This document summarizes Timothée Hunter's presentation on TensorFrames, which allows running Google TensorFlow models on Apache Spark. Some key points:
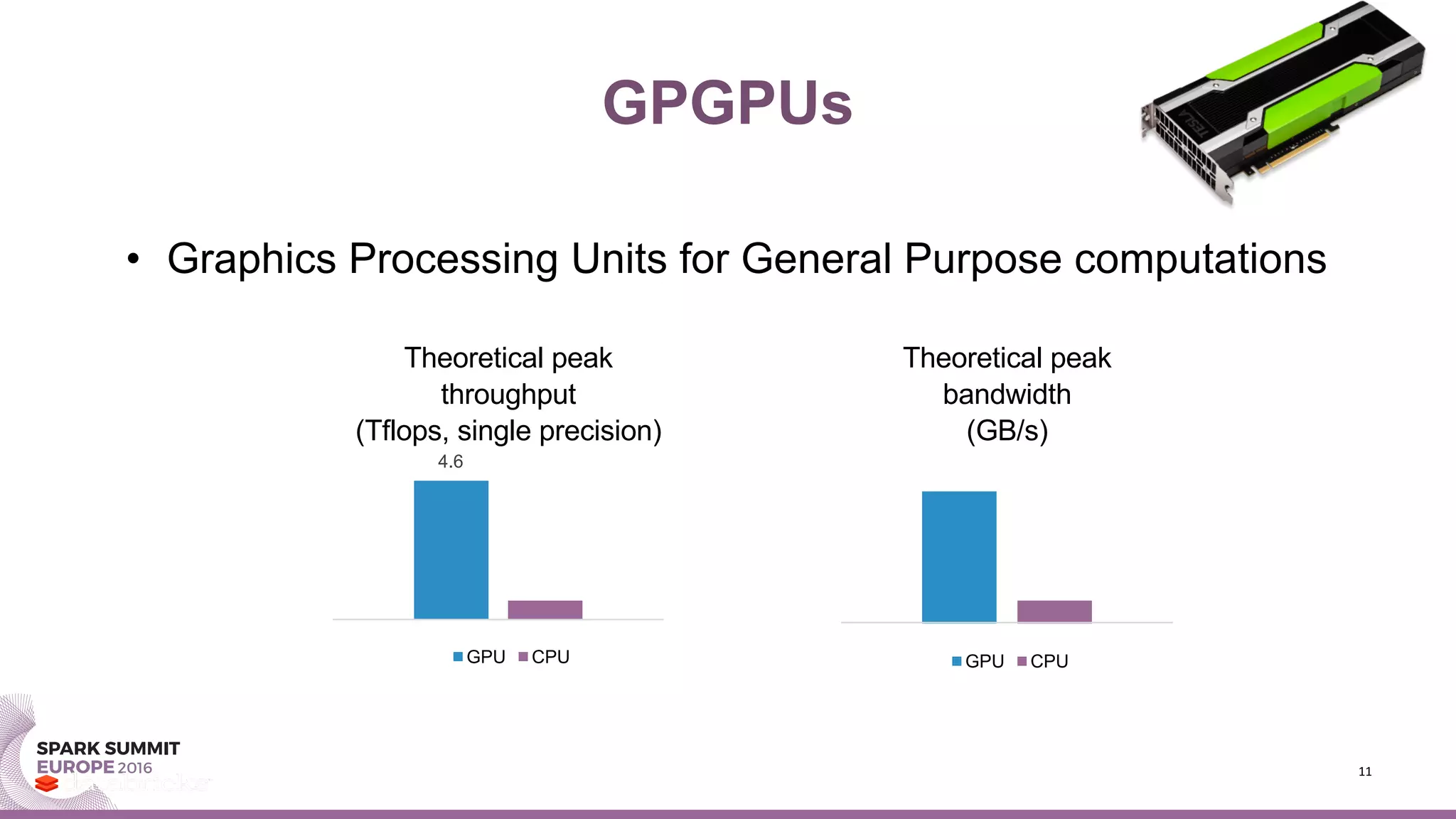
- TensorFrames embeds TensorFlow into Spark to enable distributed numerical computing on big data. This leverages GPUs to speed up computationally intensive machine learning algorithms.
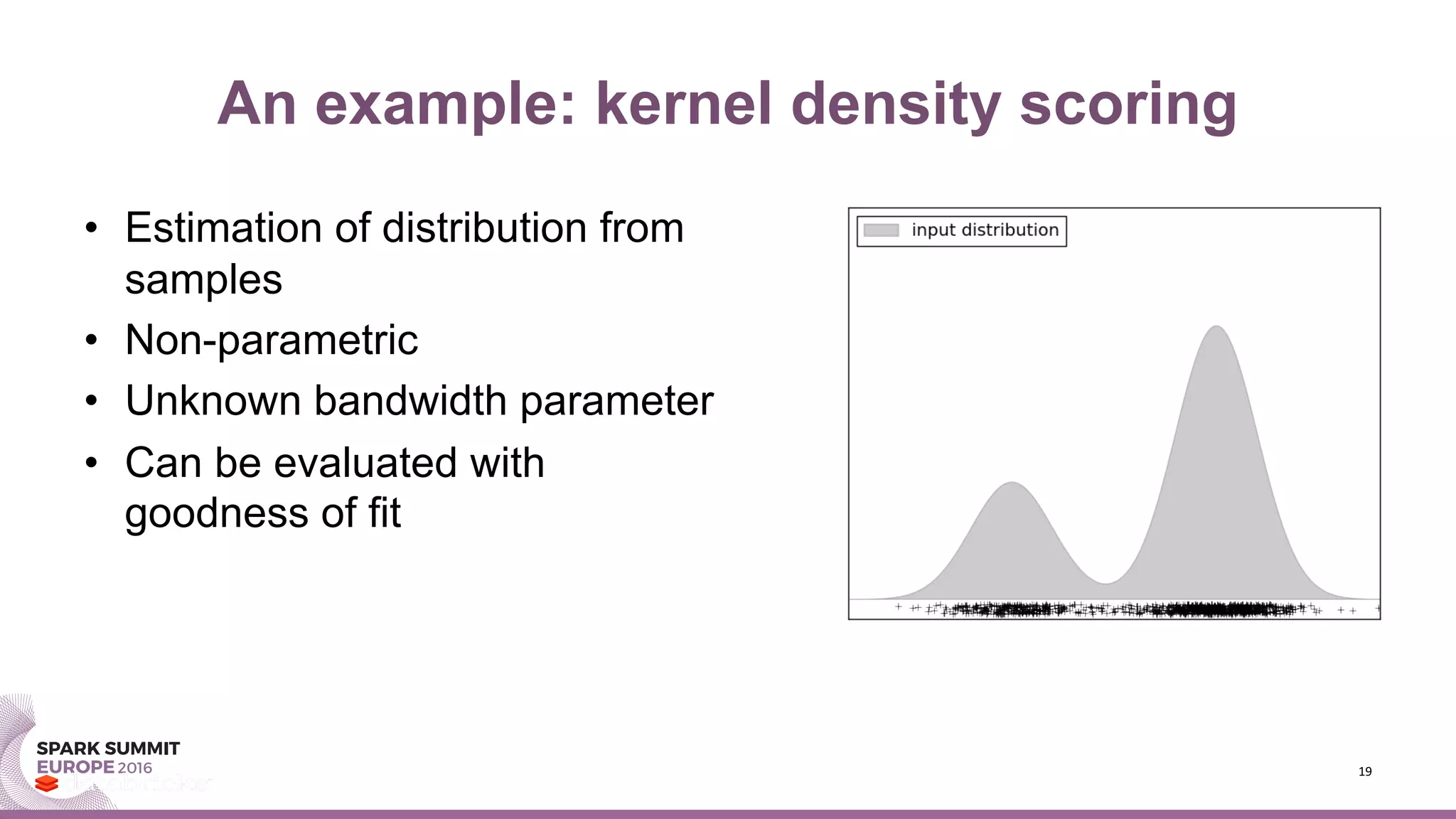
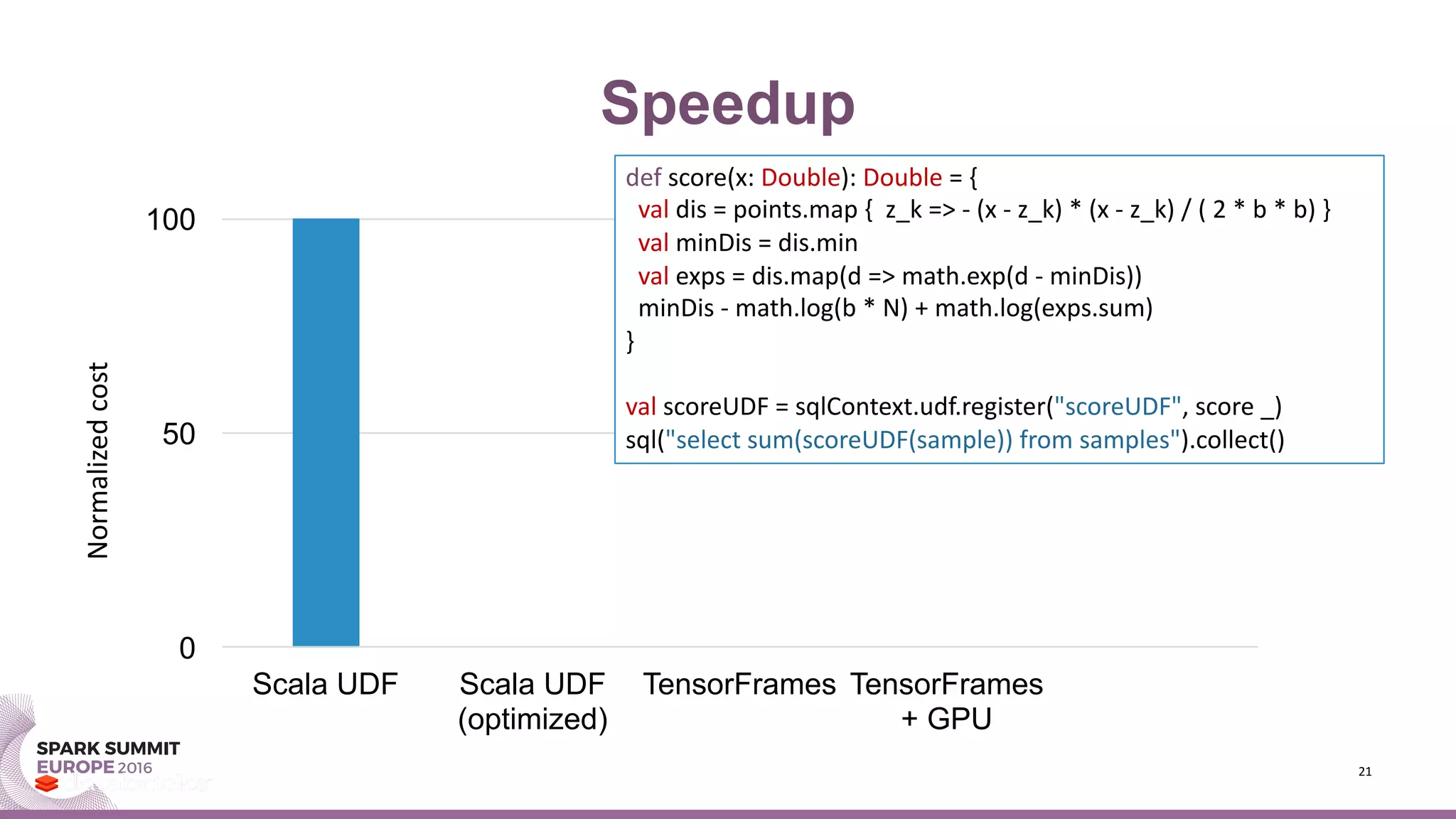
- An example demonstrates speedups from using TensorFrames and GPUs for kernel density estimation, a non-parametric statistical technique.
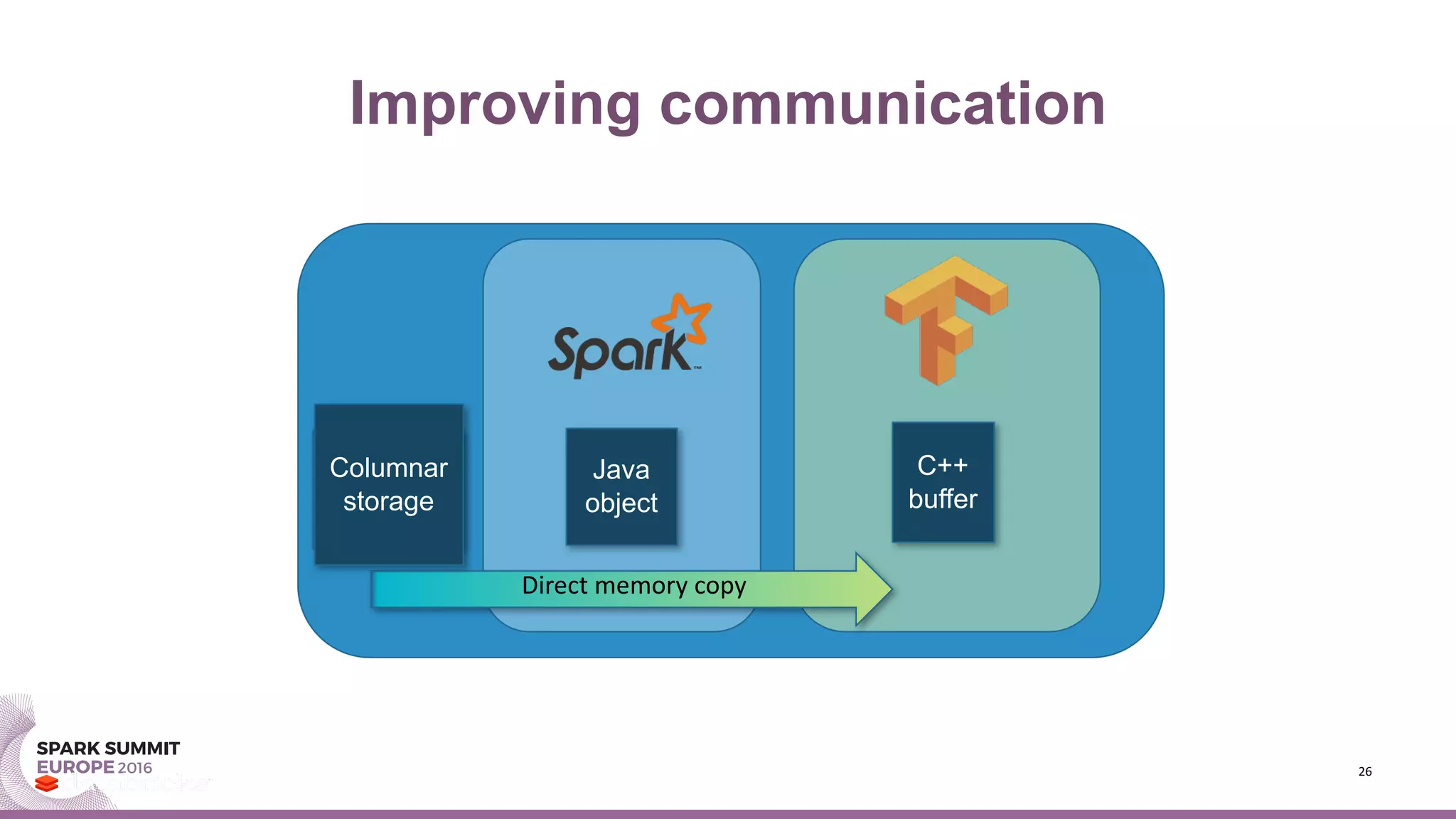
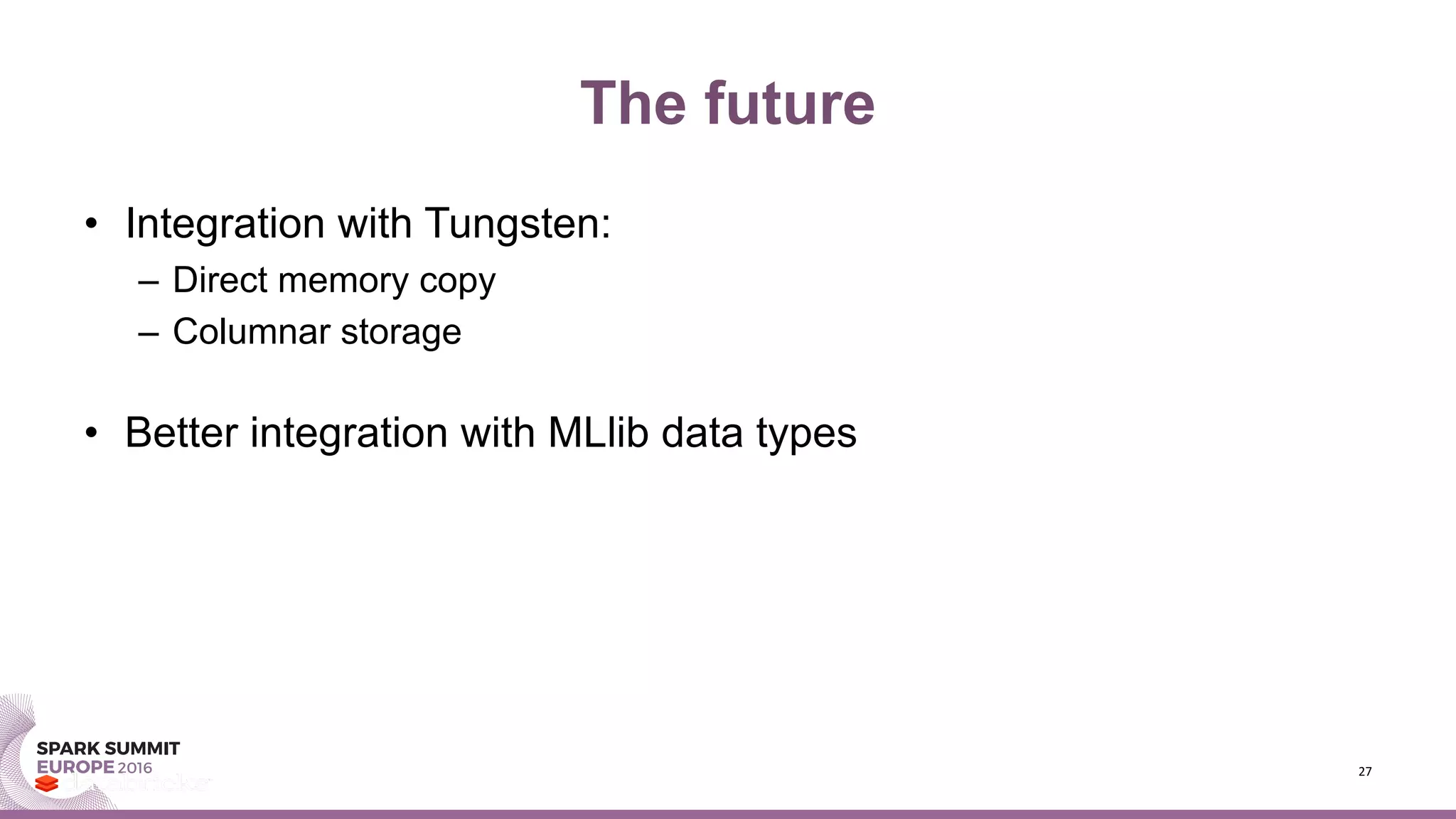
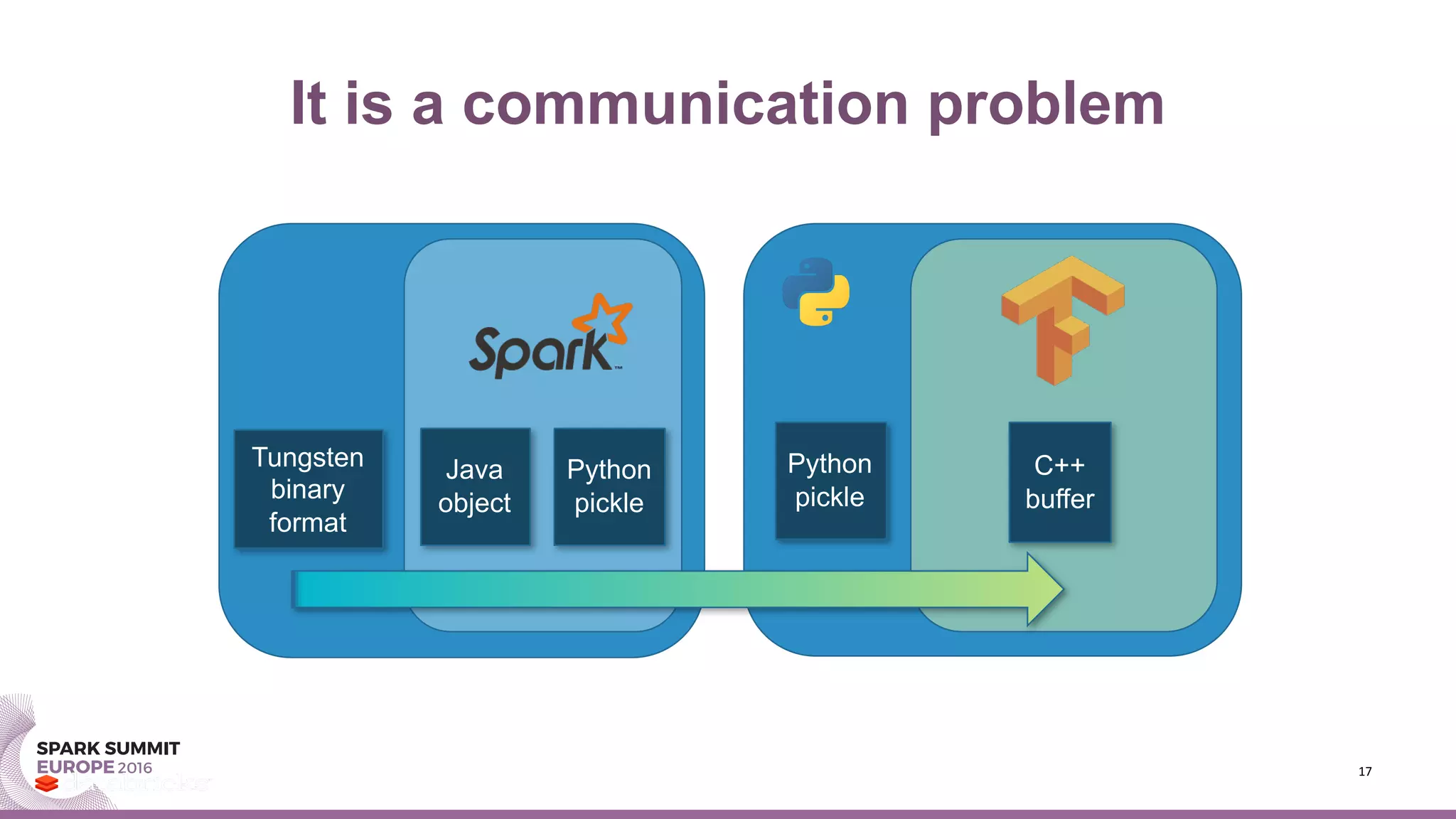
- Future improvements include better integration with Tungsten in Spark for direct memory copying and columnar storage to reduce communication costs.










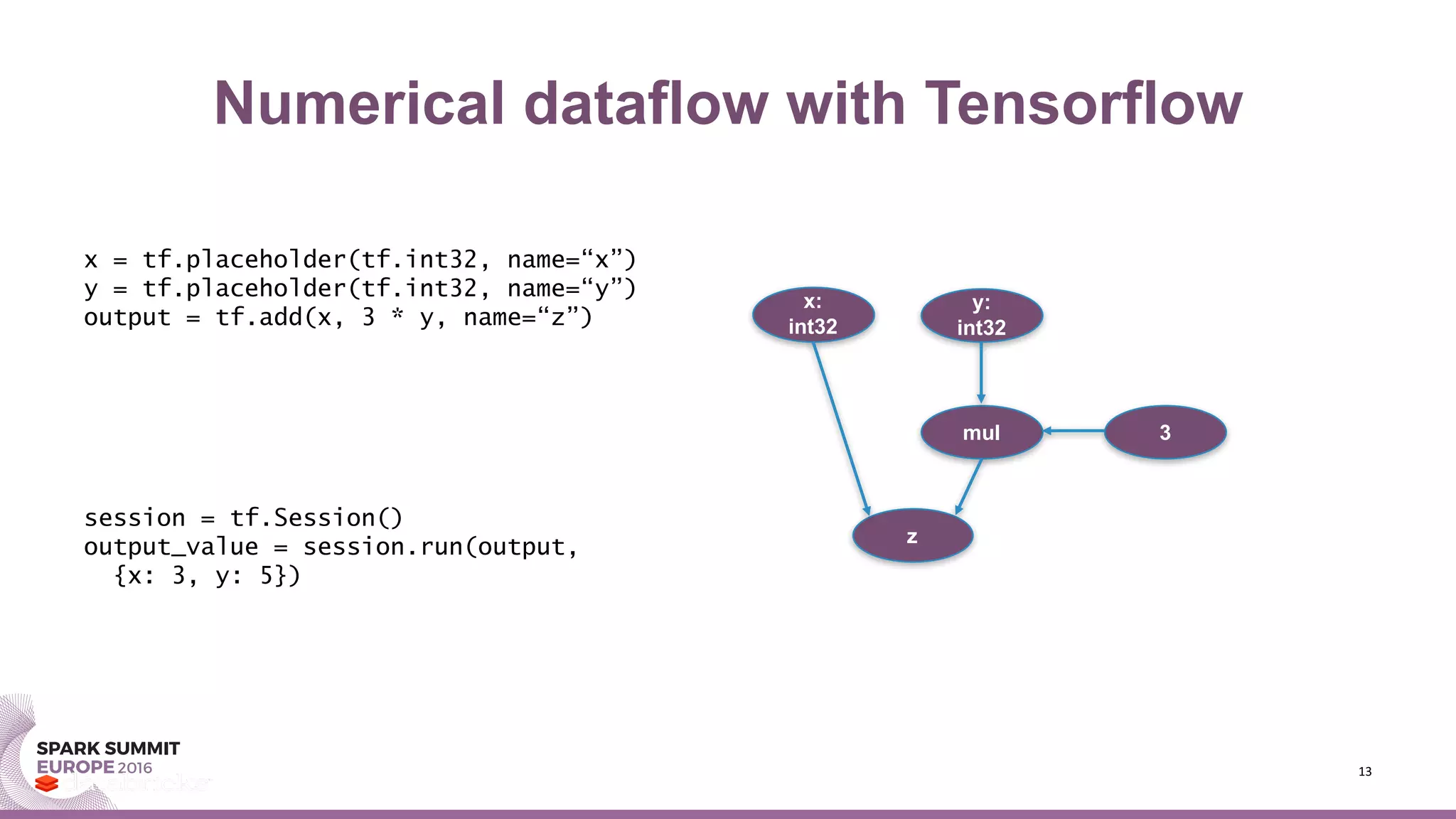
![Numerical dataflow with Spark
df = sqlContext.createDataFrame(…)
x = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, name=“x”)
y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, name=“y”)
output = tf.add(x, 3 * y, name=“z”)
output_df = tfs.map_rows(output, df)
output_df.collect()
df: DataFrame[x: int, y: int]
output_df:
DataFrame[x: int, y: int, z: int]
x:
int32
y:
int32
mul 3
z](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1gtimhunter-161103200336/75/Spark-Summit-EU-talk-by-Tim-Hunter-14-2048.jpg)





var idx = 0
while(idx < N) {
val z_k = points(idx)
dis(idx) = - (x - z_k) * (x - z_k) / ( 2 * b * b)
idx += 1
}
val minDis = dis.min
var expSum = 0.0
idx = 0
while(idx < N) {
expSum += math.exp(dis(idx) - minDis)
idx += 1
}
minDis - math.log(b * N) + math.log(expSum)
}
val scoreUDF = sqlContext.udf.register("scoreUDF", score _)
sql("select sum(scoreUDF(sample)) from samples").collect()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1gtimhunter-161103200336/75/Spark-Summit-EU-talk-by-Tim-Hunter-22-2048.jpg)