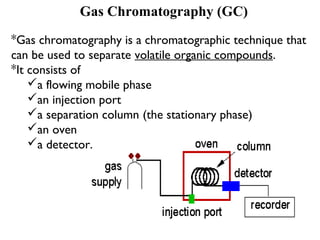
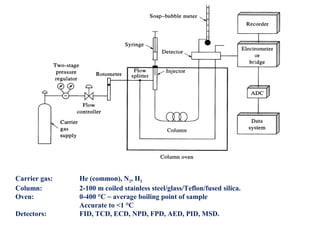
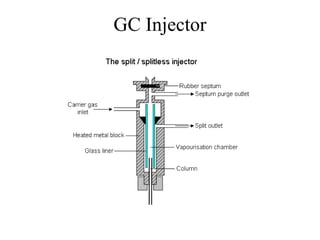
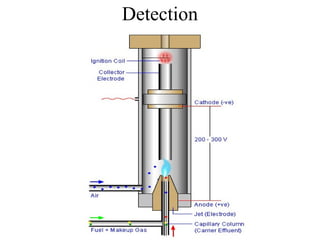
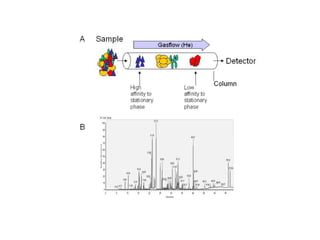
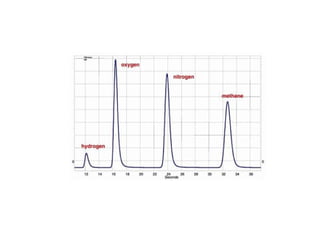
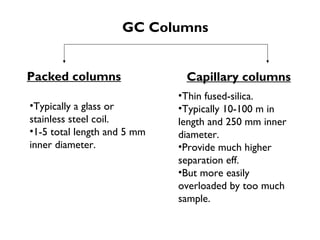
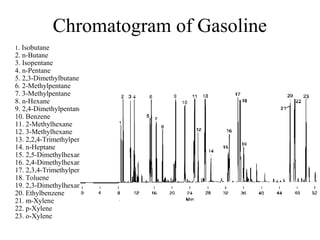
Gas chromatography is a technique used to separate volatile organic compounds using a mobile gas phase and stationary phase in a column. Key components include an injection port to introduce the sample, an oven to heat the column and volatilize compounds, and a detector. Differences in how compounds partition between the mobile and stationary phases allows separation as they migrate through the column at different rates. Common detectors include the flame ionization detector.