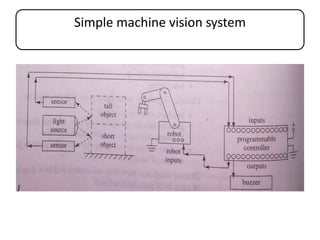
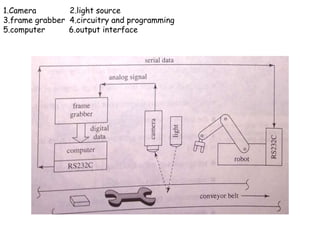
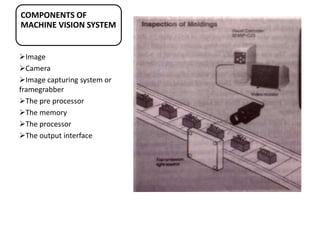
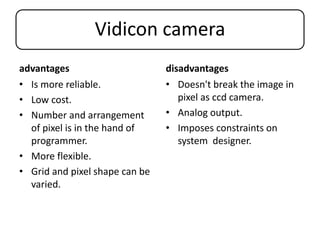
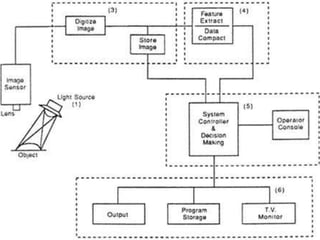
This document discusses machine vision systems and their components. A basic machine vision system includes a camera, light source, frame grabber, circuitry and programming, and a computer. Key components of machine vision systems are the image, camera, framegrabber, preprocessor, memory, processor, and output interface. The document also describes CCD and vidicon cameras, their advantages and disadvantages, and the functions of framegrabbers in sampling and quantizing images. Object properties that can be analyzed from pixel grey values include color, specular properties, non-uniformities, lighting. Applications of machine vision systems are also mentioned.