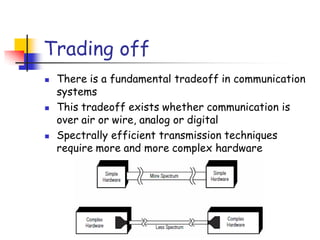
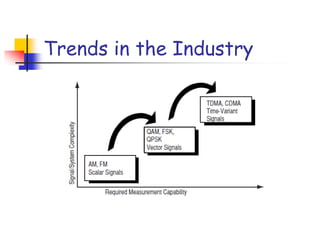
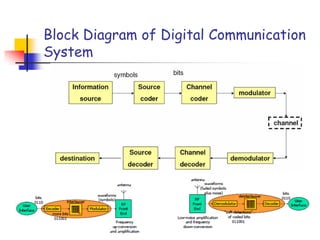
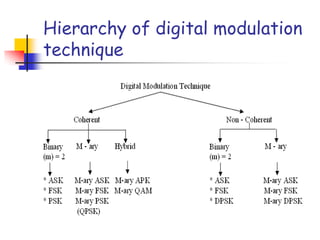
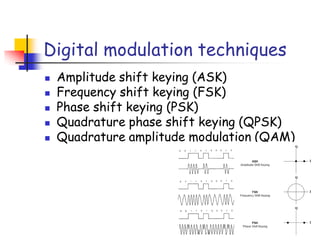
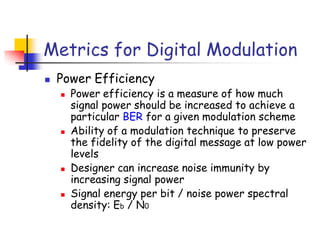
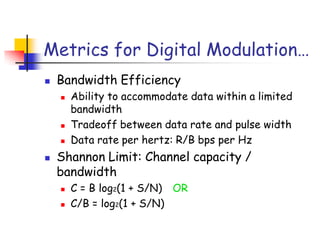
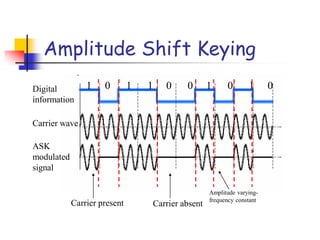
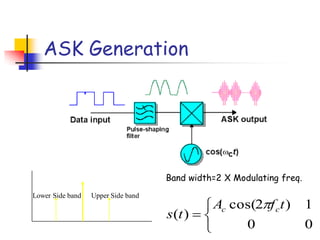
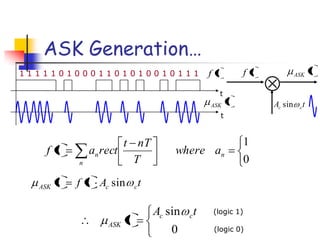
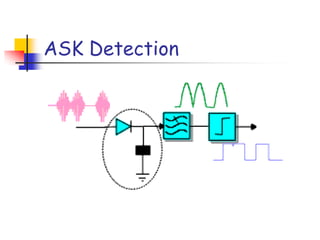
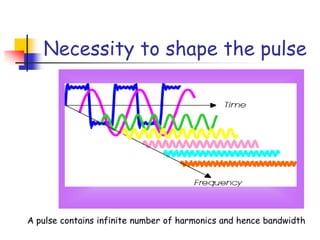
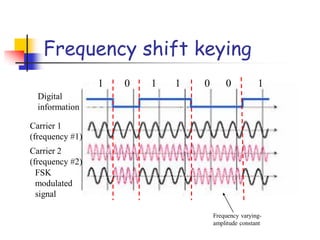
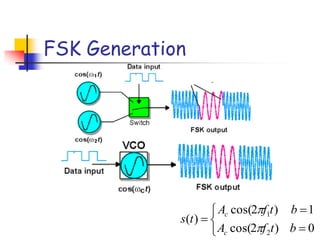
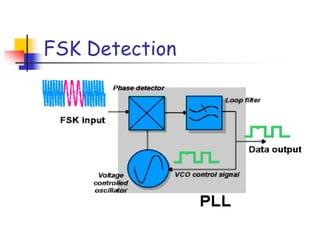
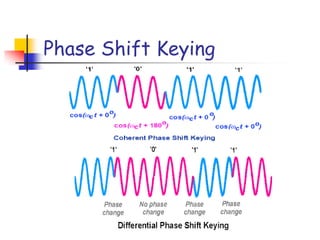
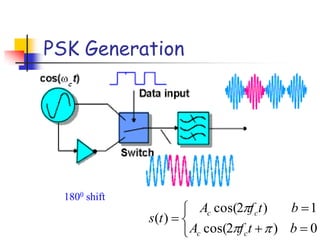
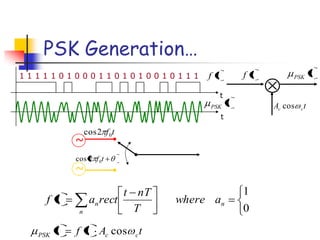
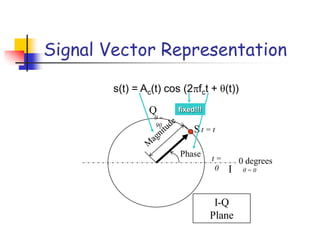
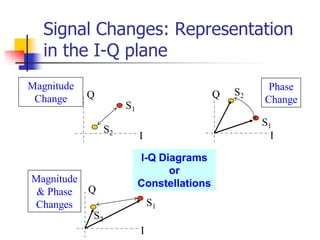
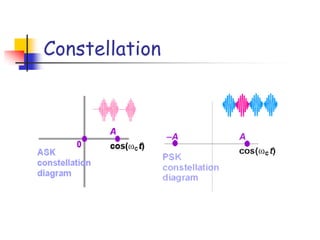
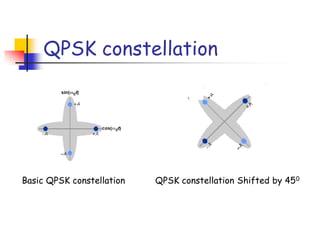
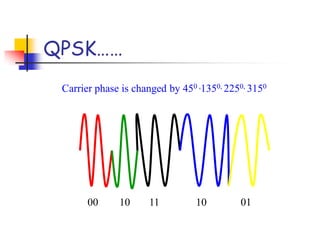
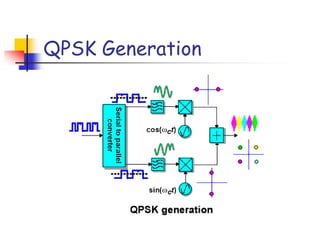
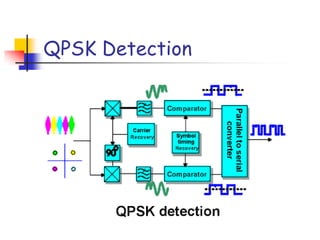
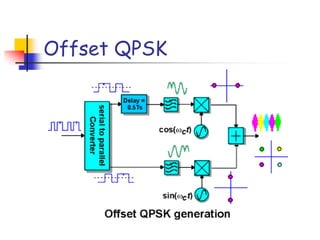
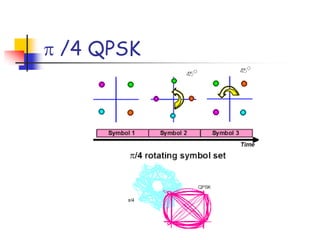
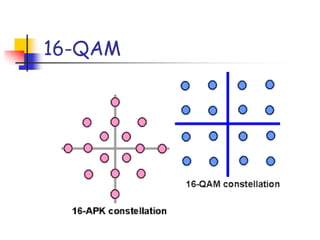
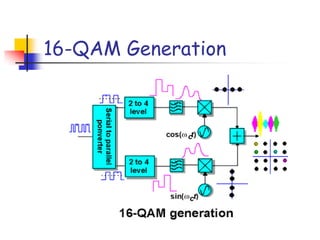
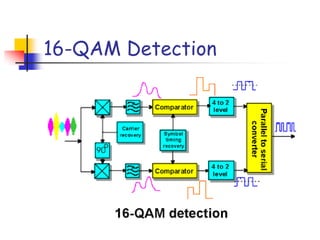
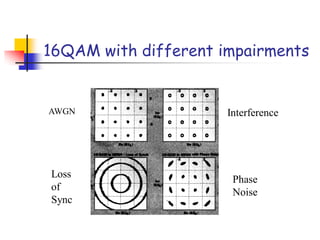
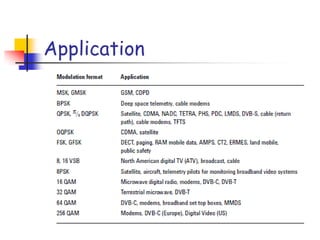
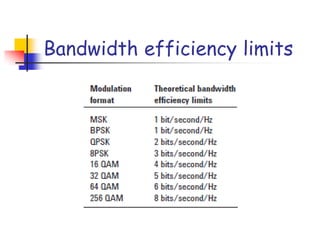
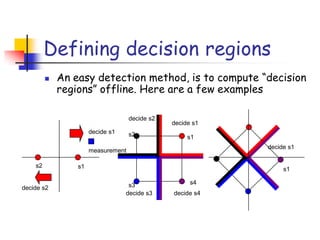
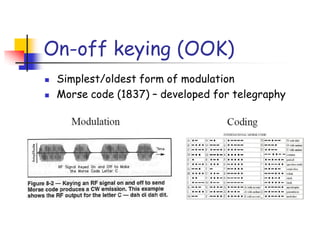
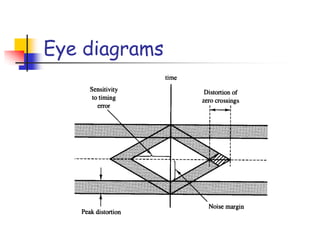
Digital modulation techniques allow for more efficient transmission of digital data by varying certain properties of the carrier signal, such as amplitude, frequency, or phase, based on the digital bit stream. There are tradeoffs between bandwidth efficiency, power efficiency, and implementation complexity for different modulation schemes. Common digital modulation techniques include amplitude-shift keying (ASK), frequency-shift keying (FSK), phase-shift keying (PSK), and quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), with higher-order schemes transmitting more than one bit per symbol. Performance metrics like bit error rate (BER) are used to evaluate and compare modulation techniques.