The document discusses modulation techniques, focusing on how modulation encodes information in transmitted signals by varying the characteristics of a high-frequency carrier wave. It explains the importance of modulation for efficient long-distance transmission, multiple channel use, and improved signal quality, as well as detailing categories and techniques of digital modulation, including Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK), Frequency Shift Keying (FSK), and Phase Shift Keying (PSK). Overall, it highlights the process by which digital or analog data is transformed for suitable transmission across various mediums.


![11/15/2024
4
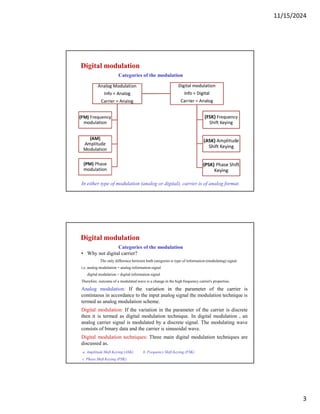
Digital modulation techniques
a. Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK)
o It is a simplest digital modulation technique where digital data is converted into analog signal.
o The amplitude of carrier signal varies with respect to amplitude of message signal.
o Bit 1 is transmitted by a signal of one particular amplitude, to transmit 0,only change the amplitude
while keeping the frequency constant.
Digital modulation techniques
a. Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK)
The outcome:
o The information signal carries the discrete bit, only two voltage levels occur at input (either +1V or -1V)
o Thus, only two voltage levels at output are available (either [Ac cos(ωct)] or OV)
o because of these two output voltage levels, the carrier is either in ON or OFF state.
o Therefore, ASK is also known as ON-OFF Keying (OOK)
Applications
o Broadcasting of signal
o Lazer intensity modulation in optical fiber communication](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture03-modulationtechniques-241121175038-8f4d513a/85/Lecture-03-Digital-modulation-techniques-4-320.jpg)


