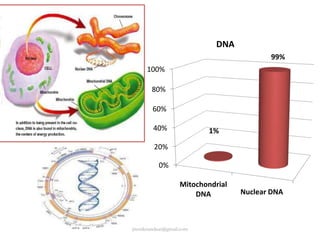
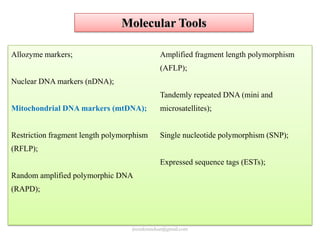
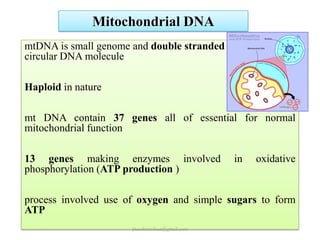
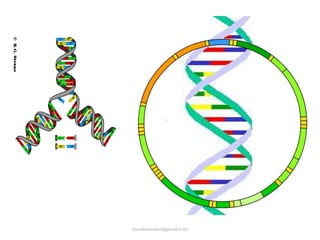
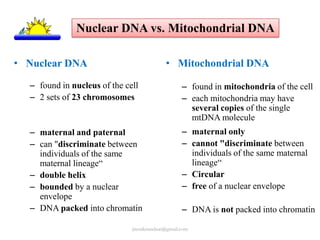
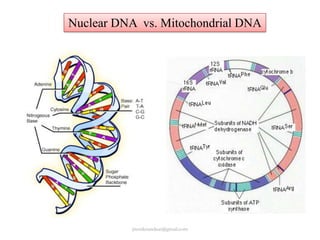
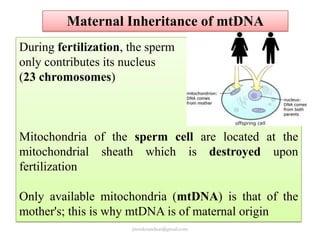
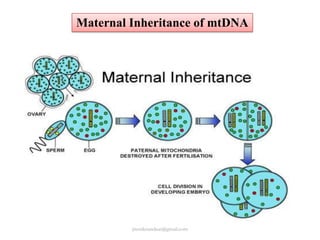
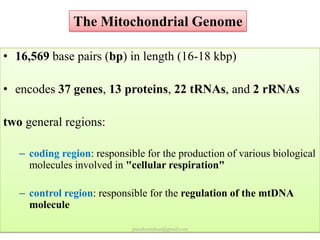
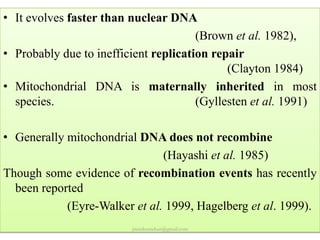
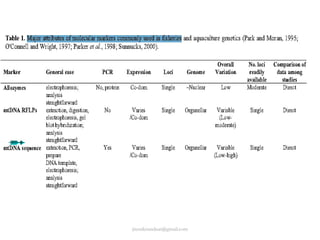
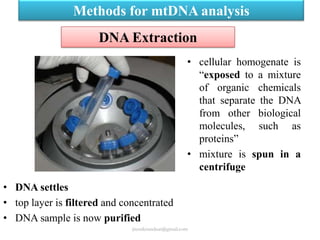
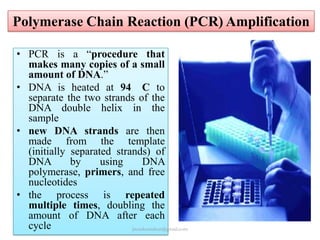
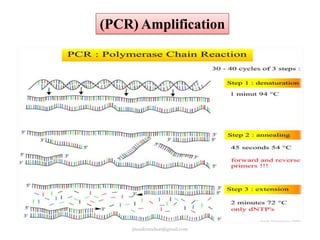
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is small, circular, double-stranded DNA located in cell mitochondria. It is maternally inherited and does not recombine. mtDNA contains 37 genes essential for mitochondrial function and ATP production through oxidative phosphorylation. Compared to nuclear DNA, mtDNA evolves more rapidly, lacks introns, and is not bound in histones. Forensic analysis of mtDNA is useful when evidence is degraded or limited. Methods include DNA extraction, PCR amplification of mtDNA regions, sequencing, and comparing sequences to identify matches or mismatches. mtDNA analysis has applications in fisheries including individual identification, mixed stock analysis, and determining phylogenetic relationships between fish species.

![Uses for mtDNA in Forensics
•mtDNA will be used when "biological evidence
may be degraded [i.e. charred remains] or in small
quantity“
•Cases in which evidence consists only of:
–hairs
–bones
–Teeth
•Missing Persons Cases (use of skeletal remains)
•Establishing Individuals as suspects (hair evidence)
jitenderanduat@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mtdna-131105032304-phpapp02/85/Mt-DNA-14-320.jpg)
![References
•
•
•
•
•
•
Ibrahim Okumus and Y. Çiftci / Turk. Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 3: 5179 (2003)
ARIAGNA LARA,* JOSE LUIS PONCE DE, Molecular Ecology Resources (2010)
10, 421–430
Vallone, P.M., Just, R.S., Coble, M.D., Butler, J.M., Parsons, T.J. (2004) A multiplex allelespecific primer extension assay for forensically informative SNPs distributed throughout the
mitochondrial genome. Int. J. Legal Med., 118: 147-157. [Protocol for 11plex SNP assay
developed at NIST] [Genotyper macro for mtSNP 11plex]
Coble, M.D., Just, R.S., O'Callaghan, J.E., Letmanyi, I.H., Peterson, C.T., Irwin, J.A.,
Parsons, T.J. (2004) Single nucleotide polymorphisms over the entire mtDNA genome that
increase the power of forensic testing in Caucasians. Int. J. Legal Med., 118: 137-146.
Coble, M.D. (2004) The identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the entire
mitochondrial genome to increase the forensic discrimination of common HV1/HV2 types in
the Caucasian population. PhD dissertation, George Washington University, 206 pp.
www.google.co.in/mtdna/wikipedia/in
jitenderanduat@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mtdna-131105032304-phpapp02/85/Mt-DNA-23-320.jpg)
