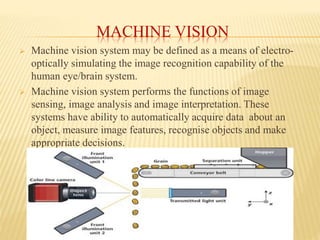
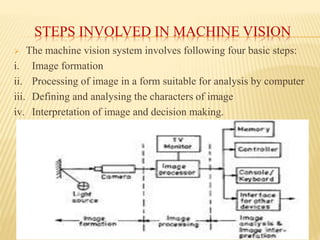
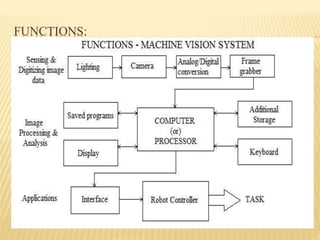
A machine vision system uses cameras and computer processing to simulate the human ability to recognize images. It performs image sensing, analysis, and interpretation to automatically acquire data about objects, measure image features, recognize objects, and make decisions. The process involves a camera capturing an image of an object under light, the computer analyzing the image characteristics, and either communicating defects to a rejection unit or sending defect-free parts for further processing. Key steps are image formation, processing the image for computer analysis, defining and analyzing image characteristics, and interpreting the image and making decisions. Machine vision is used for inspection, identification, guidance and control in various applications like quality assurance, defect detection, testing and calibration.