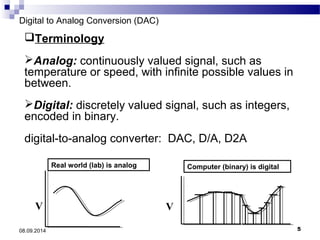
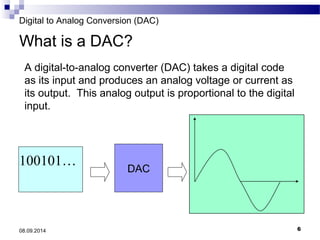
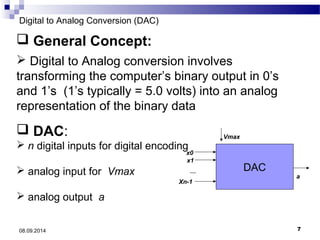
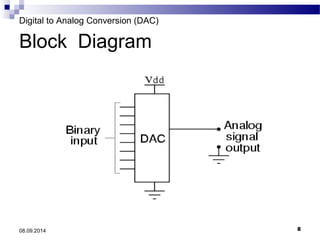
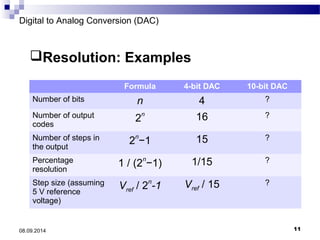
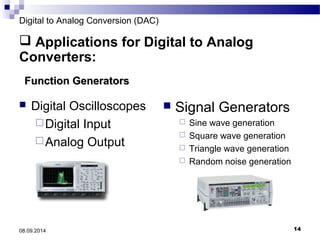
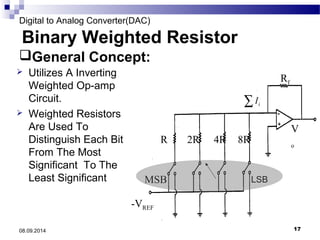
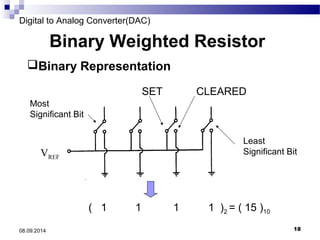
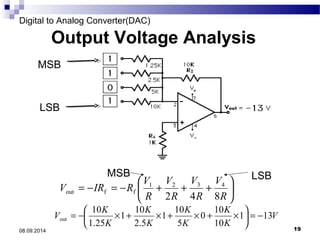
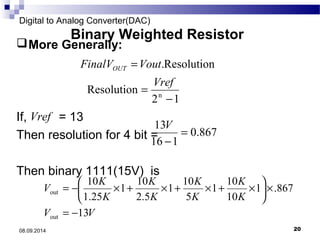
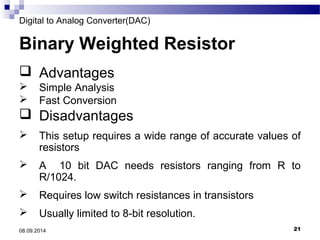
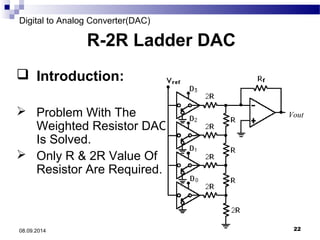
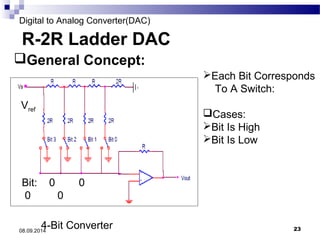
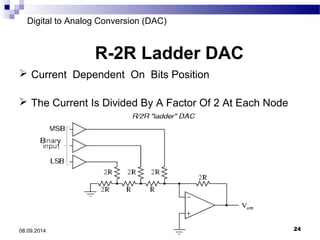
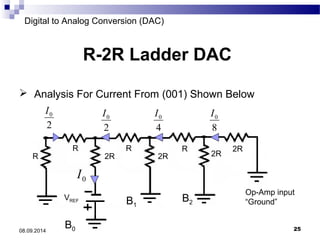
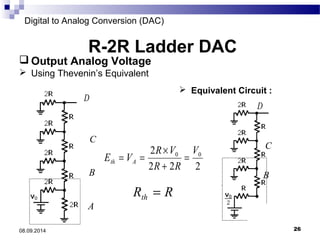
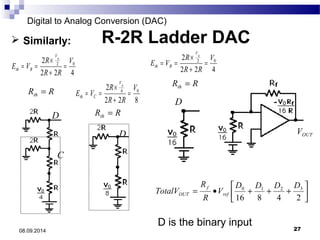
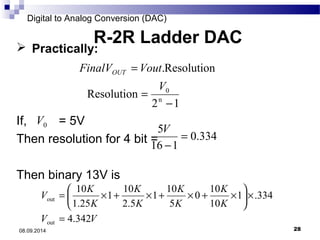
The document presents information on digital to analog conversion (DAC). It discusses the basic concept of DAC, where a digital input is converted to a proportional analog output. It then describes two common types of DAC - the weighted resistor DAC and R-2R ladder DAC. Applications of DACs are also highlighted, such as in digital audio, function generators, and motor controllers. The document provides details on the circuit design and output calculation for both weighted resistor and R-2R ladder DACs. It concludes that the R-2R ladder DAC only requires two resistor values but has slower conversion than the weighted resistor DAC.