Embed presentation
Downloaded 279 times

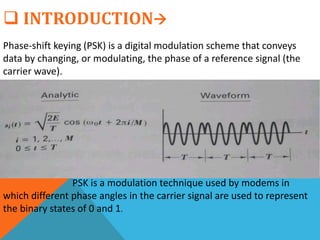
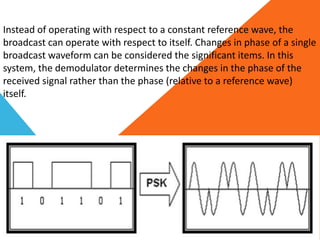
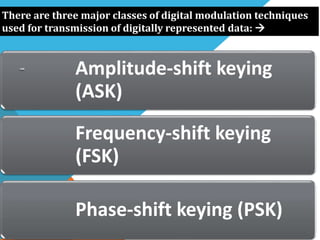
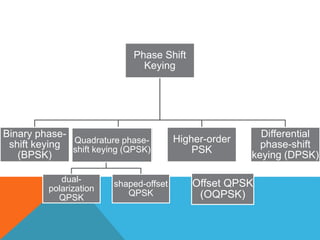
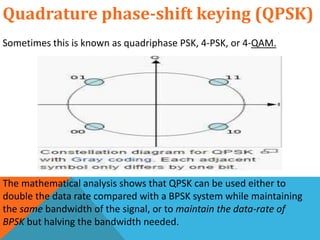
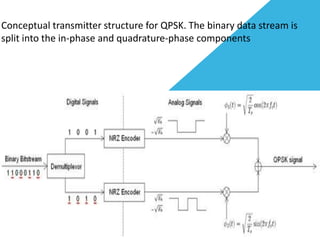
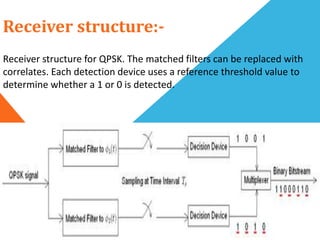

Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation technique that conveys data by changing the phase of a carrier signal. There are three major classes of digital modulation: amplitude-shift keying, frequency-shift keying, and phase-shift keying. Quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK) is a type of PSK that can either double the data rate compared to binary phase-shift keying (BPSK) while maintaining bandwidth, or maintain the BPSK data rate while halving the required bandwidth. QPSK works by splitting the binary data stream into in-phase and quadrature-phase components at the transmitter, and using matched filters or correlates to detect symbols at the receiver.







