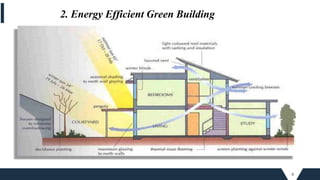
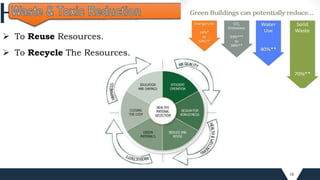
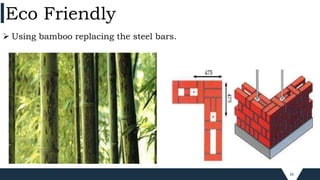
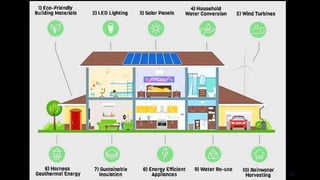
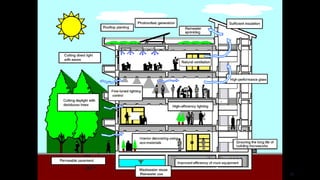
The document outlines the principles and practices of sustainable green building, emphasizing energy efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and occupant health. Key objectives include minimizing waste, conserving resources, and leveraging renewable energy sources. It also discusses various green building rating systems, particularly in India, and showcases successful green building projects.



























![34
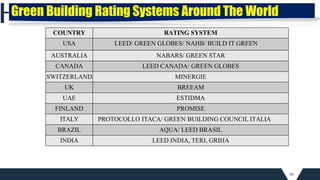
• LEED [Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design]
• GRIHA [Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment]
• TERI [The Energy and Resources Institute]
• ADaRSH [Association for Develop. & Research of Sustainable Habitats]
• MNRE [Ministry of New and Renewable Energy]
Government Agencies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module2planningforsmartcities-211013035443/85/INFRASTRUCTURE-FOR-SMART-CITIES_MOD-2_planning-for-smart-cities-34-320.jpg)




![39
LEED INDIA: An Indian adaptation of LEED USA, by Indian green
building council [IGBC]
TERI- GRIHA
A National Rating System for Green Buildings developed by MNRE in
association with TERI.
Green Building Rating Systems in INDIA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module2planningforsmartcities-211013035443/85/INFRASTRUCTURE-FOR-SMART-CITIES_MOD-2_planning-for-smart-cities-39-320.jpg)















![57
Raintree Hotels – Chennai 1st Eco-sensitive Hotel In
India. [The entire chain]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module2planningforsmartcities-211013035443/85/INFRASTRUCTURE-FOR-SMART-CITIES_MOD-2_planning-for-smart-cities-57-320.jpg)








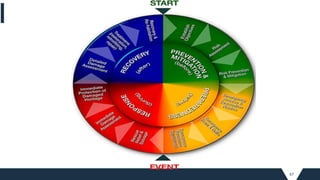



![71
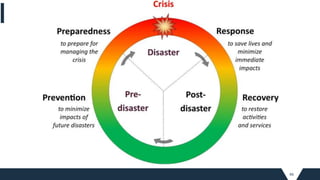
PREPAREDNESS [examples]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module2planningforsmartcities-211013035443/85/INFRASTRUCTURE-FOR-SMART-CITIES_MOD-2_planning-for-smart-cities-71-320.jpg)

![73
RESPONSE [examples]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module2planningforsmartcities-211013035443/85/INFRASTRUCTURE-FOR-SMART-CITIES_MOD-2_planning-for-smart-cities-73-320.jpg)


![76
RECOVERY [examples]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module2planningforsmartcities-211013035443/85/INFRASTRUCTURE-FOR-SMART-CITIES_MOD-2_planning-for-smart-cities-76-320.jpg)

![78
Ministry of Water Resources [Central Water Commission] :- Floods, Drought
Indian Meteorological Department :- Cyclones, heat waves, cold waves
Indian Meteorological Department :- Earthquakes
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare :- Epidemics
Indian national center for oceanic information services :- Tsunami
Ministry of Environment and Forests :- Chemical Disasters
Ministry of Labor :- Industrial Disasters
Ministry of Railways :- Rail Accidents
Ministry of Civil Aviation :- Air Accidents
Department of Atomic Energy :- Nuclear Incidents](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module2planningforsmartcities-211013035443/85/INFRASTRUCTURE-FOR-SMART-CITIES_MOD-2_planning-for-smart-cities-78-320.jpg)
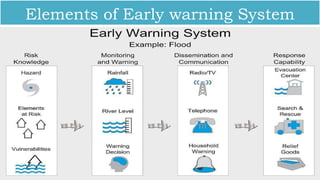
![[Ews]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module2planningforsmartcities-211013035443/85/INFRASTRUCTURE-FOR-SMART-CITIES_MOD-2_planning-for-smart-cities-79-320.jpg)