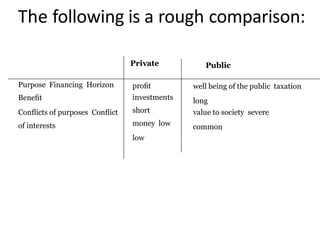
The document discusses the role of economic decision-making in construction management, emphasizing methods such as the out-of-pocket commitment, payback period, and average annual rate of return for evaluating project alternatives. It outlines a five-step framework for making project economic decisions, addressing problem identification, alternatives, criteria, evaluation, and decision-making. Additionally, it contrasts public and private projects, highlighting the importance of the benefit-cost ratio in evaluating public projects funded by the government.