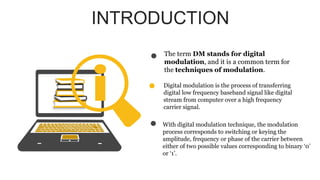
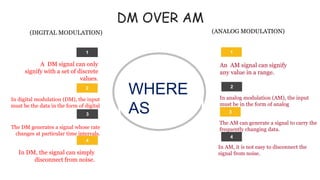
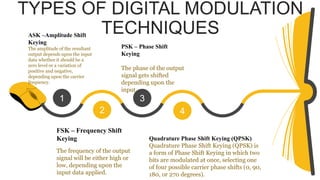
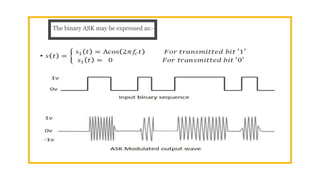
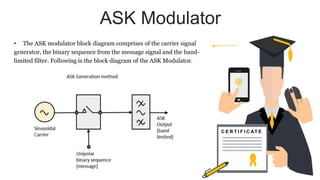
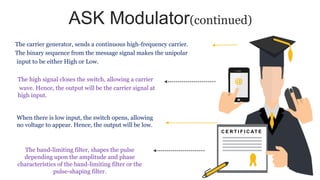
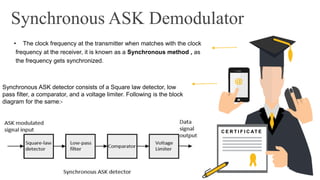
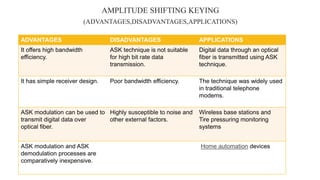
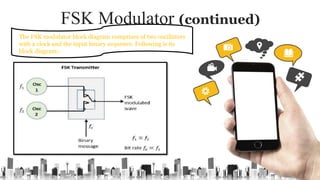
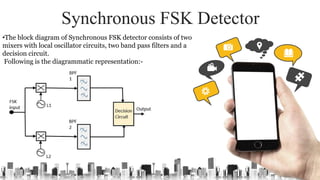
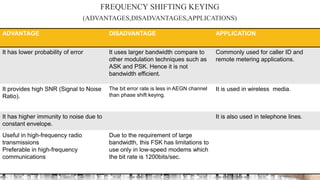
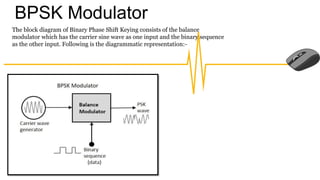
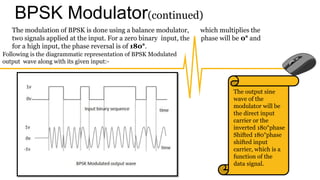
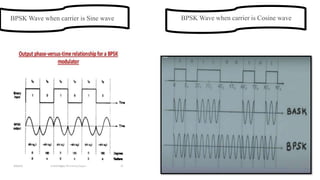
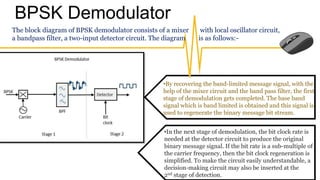
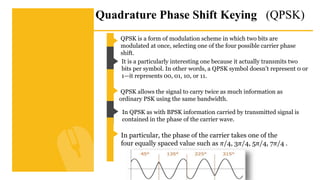
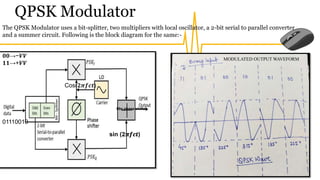
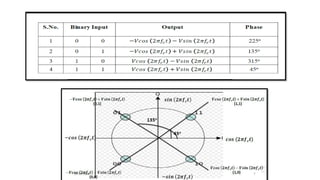
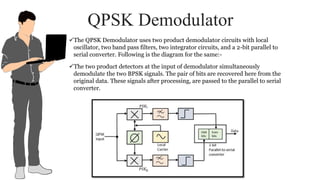
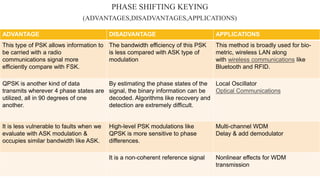
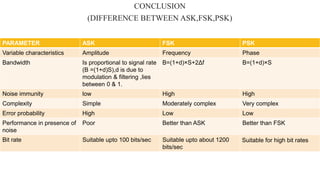
The document provides an overview of digital modulation techniques including Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK), Frequency Shift Keying (FSK), and Phase Shift Keying (PSK), detailing their generation, detection methods, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Digital modulation is preferred over analog due to higher noise immunity and efficient bandwidth usage. Key distinctions and performance metrics related to each technique are also discussed, illustrating their suitability for various communication scenarios.