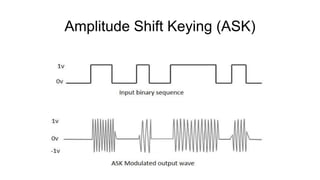
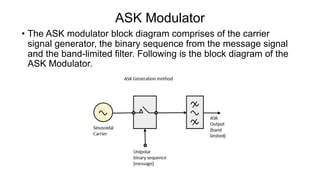
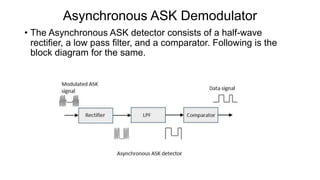
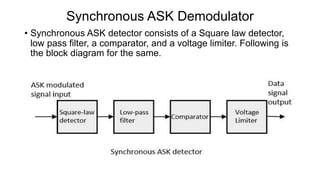
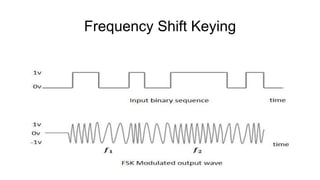
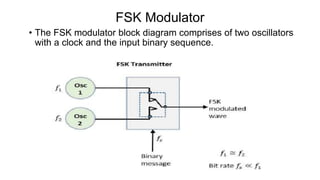
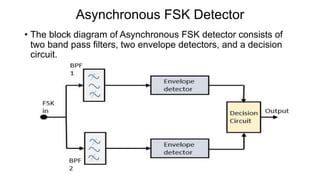
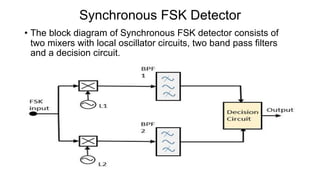
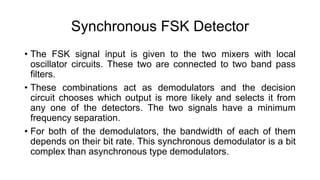
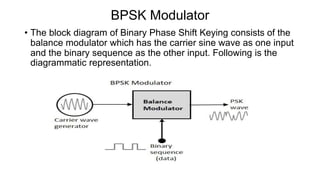
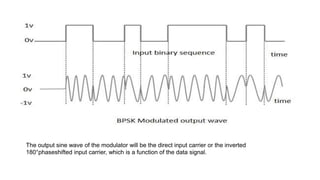
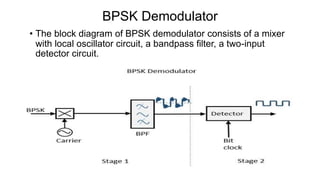
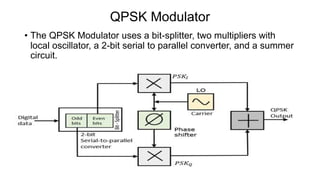
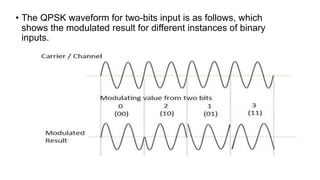
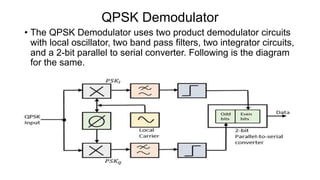
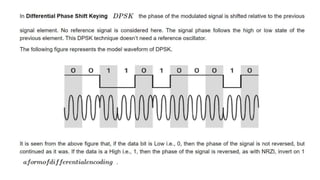
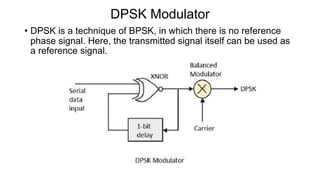
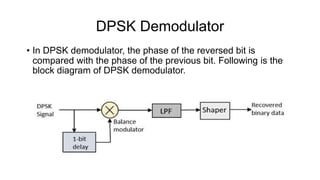
This document discusses various digital modulation techniques used in digital communications. It describes amplitude shift keying (ASK), frequency shift keying (FSK), phase shift keying (PSK) including binary PSK (BPSK) and quadrature PSK (QPSK). It provides block diagrams and explanations of modulators and demodulators for ASK, FSK, BPSK and QPSK. It also discusses M-ary encoding techniques that can transmit more than two bits simultaneously to reduce bandwidth.