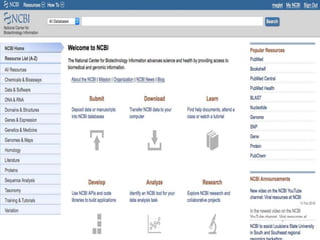
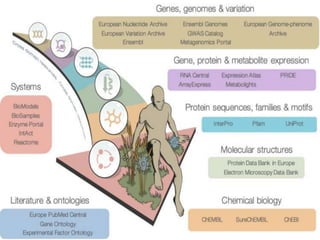
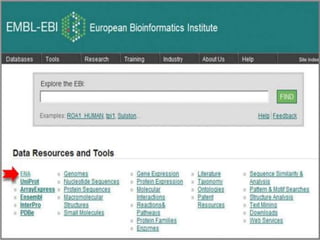
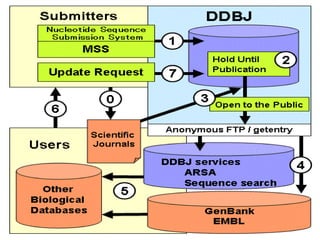
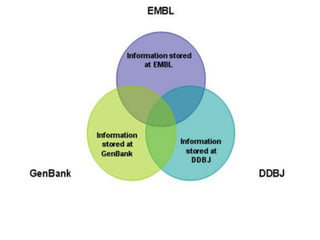
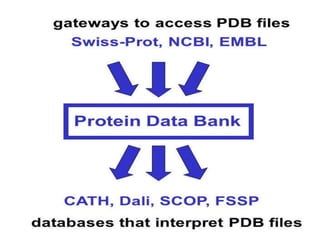
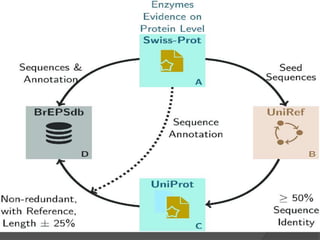
The document discusses several key nucleic acid and protein databases. It describes the Nucleic Acid Database, which provides 3D structure information about nucleic acids. It also discusses NCBI, a collection of biomedical databases including GenBank that are freely accessible online. Other databases mentioned include EMBL, DDBJ, PDB, Swiss-Prot, and UniProt, each of which archives and provides access to nucleotide or protein sequence data.