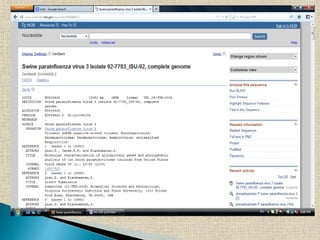
The document discusses three major biological databases - NCBI, EMBL, and DDBJ. It states that NCBI houses databases including GenBank for DNA sequences and PubMed. EMBL was created in 1974 and operates sites in multiple countries, including the European Bioinformatics Institute. The DDBJ collects DNA sequences from Japanese researchers and exchanges data daily with EMBL and NCBI to maintain identical data.