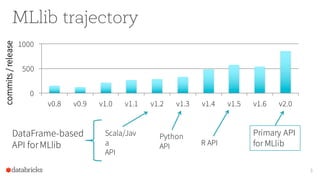
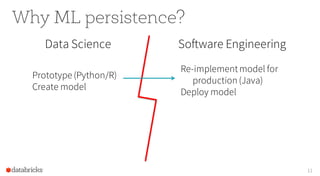
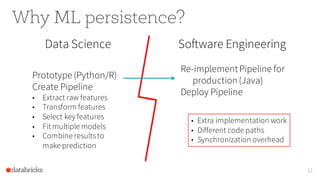
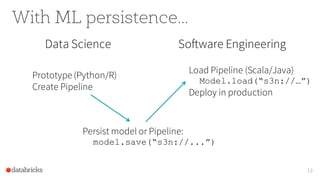
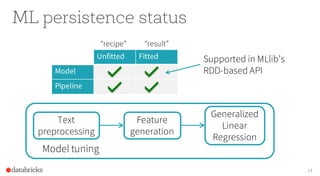
The document provides an overview of the Apache Spark MLlib 2.0, highlighting its shift to a DataFrame-based API as the primary interface for machine learning tasks, while the previous RDD-based API will enter maintenance mode. It discusses major initiatives for the upcoming version, including enhanced support for generalized linear models, expanded Python and R APIs, and model persistence features aimed at improving production readiness. Furthermore, it outlines customization options for ML pipelines and encourages community involvement in its development.












![Persistence for customized algorithms
2 traits provide persistence for simple Transformers:
•DefaultParamsWritable
•DefaultParamsReadable
Simply mix in these traits to provide persistence in Scala/Java.
à Saves & loadsalgorithmparameters
val myParam: Param[Double]
à Does notsave member data
val myCoefficients: Vector
For an example, see UnaryTransformerExample.scala
in spark/examples/
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16-06-08sswml2-160608235652/85/Apache-Spark-MLlib-2-0-Preview-Data-Science-and-Production-18-320.jpg)



