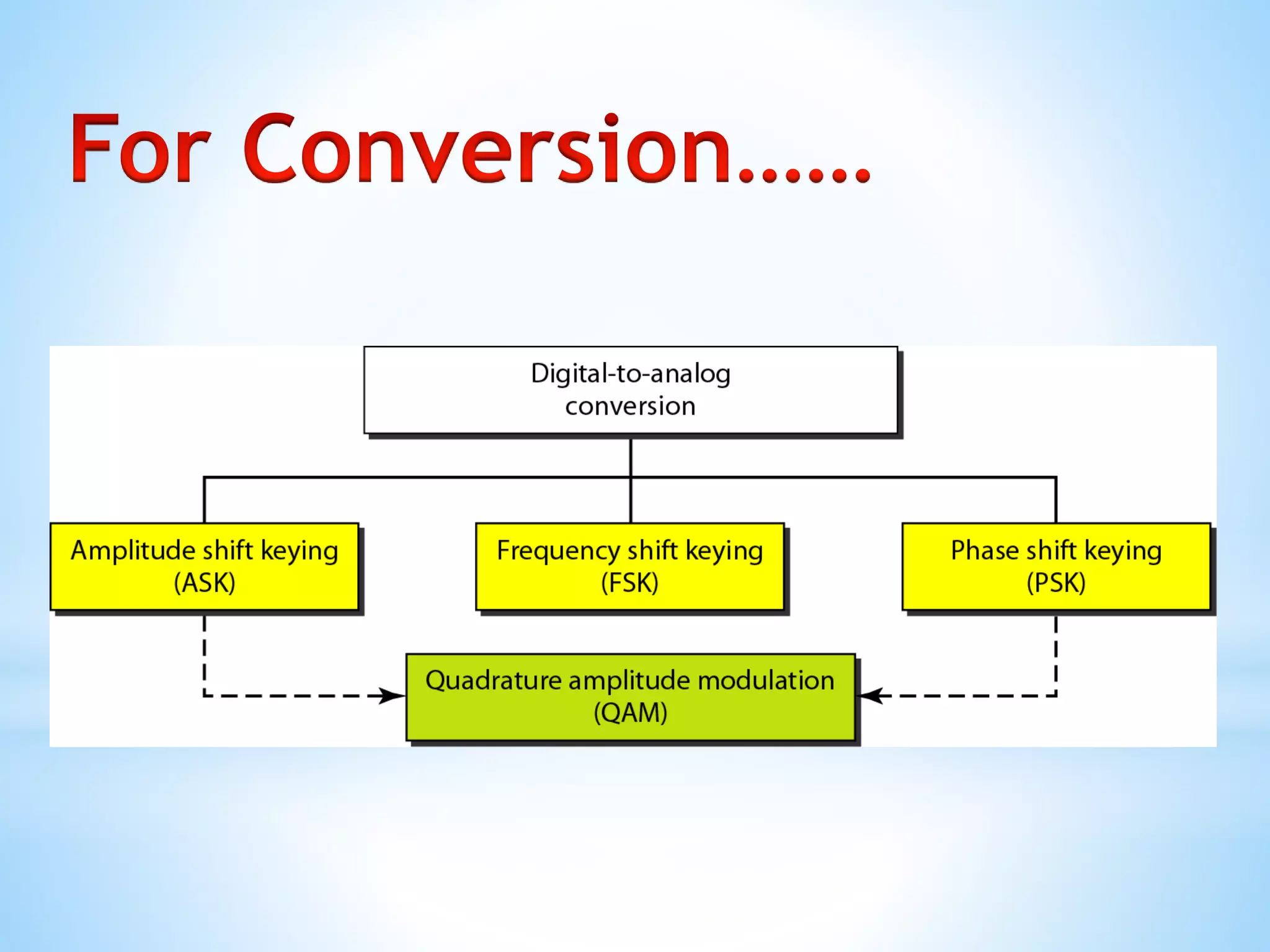
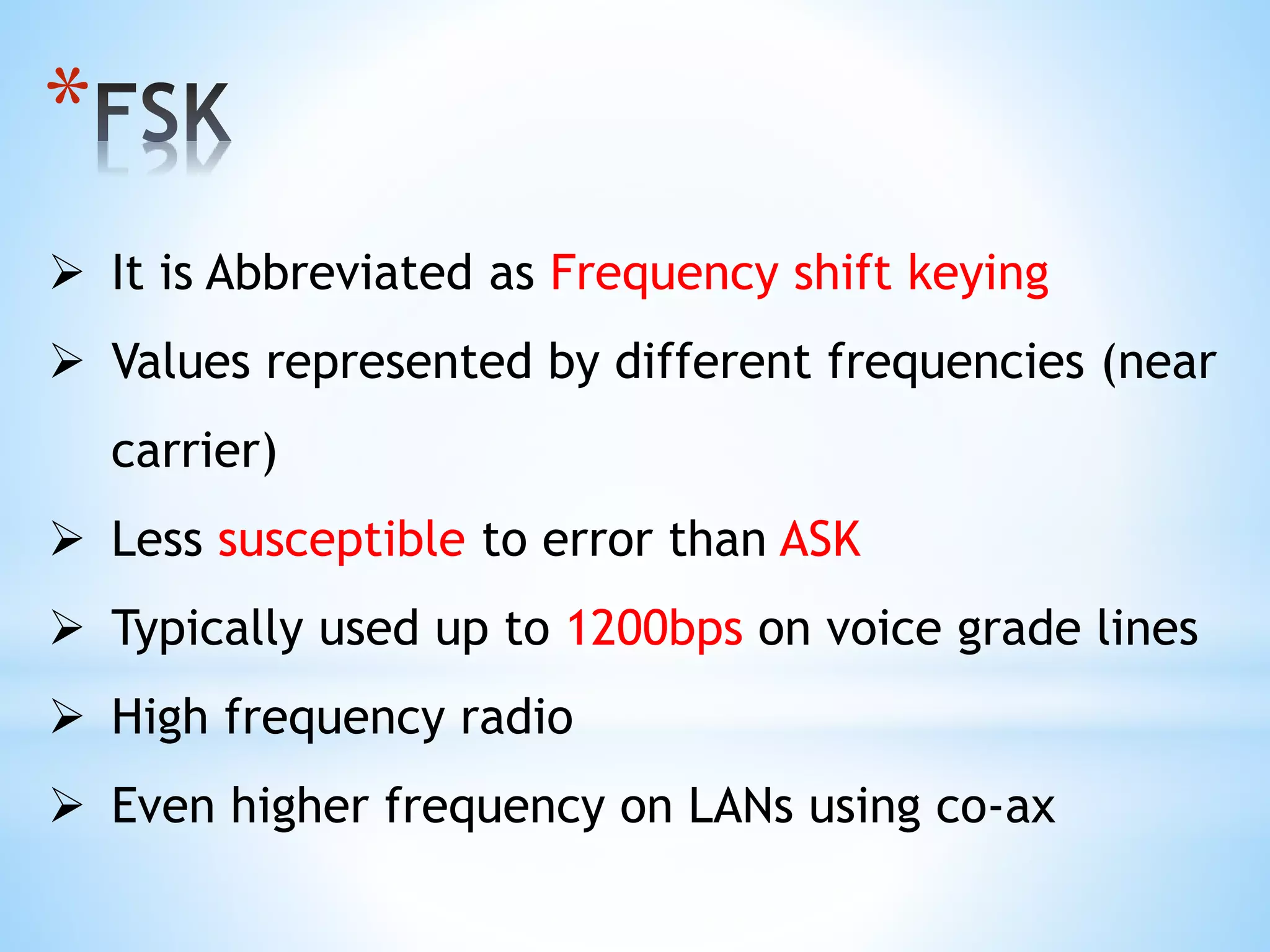
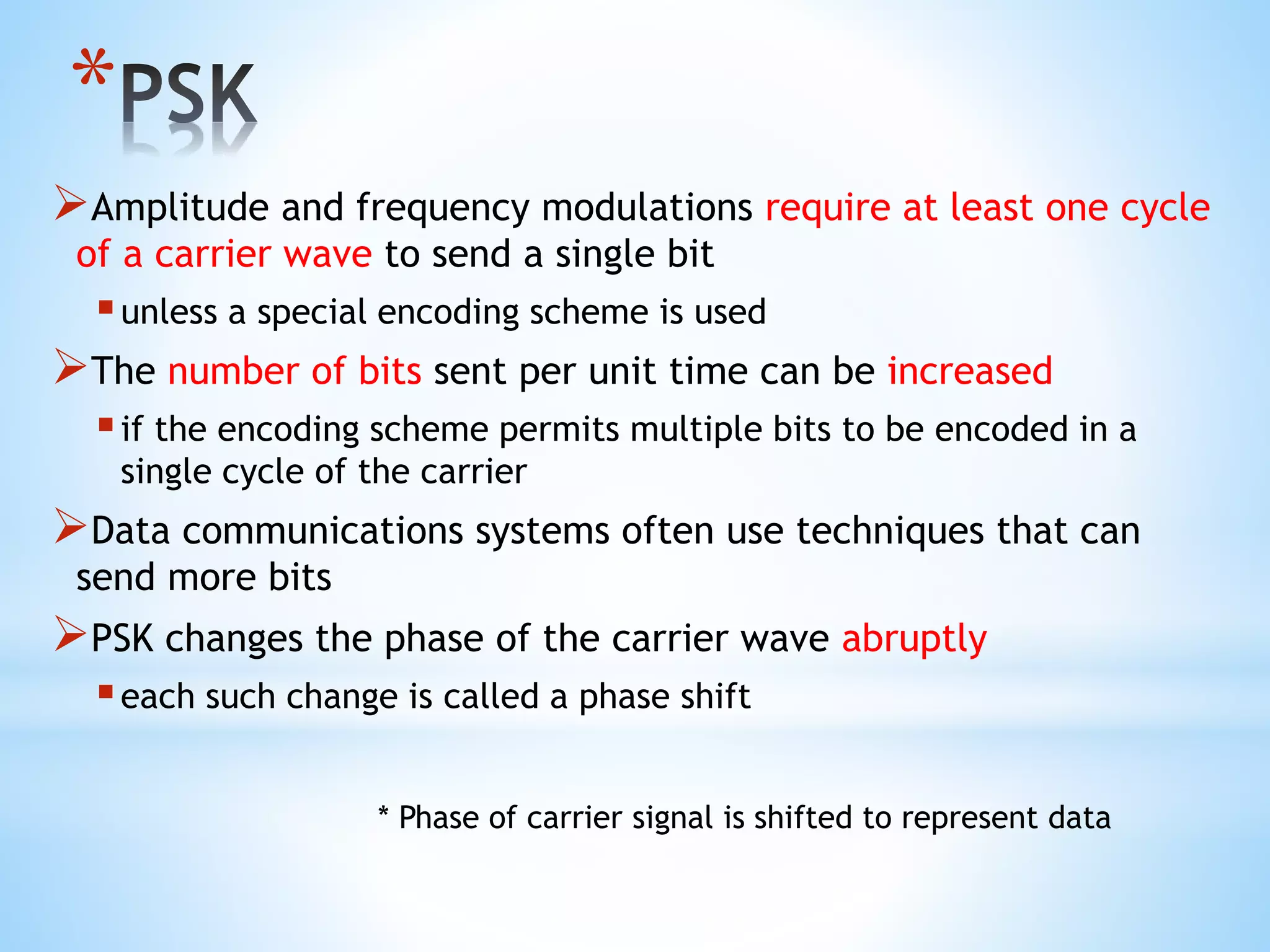
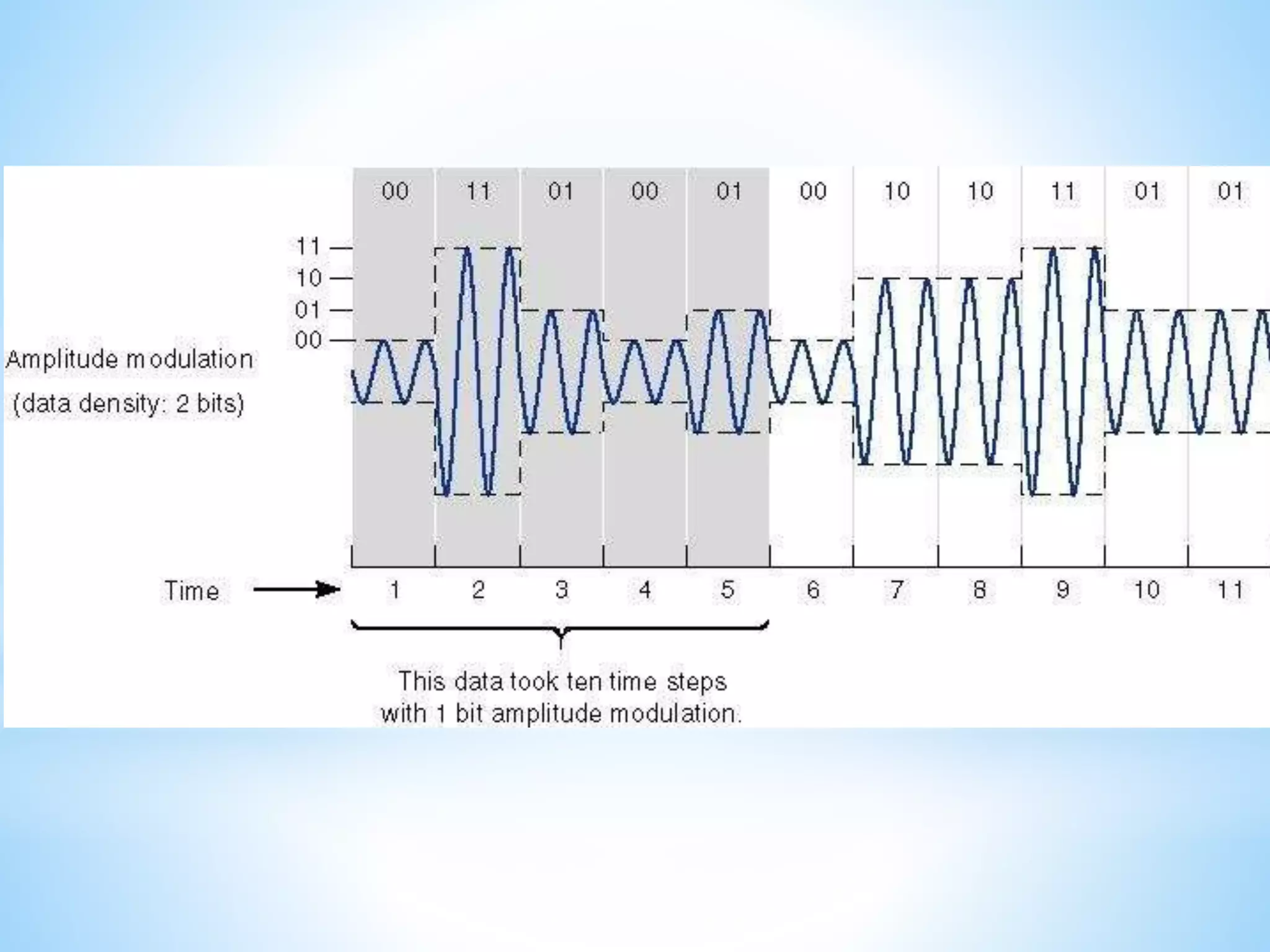
This document discusses various digital modulation techniques including:
- Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) which represents data as changes in signal amplitude.
- Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) which represents data as changes in carrier frequency.
- Phase Shift Keying (PSK) which represents data as changes in the phase of the carrier signal.
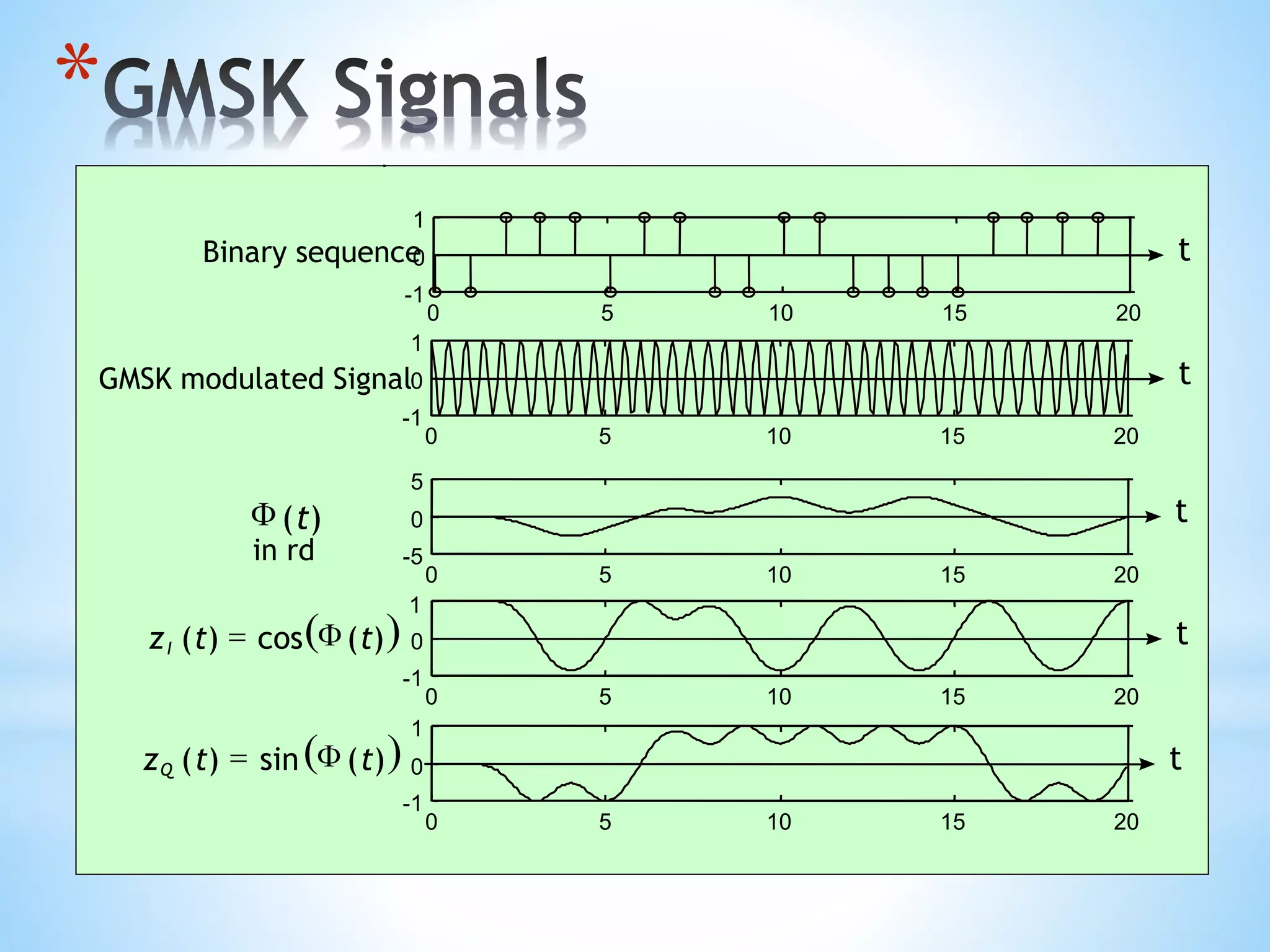
- Minimum Shift Keying (MSK) and Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) which are continuous phase modulation schemes used in wireless communications for their spectral efficiency.
- Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) which combines ASK and PSK to send multiple bits per symbol.