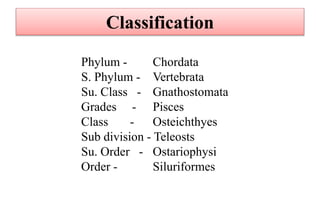
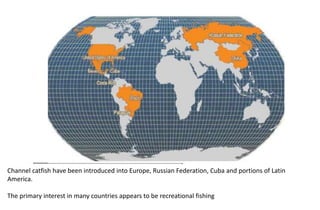
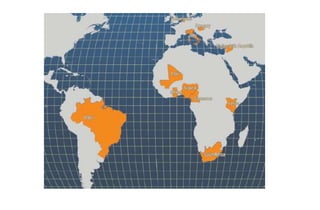
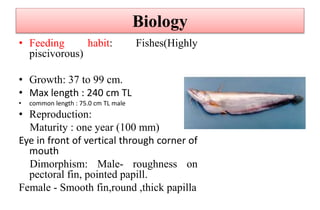
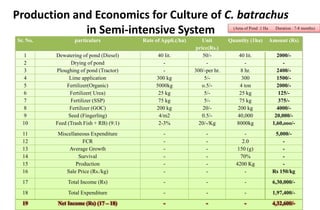
This document provides information on 11 species of catfish from 7 families. It discusses their classification, distribution, biology, culture practices, and production. Some of the main points covered include:
- Channel catfish, African sharptooth catfish, and river catfish are among the most commercially important species.
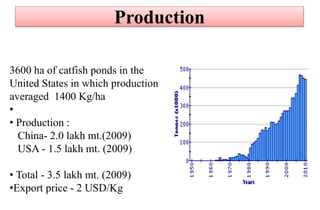
- Catfish are farmed using cages, ponds and pens. They grow quickly and can be raised at high densities, yielding 6-10 tons/ha/year.
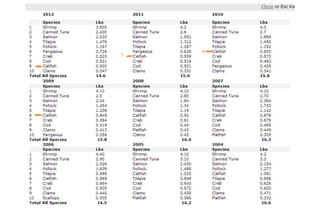
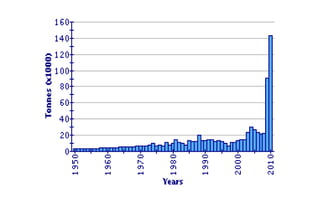
- Major producers include Vietnam, China, USA, Nigeria, and Bangladesh. Vietnam is the world's largest producer of catfish, yielding over 1.1 million tons in 2010 for export.