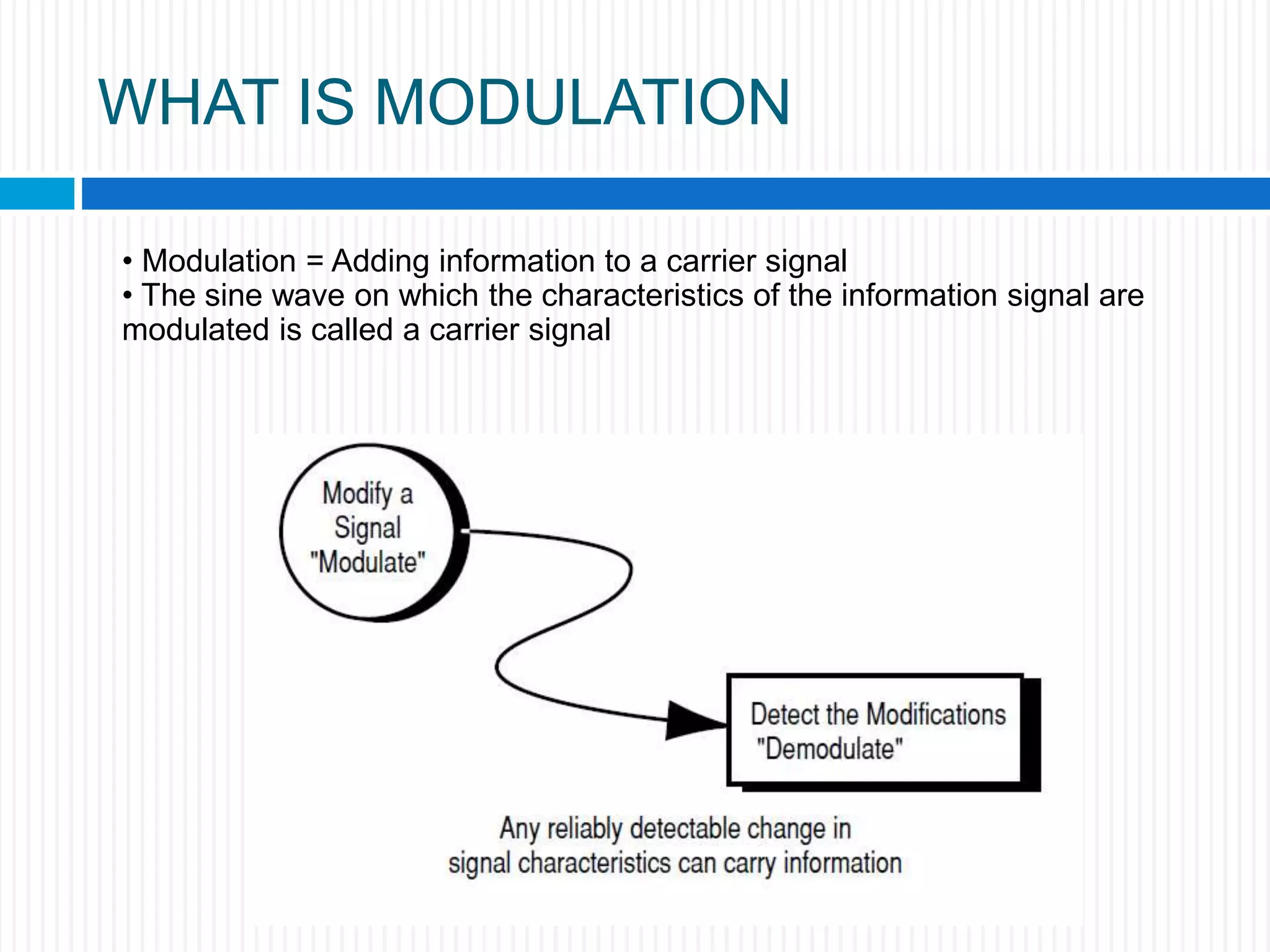
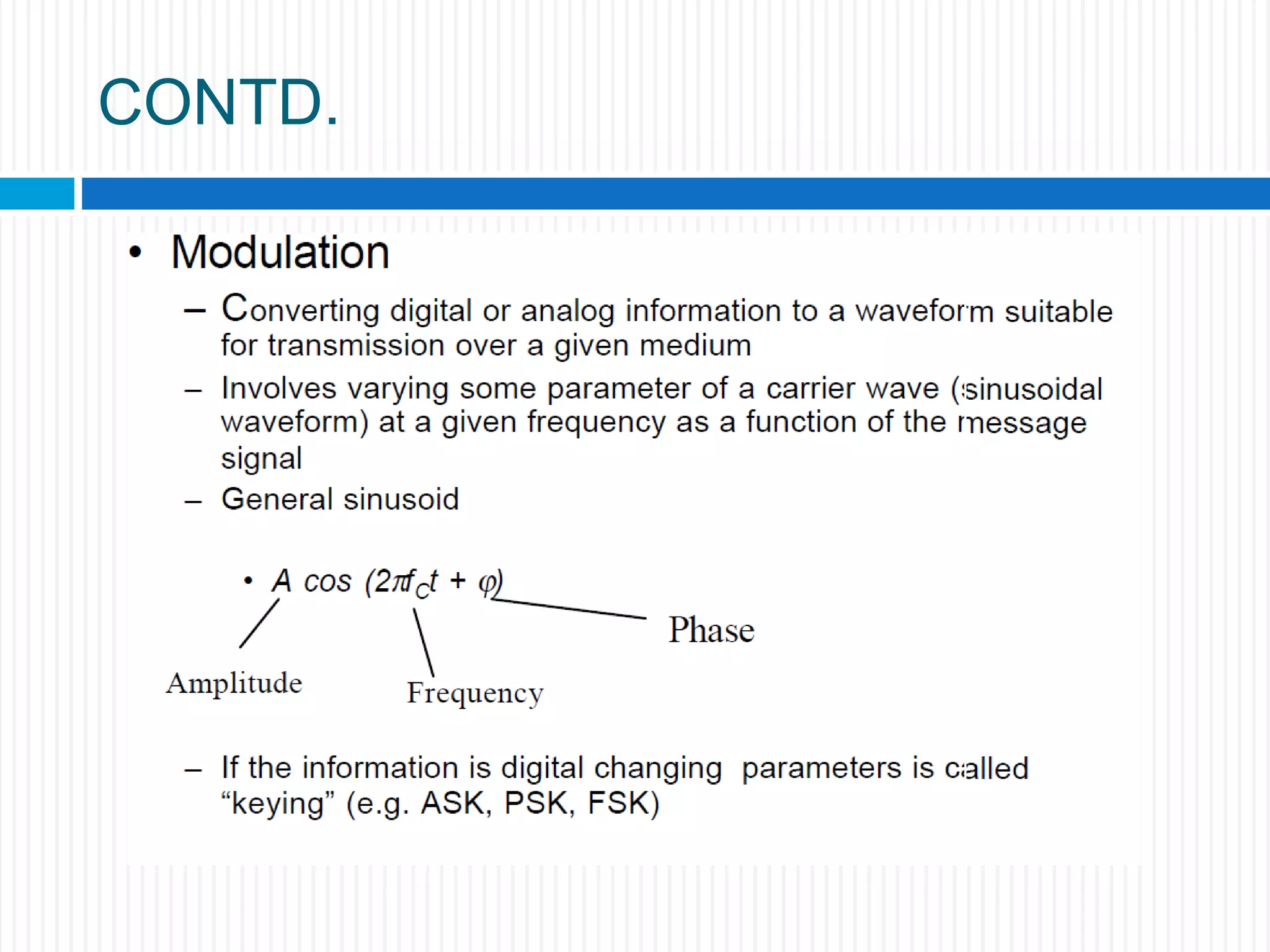
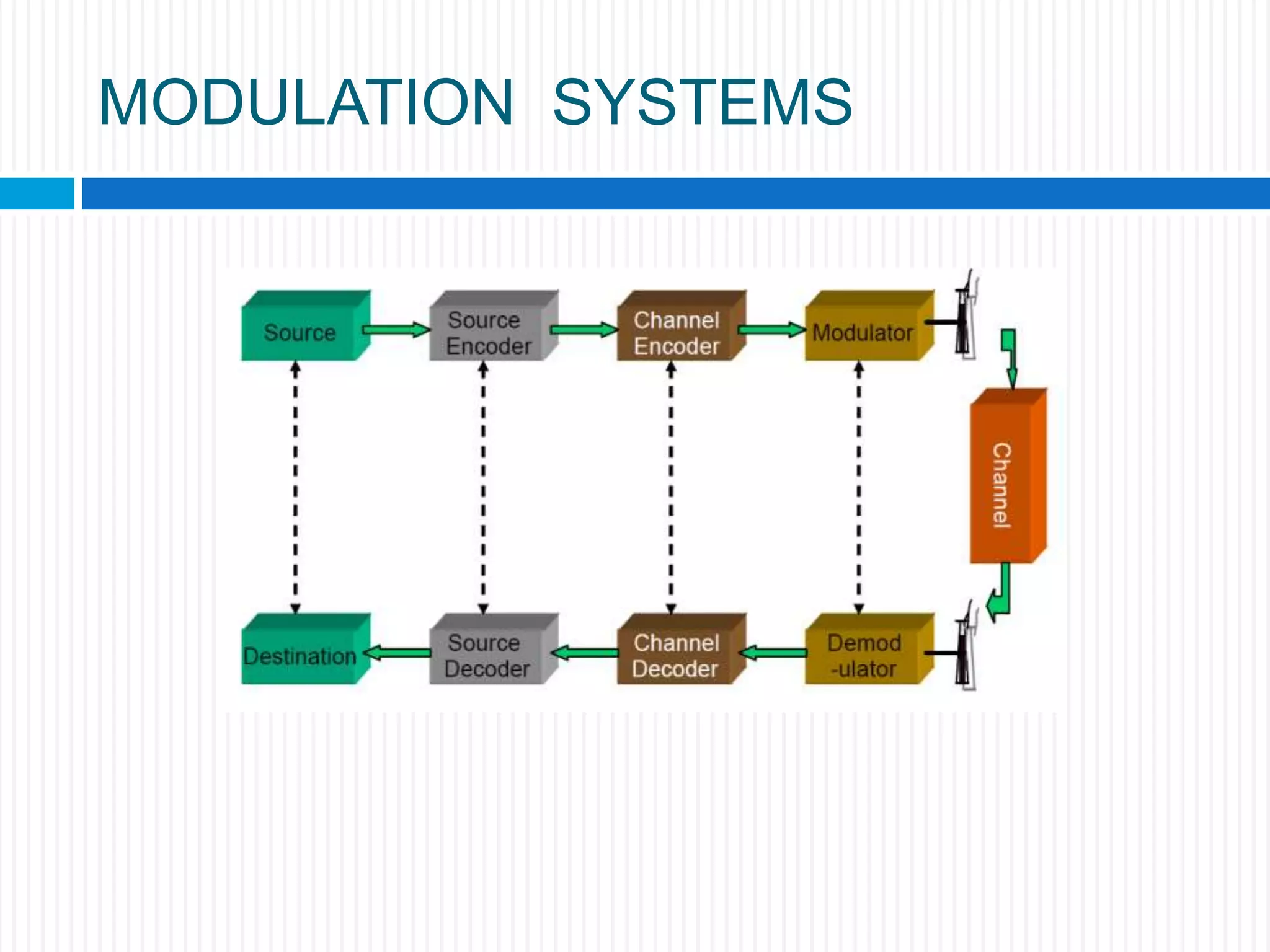
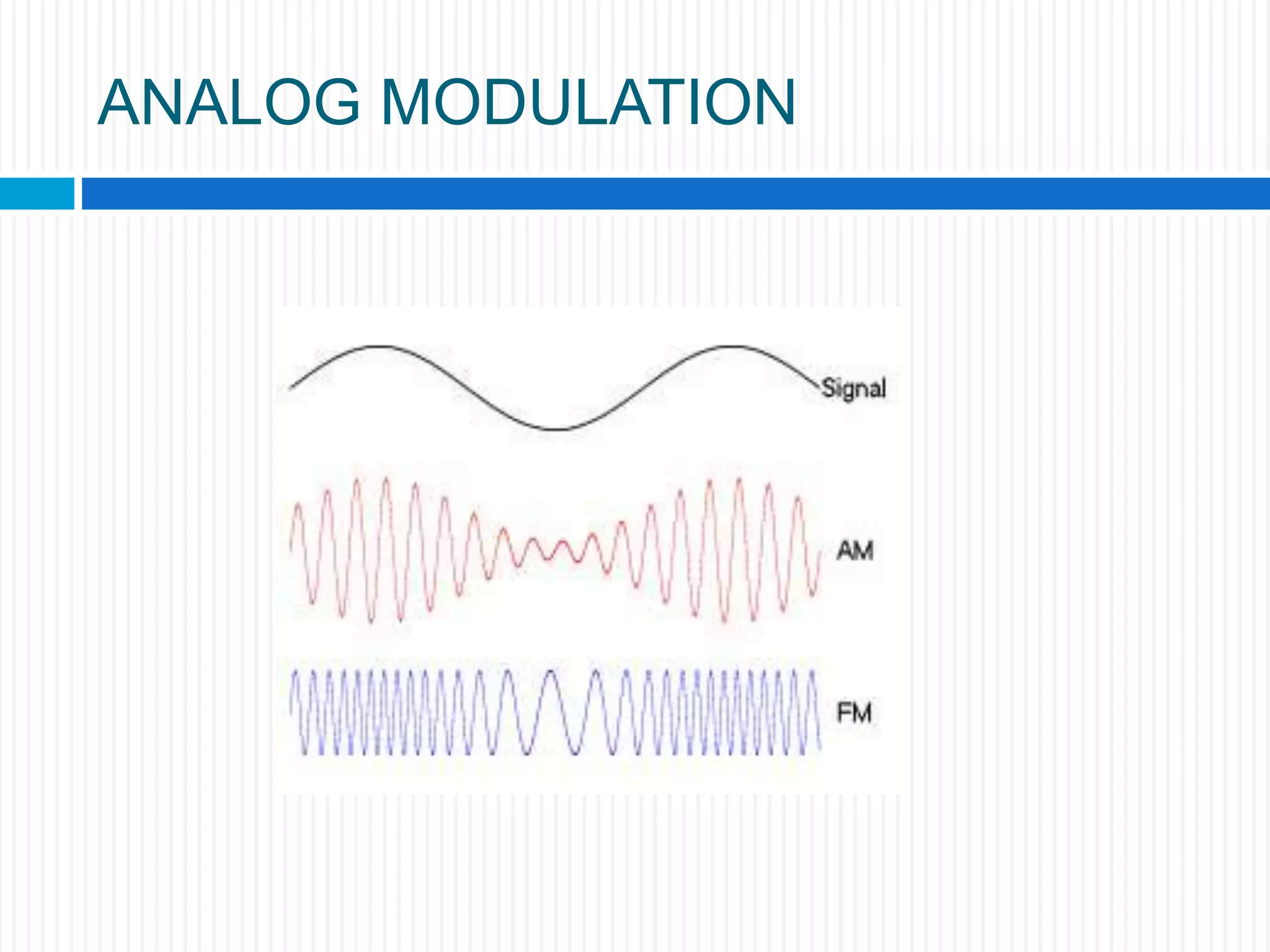
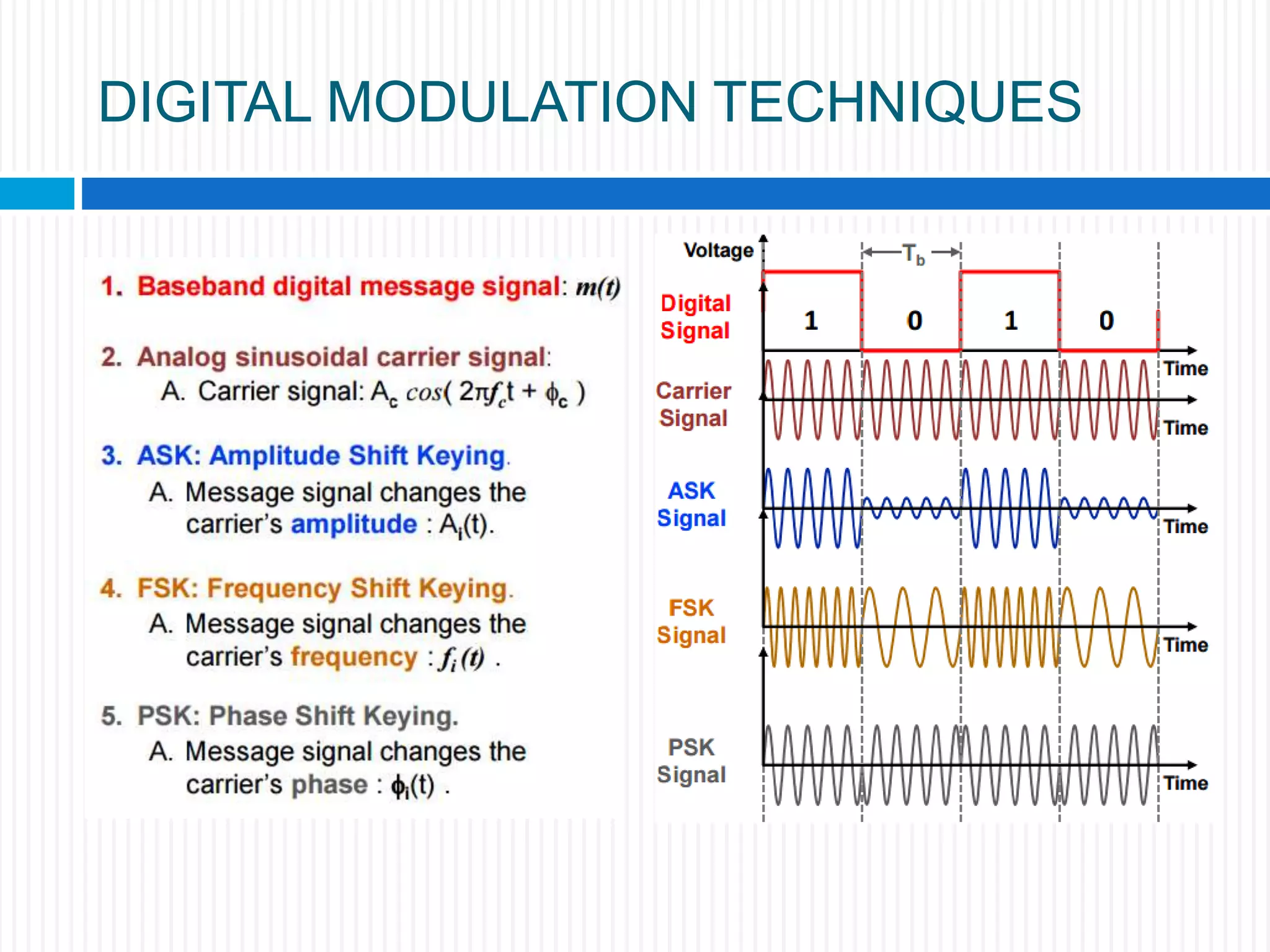
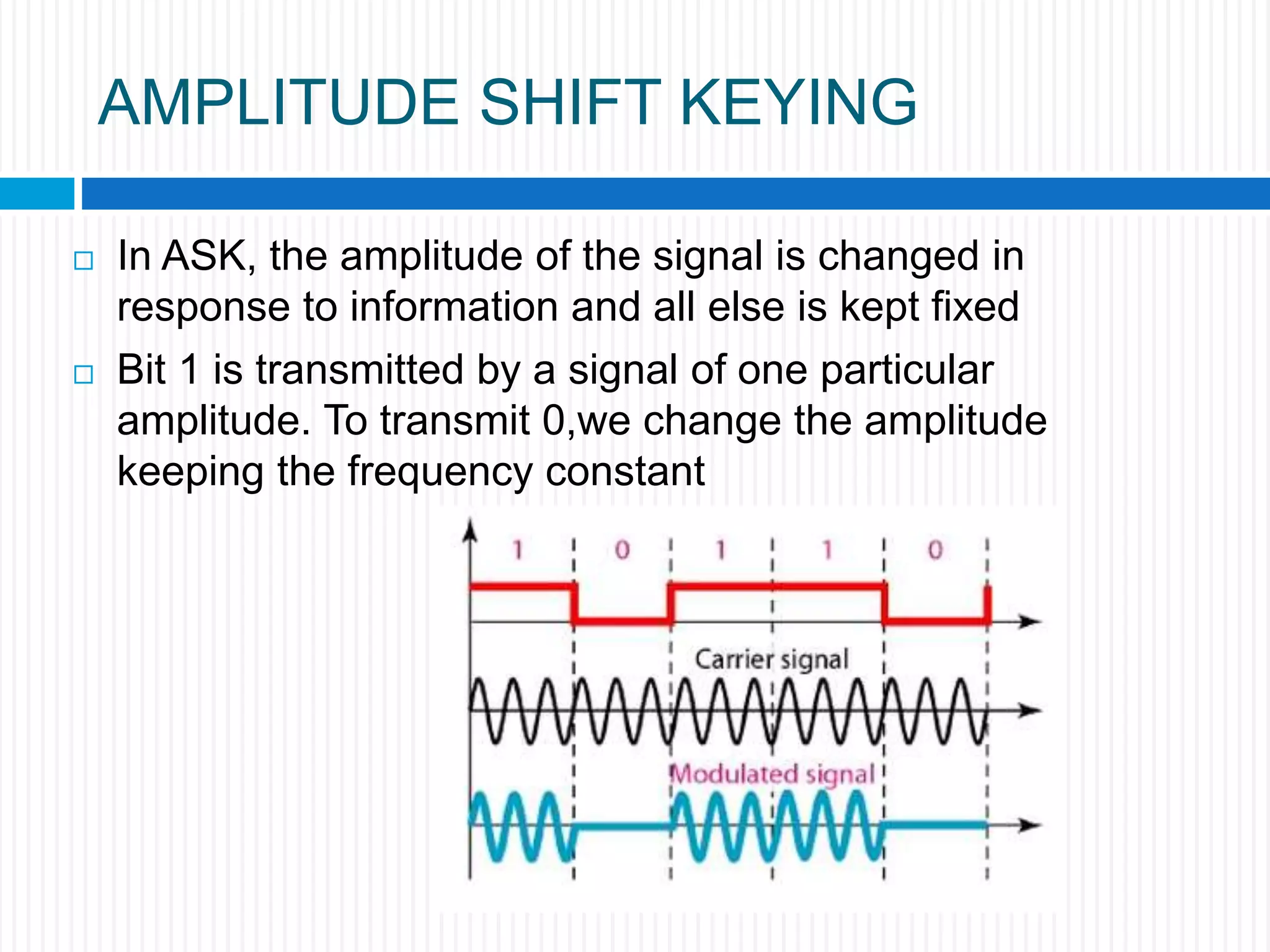
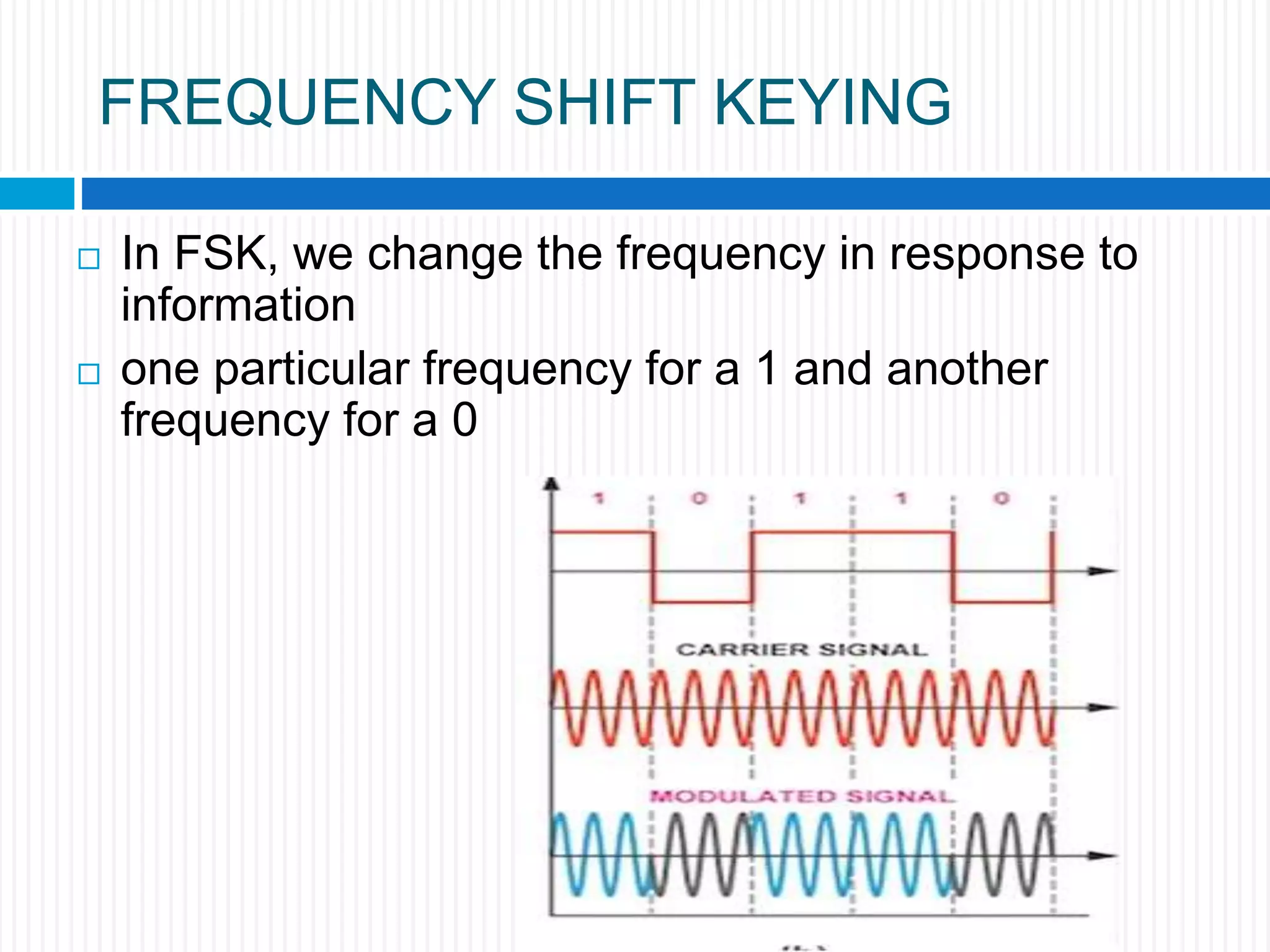
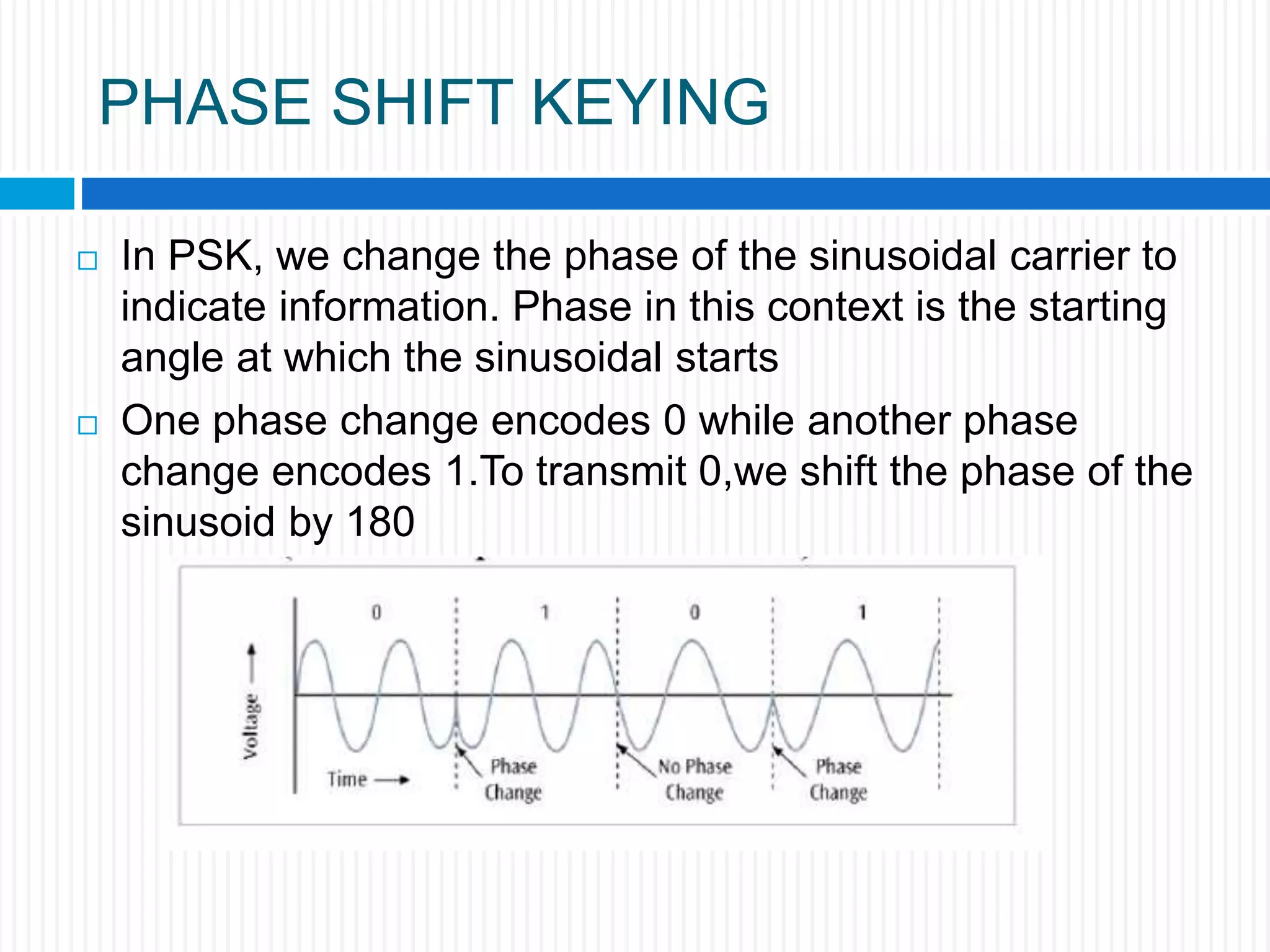
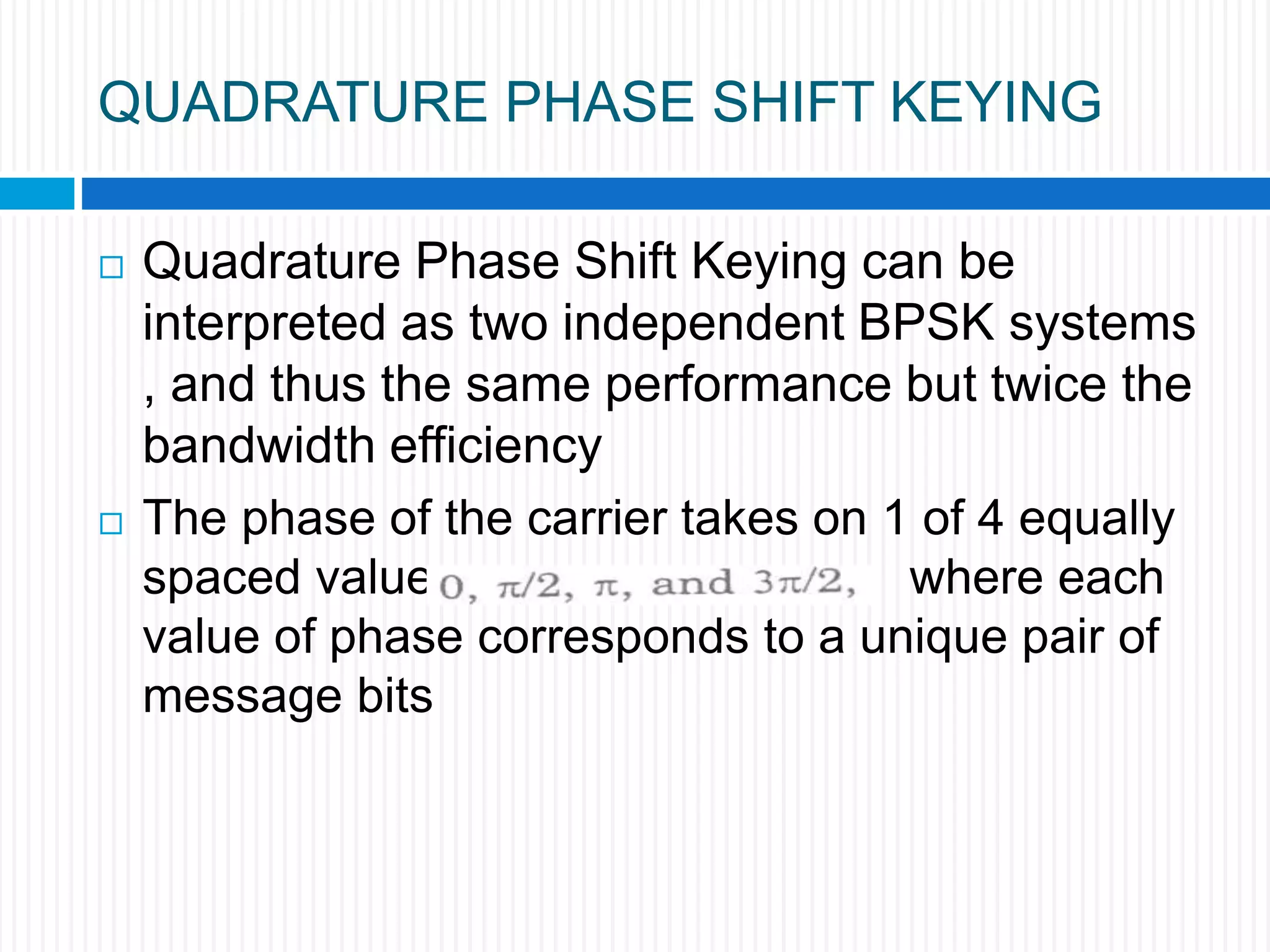
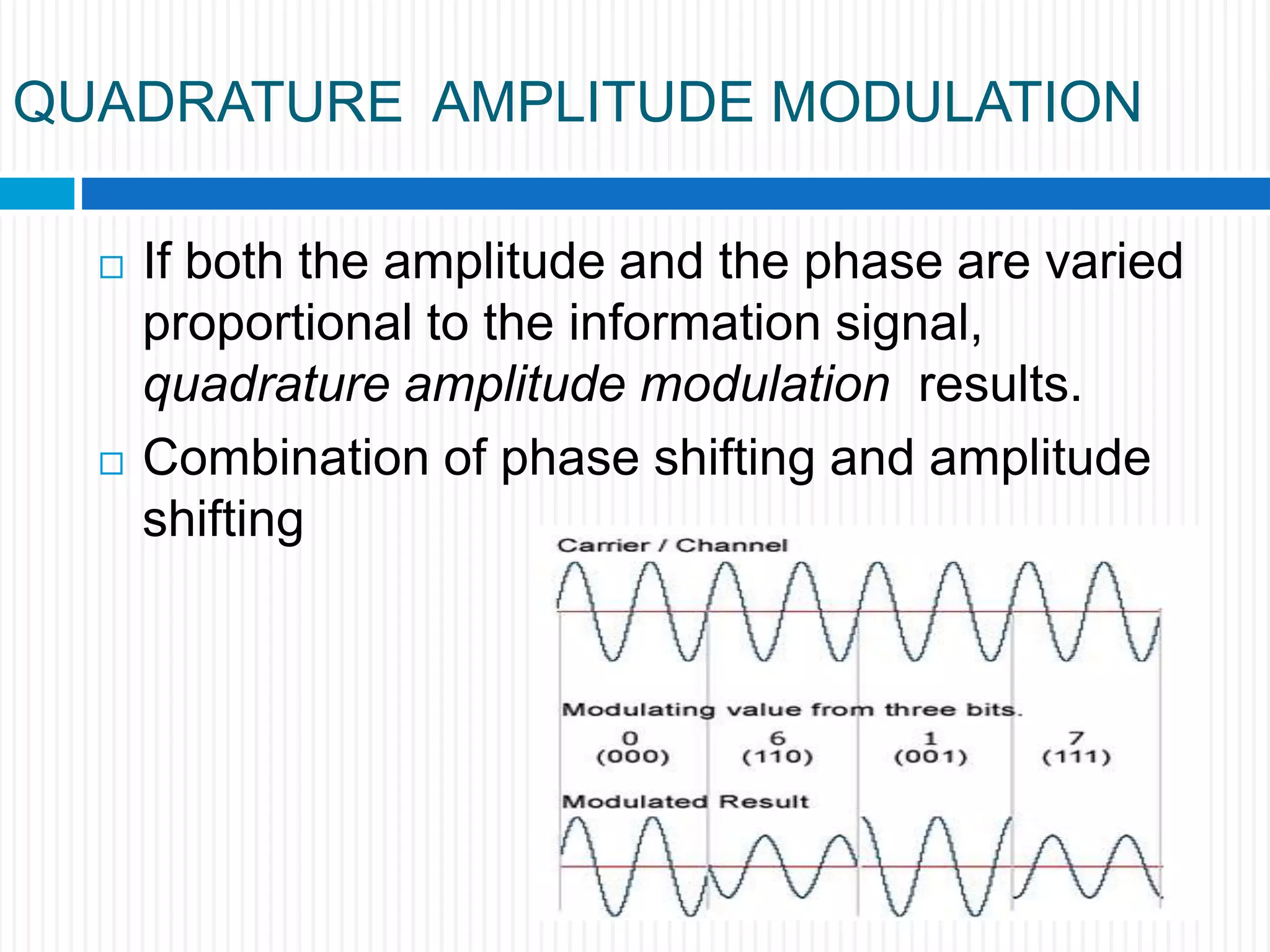
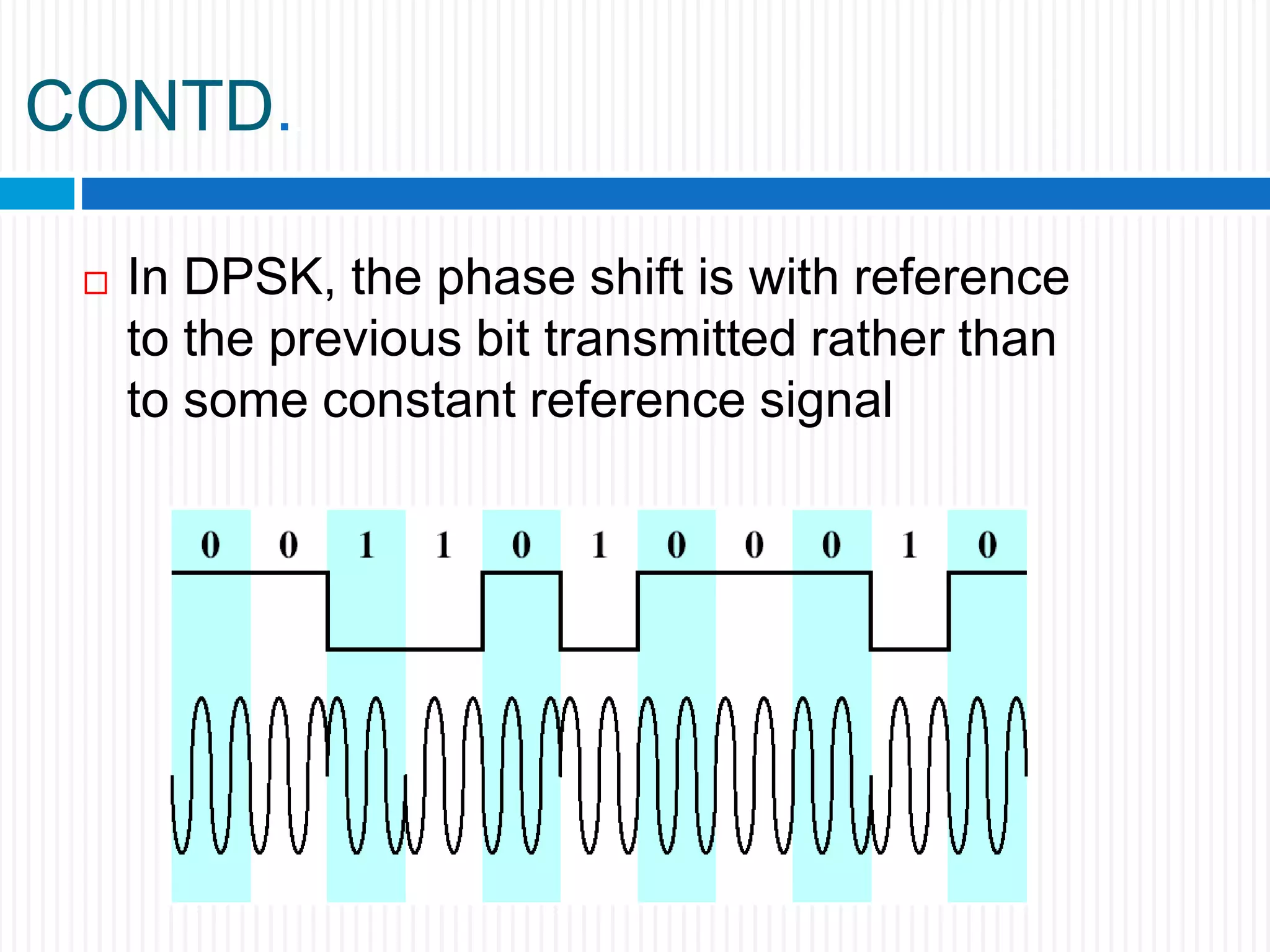
This document discusses various digital modulation techniques. It begins by defining modulation as adding information to a carrier signal. It then distinguishes between analog and digital modulation. Digital modulation modulates an analog carrier signal with a discrete signal, and can be considered as converting digital-to-analog and vice versa. Some key digital modulation techniques discussed include amplitude shift keying (ASK), frequency shift keying (FSK), phase shift keying (PSK), quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), and differential phase shift keying (DPSK). Metrics for comparing digital modulation techniques include power efficiency, bandwidth efficiency, and implementation cost-effectiveness.