Embed presentation
Downloaded 241 times



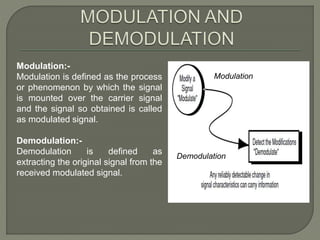
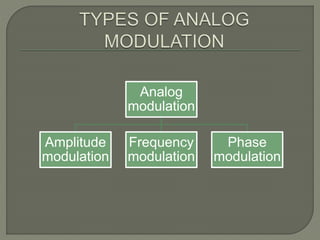
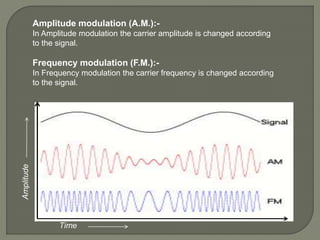
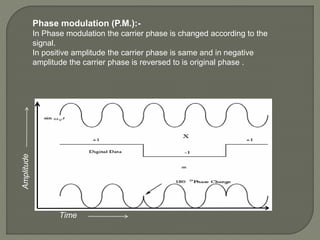

This document discusses different types of analog modulation techniques used in communication systems. It defines key concepts like signals, carriers, modulation and demodulation. There are three main types of analog modulation covered - amplitude modulation, frequency modulation, and phase modulation. Each works by varying a different property of the carrier signal (amplitude, frequency, or phase respectively) according to the information-bearing signal.






