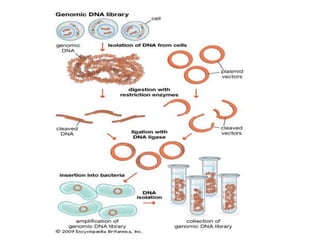
The document discusses genomic libraries. A genomic library contains DNA fragments representing the entire genome of an organism. It is constructed by inserting fragments of partially digested genomic DNA into vectors like plasmids or bacteriophages, which are then introduced into bacteria or yeast. The bacteria replicate and produce clones containing fragments of the original genome, theoretically representing all its sequences. Genomic libraries allow researchers to explore genomic structure and function, map genomes to identify gene locations, and clone DNA segments.