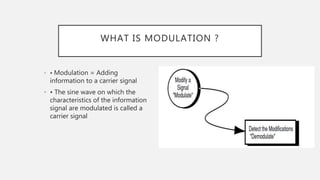
This presentation discusses digital modulation techniques. It introduces digital modulation, where a digital bit stream modulates a high frequency analog carrier signal. It describes the key aspects of modulation and different digital modulation techniques, including:
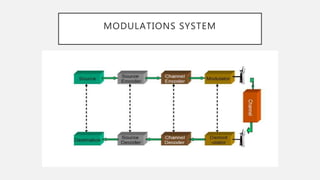
- Coherent and non-coherent modulation techniques. Coherent requires a reference wave, non-coherent does not.
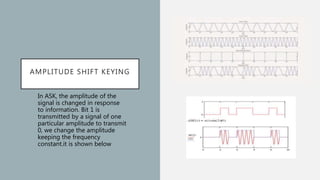
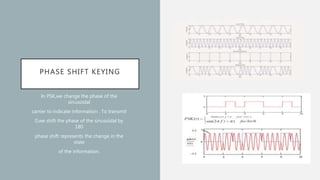
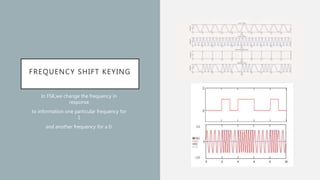
- Common digital modulation techniques: Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK), Phase Shift Keying (PSK), and Frequency Shift Keying (FSK). ASK varies amplitude, PSK varies phase, and FSK varies frequency to encode bits.
- It provides examples of how each technique (ASK, PSK, FSK) encodes bits into the signal. Digital modulation