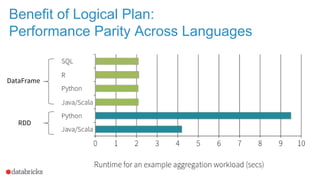
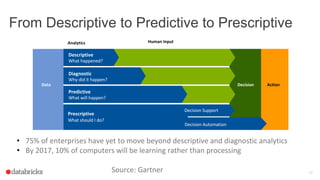
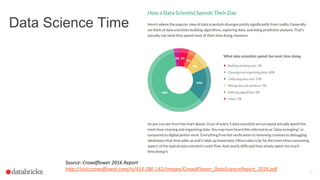
Miklos Christine is a solutions architect at Databricks who helps customers build big data platforms using Apache Spark. Databricks is the main contributor to the Apache Spark project. Spark is an open source engine for large-scale data processing that can be used for machine learning. Spark ML provides machine learning algorithms and pipelines to make machine learning scalable and easier to use at an enterprise level. Spark 2.0 includes improvements to Spark ML such as new algorithms and better support for Python.




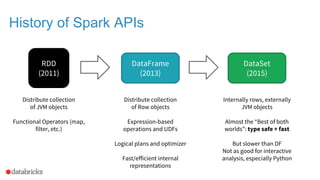
![Apache Spark 2.0 API
DataSet
(2016)
• DataFrame = Dataset[Row]
• Convenient for interactive analysis
• Faster
DataFrame
DataSet
Untyped API
Typed API
• Optimized for data engineering
• Fast](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fightingfraudwithapachespark-160916145105/85/Fighting-Fraud-with-Apache-Spark-12-320.jpg)