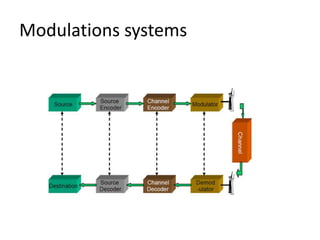
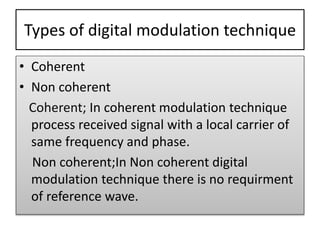
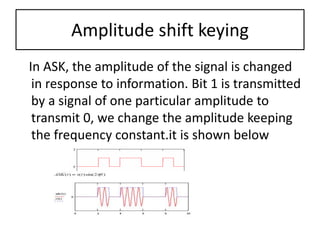
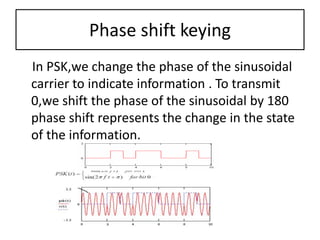
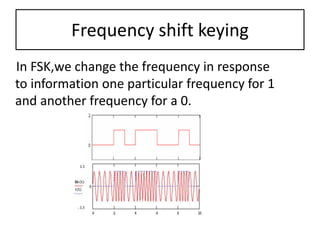
The presentation discusses digital modulation techniques within digital communication systems, focusing on the modulation of high-frequency analog carrier signals by digital bit streams. It covers the definitions and types of modulation, specifically coherent and non-coherent methods, and highlights three techniques: Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK), Phase Shift Keying (PSK), and Frequency Shift Keying (FSK). Advantages of digital modulation include improved noise detection and correction, increased security, and the ability to transmit signals over long distances.