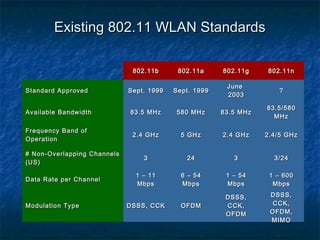
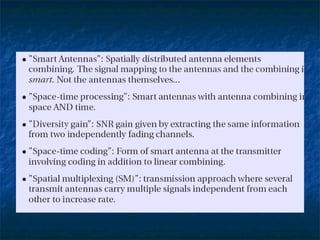
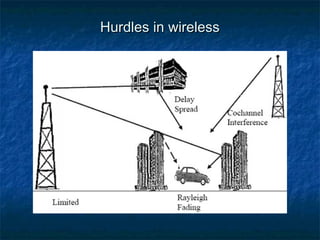
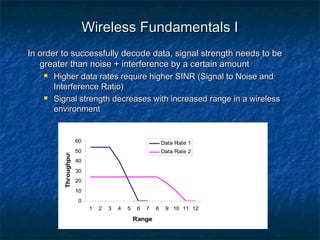
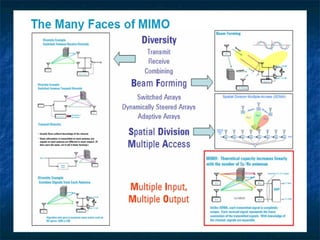
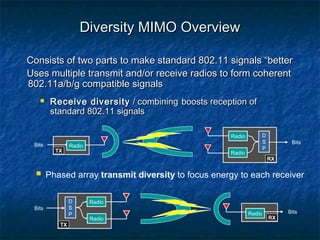
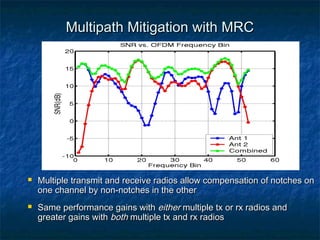
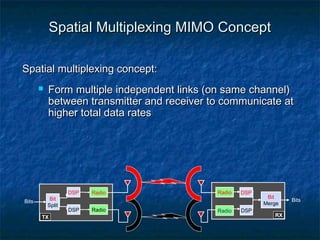
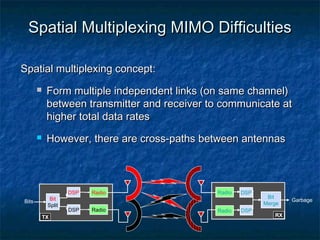
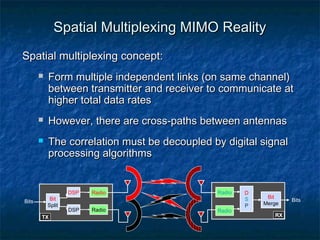
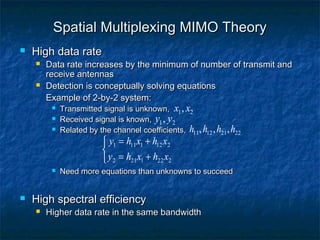
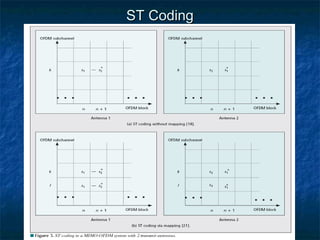
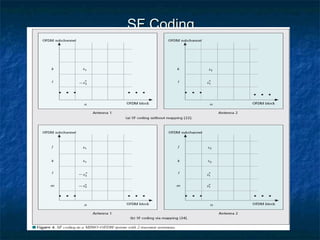
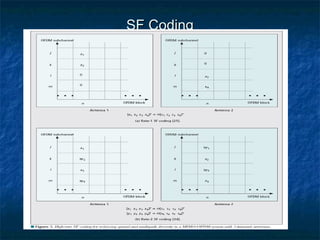
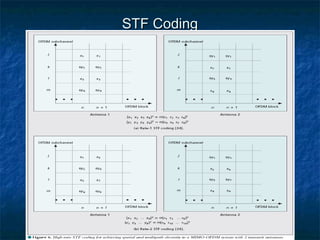
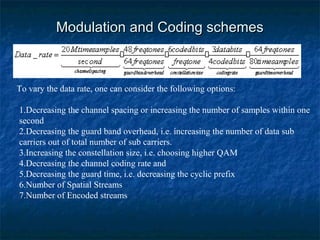
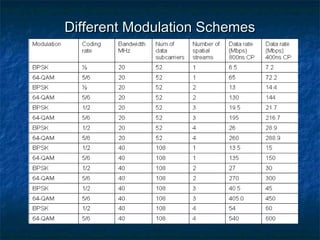
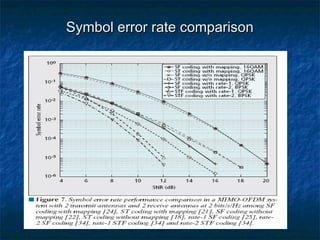
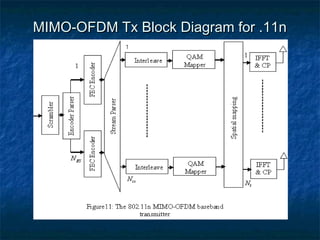
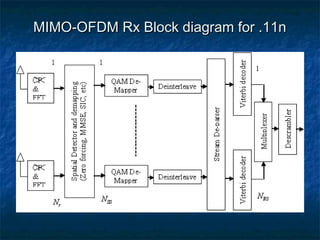
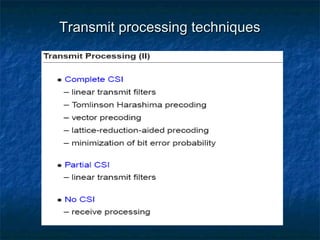
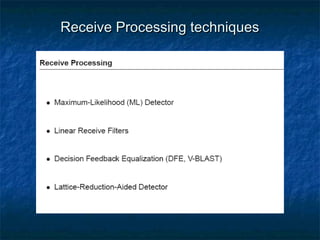
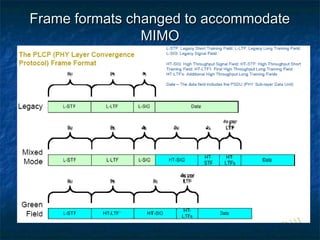
This document provides an overview of MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) technology and its use in 802.11n wireless networks. MIMO works by using multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication in three ways: by providing signal diversity to increase range and resilience, by enabling spatial multiplexing to increase data rates, and by allowing beamforming to focus signals in certain directions. The 802.11n standard will incorporate MIMO to achieve data rates up to 600Mbps using techniques like multi-path mitigation, modulation schemes, channel coding, and frame formatting adapted for MIMO transmissions. MIMO thus allows 802.11n to continue advancing wireless LAN speeds and performance.