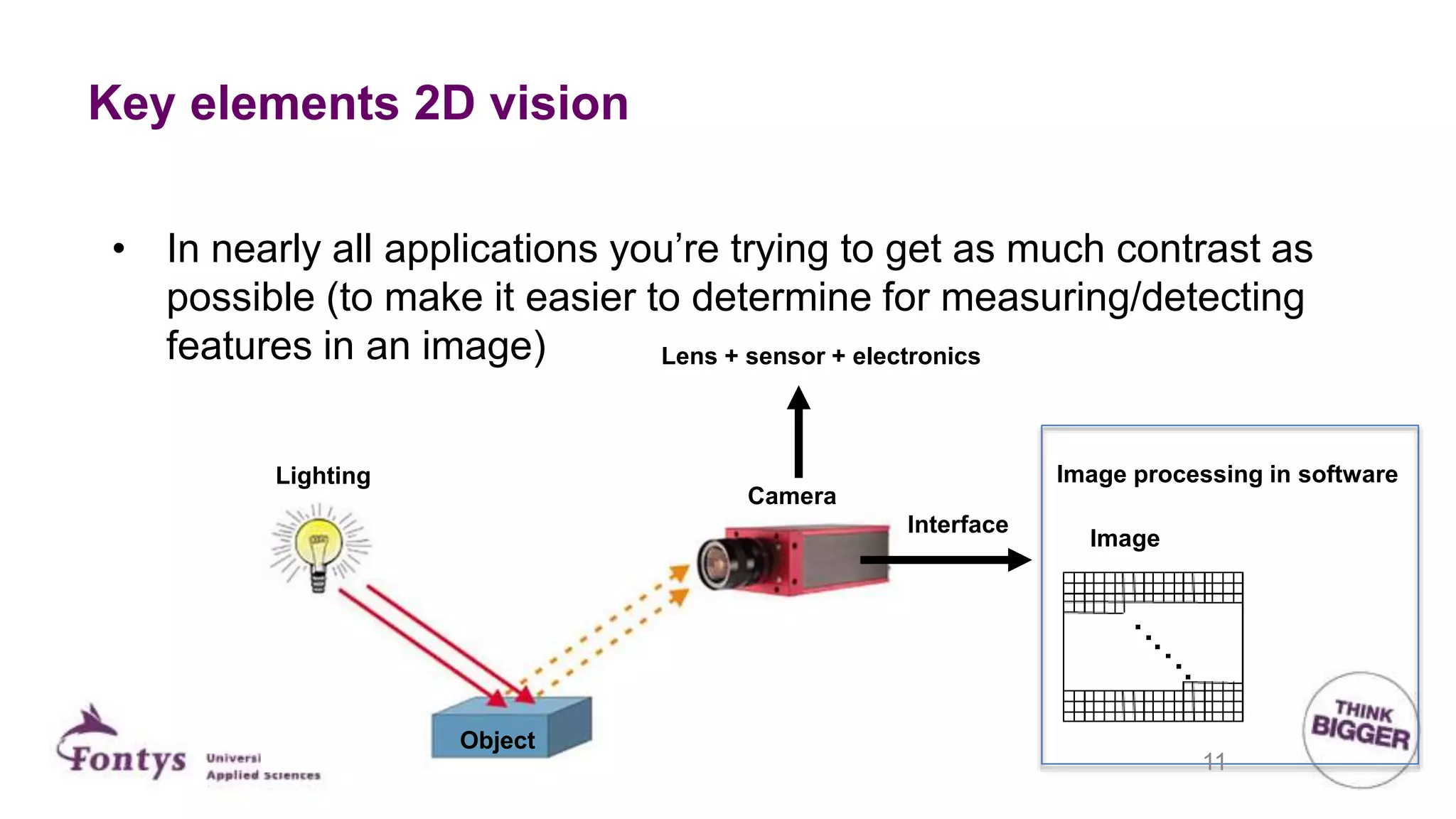
This document discusses 2D machine vision. It defines machine vision, computer vision, and image processing, noting their overlap. It explains that machine vision is used for automatic inspection and analysis in industry applications like quality control and robot guidance. Computer vision involves acquiring, processing, and understanding images to produce information for decisions. Image processing involves mathematical operations on images. The document outlines four main application areas for 2D machine vision: locating, measuring, inspecting, and identifying. It provides brief examples for each. Finally, it summarizes the typical steps and key elements involved in 2D machine vision systems.