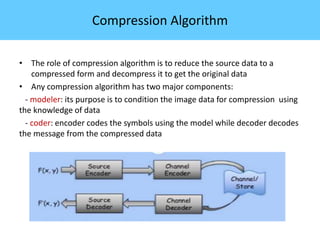
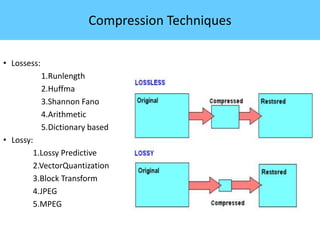
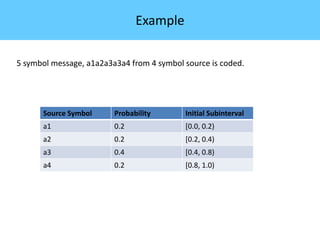
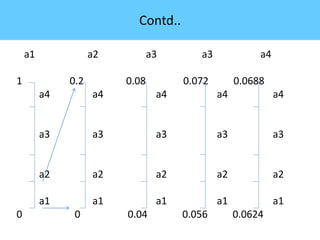
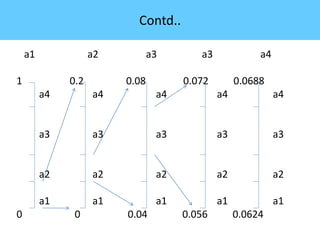
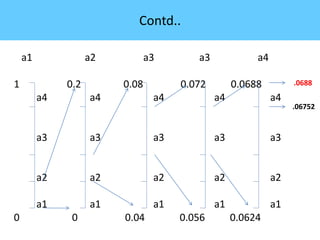
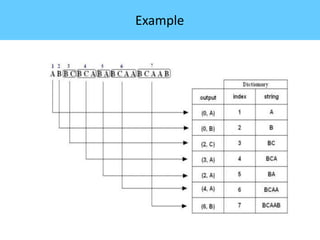
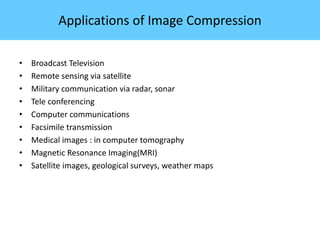
The document discusses image compression, highlighting its necessity for reducing data storage and transmission bandwidth while maintaining acceptable image quality. It details various compression techniques, including lossless and lossy methods, and outlines the roles of compression algorithms, particularly focusing on redundancy types. Additionally, it explores application areas such as military communication, medical imaging, and remote sensing.