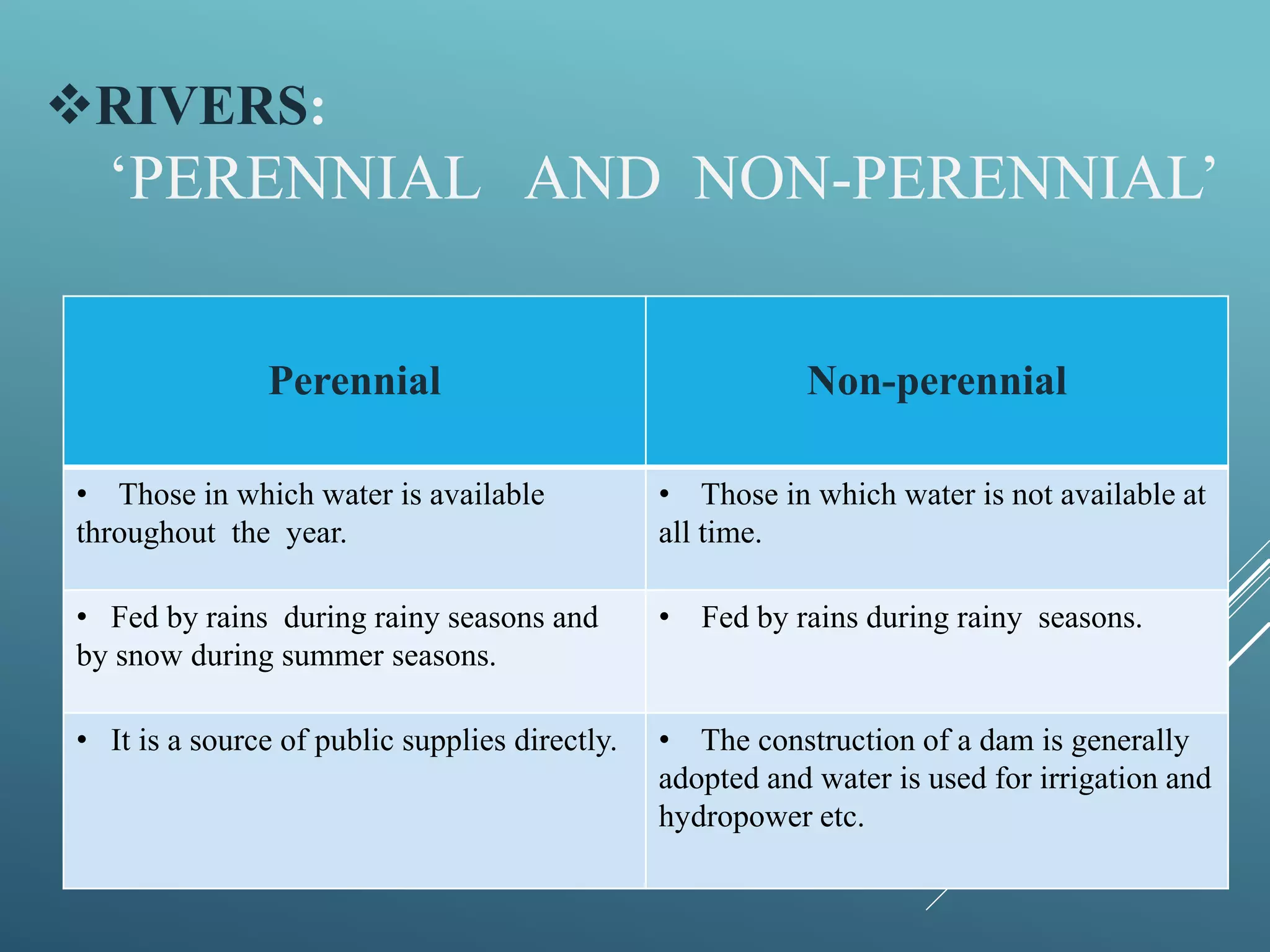
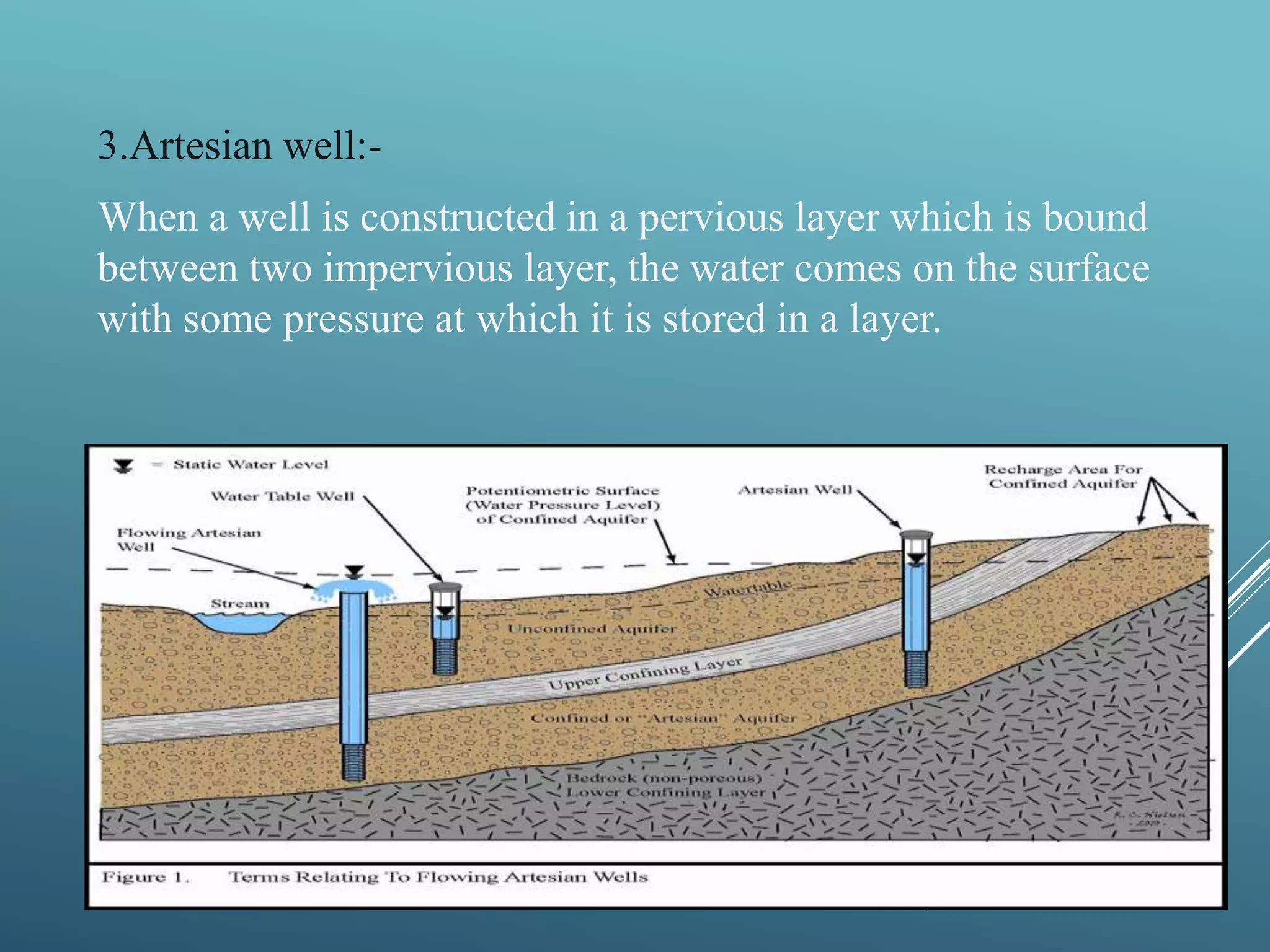
This document provides information about water resources in India. It discusses the different sources of water including surface water sources like rivers, lakes, ponds, and reservoirs, as well as groundwater sources like wells, springs, and infiltration galleries. It outlines how people use water resources for agriculture, industry, households, and other activities. It also discusses overuse of water resources from population growth and increased demand, as well as the importance of conserving this critical resource for a sustainable future.