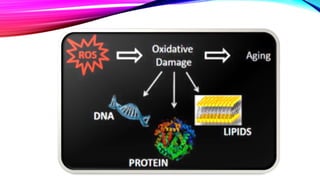
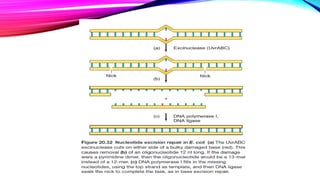
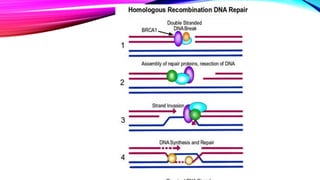
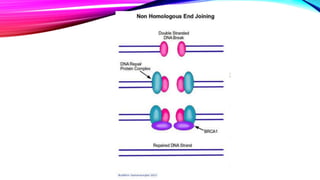
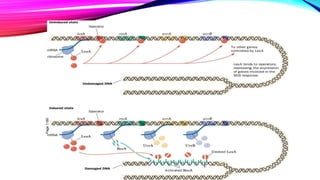
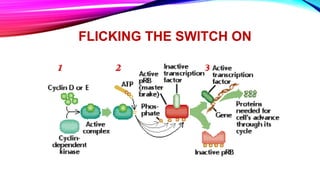
DNA repair is a collection of processes cells use to identify and correct damage to DNA molecules. Around 1 million lesions can occur per cell per day due to normal metabolic activities and environmental factors like UV light. Unrepaired lesions can alter gene transcription or cause mutations. The main types of DNA repair are direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, and double-strand break repair. Cells have checkpoint mechanisms to detect DNA damage and initiate repair or induce apoptosis if damage is too severe. Defects in DNA repair can cause diseases like xeroderma pigmentosum or increase cancer risks. Telomere shortening due to factors like oxidation also contributes to cellular aging, and telomerase may help counter this





![SOURCE OF DAMAGE
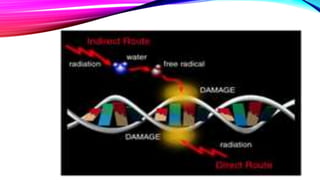
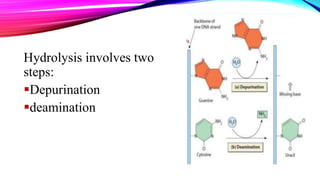
DNA damage can be subdivided into two main types:
endogenous damage such as attack by reactive oxygen species produced
from normal metabolic byproducts (spontaneous mutation), especially the
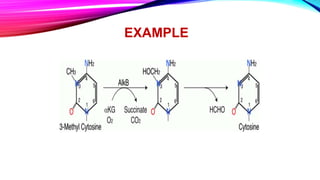
process of oxidative deamination
also includes replication errors
exogenous damage caused by external agents such as
ultraviolet [UV 200-400 nm] radiation from the sun
other radiation frequencies, including x-rays and gamma rays
certain plant toxins
viruses](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnareparing-171016115415/85/DNA-reparing-6-320.jpg)