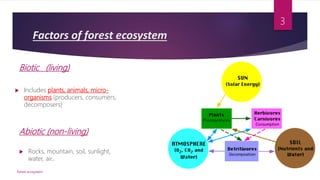
This document discusses forest ecosystems. A forest ecosystem is a biological community consisting of interacting plants, animals, microorganisms, and their physical environment within a forest. Forest ecosystems contain biotic factors like plants, animals, and microbes, as well as abiotic factors such as soil, water, and sunlight. The main layers in forests are the canopy, understory, and forest floor. There are several different types of forests including deciduous forests, rainforests, coastal forests, coniferous forests, and broad-leaved forests. Forests provide many important services but are threatened by deforestation and other human activities. Conservation of forest ecosystems is important to maintain their services and balance.